|
Deane B. Judd
Deane Brewster Judd (November 15, 1900 – October 15, 1972) was an American physicist who made important contributions to the fields of colorimetry, color discrimination, color order, and color vision. Education Judd was born in South Hadley Falls, Massachusetts and attended Ohio State University and Cornell University, where he received a Ph.D. degree in physics in 1926. He was a Munsell Research Associate in colorimetry at the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) in Washington, D.C. in 1926. Career In 1927, Judd joined the National Bureau of Standards' permanent staff where he remained until his retirement in 1969 and subsequently continued as a guest worker. During this time he "… made monumental contributions to the science of colorimetry." In addition to his work in research and standardization related to color he represented the United States in international commissions on color science. He was the U.S.'s representative in colorimetry in eight meetings of the Inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Hadley, Massachusetts
South Hadley (, ) is a town in Hampshire County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 18,150 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Springfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area. South Hadley is home to Mount Holyoke College, South Hadley High School, Pioneer Valley Performing Arts Charter Public School, and the Berkshire Hills Music Academy. History South Hadley was an unsettled area of Hadley from 1659 until 1721, when English settlers moved in from Hadley. A separate town meeting was held in 1753, and the town was officially split and incorporated in 1775. The town is the home of the nation's first successful navigable canal as well as [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Triangle
A color triangle is an arrangement of colors within a triangle, based on the additive combination of three primary colors at its corners. An additive color space defined by three primary colors has a chromaticity gamut that is a color triangle, when the amounts of the primaries are constrained to be nonnegative. Before the theory of additive color was proposed by Thomas Young and further developed by James Clerk Maxwell and Hermann von Helmholtz, triangles were also used to organize colors, for example around a system of red, yellow, and blue primary colors. After the development of the CIE system, color triangles were used as chromaticity diagrams, including briefly with the trilinear coordinates representing the chromaticity values. Since the sum of the three chromaticity values has a fixed value, it suffices to depict only two of the three values, using Cartesian co-ordinates. In the modern ''x,y'' diagram, the large triangle bounded by the imaginary primaries X, Y, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Günter Wyszecki
Günter Wyszecki (1925 – June 22, 1985) was a German-Canadian physicist who made important contributions to the fields of colorimetry, color discrimination, color order, and color vision. Education Wyszecki was born in Tilsit, East Prussia, Germany (today Sovetsk, Russia). He attended the Technische Universität Berlin where he was awarded a Dr.-Ing. degree, with a dissertation on normal and anomalous trichromacy. In 1953 he was awarded a Fulbright Scholarship and for a year joined Deane B. Judd at the Colorimetry and Photometry section of the U. S. National Bureau of Standards in Washington DC. Career In 1955 Wyszecki joined the National Research Council of Canada in Ottawa where he became the leader of its Optics Section in 1960 and Assistant Director of the Division of Physics in 1982, and where he remained until his untimely death from leukemia. Wyszecki is best known for his scientific contributions to and leadership in the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Colour Association
The International Colour Association (''Association Internationale de la Couleur (AIC)'', or ''Internationale Vereinigung für die Farbe'') is a learned society whose aims are to encourage research in all aspects of colour, to disseminate the knowledge gained from this research, and to promote its application to the solution of problems in the fields of science, art, design and industry on an international basis. The AIC also aims for a close cooperation with existing international organizations, such as, for example, the International Commission on Illumination (CIE), the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Commission for Optics (ICO), regarding issues concerned with colour. The AIC will neither duplicate the work of these bodies nor will it attempt to assume any of their responsibilities. In 2009 the AIC agreed on the creation of an International Colour Day, which is celebrated in many countries around the world. History The AIC foundat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opacity (optics)
Opacity is the measure of impenetrability to electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic or other kinds of radiation, especially visible light. In radiative transfer, it describes the absorption and scattering of radiation in a transmission medium, medium, such as a plasma (physics), plasma, dielectric, radiation shield, shielding material, glass, etc. An opaque object is neither Transparency (optics), transparent (allowing all light to pass through) nor translucent (allowing some light to pass through). When light strikes an interface between two substances, in general some may be reflected, some absorbed, some scattered, and the rest transmitted (also see refraction). Reflection can be diffuse reflection, diffuse, for example light reflecting off a white wall, or specular reflection, specular, for example light reflecting off a mirror. An opaque substance transmits no light, and therefore reflects, scatters, or absorbs all of it. Both mirrors and carbon black are opaque. Opacity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of the larger visual system and is mediated by a complex process between neurons that begins with differential stimulation of different types of photoreceptors by light entering the eye. Those photoreceptors then emit outputs that are propagated through many layers of neurons and then ultimately to the brain. Color vision is found in many animals and is mediated by similar underlying mechanisms with common types of biological molecules and a complex history of evolution in different animal taxa. In primates, color vision may have evolved under selective pressure for a variety of visual tasks including the foraging for nutritious young leaves, ripe fruit, and flowers, as well as detecting predator camouflage and emotional states in other pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Blindness
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may make some academic activities more difficult. However, issues are generally minor, and the colorblind automatically develop adaptations and coping mechanisms. People with achromatopsia, total color blindness (achromatopsia) may also be Hemeralopia, uncomfortable in bright environments and have visual impairment, decreased visual acuity. The most common cause of color blindness is an Heredity, inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic disorder called congenital red–green color blindness. Males are more likely to be color blind than females, because the genes responsible for the most common for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Constancy
Color constancy is an example of subjective constancy and a feature of the human color perception system which ensures that the perceived color of objects remains relatively constant under varying illumination conditions. A green apple for instance looks green to us at midday, when the main illumination is white sunlight, and also at sunset, when the main illumination is red. This helps us identify objects. Color vision Color vision is how we perceive the objective color, which people, animals and machines are able to distinguish objects based on the different wavelengths of light reflected, transmitted, or emitted by the object. In humans, light is detected by the eye using two types of photoreceptors, Cone cells, cones and Rod cells, rods, which send signals to the visual cortex, which in turn processes those colors into a subjective perception. Color constancy is a process that allows the brain to recognize a familiar object as being a consistent color regardless of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munsell Color System
In colorimetry, the Munsell color system is a color space that specifies colors based on three properties of color: hue (basic color), chroma (color intensity), and value ( lightness). It was created by Professor Albert H. Munsell in the first decade of the 20th century and adopted by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as the official color system for soil research in the 1930s. Several earlier color order systems had placed colors into a three-dimensional color solid of one form or another, but Munsell was the first to separate hue, value, and chroma into perceptually uniform and independent dimensions, and he was the first to illustrate the colors systematically in three-dimensional space. Munsell's system, particularly the later renotations, is based on rigorous measurements of human subjects' visual responses to color, putting it on a firm experimental scientific basis. Because of this basis in human visual perception, Munsell's system has outlasted its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISCC–NBS System
The ISCC–NBS System of Color Designation is a system for naming colors based on a set of 13 basic color terms and a small set of adjective modifiers. It was first established in the 1930s by a joint effort of the Inter-Society Color Council (ISCC), made up of delegates from various American trade organizations, and the National Bureau of Standards (NBS), a US government agency. As suggested in 1932 by the first chairman of the ISCC, the system’s goal is to be "a means of designating colors in the United States Pharmacopoeia, in the National Formulary, and in general literature ... such designation to be sufficiently standardized as to be acceptable and usable by science, sufficiently broad to be appreciated and used by science, art, and industry, and sufficiently commonplace to be understood, at least in a general way, by the whole public." The system aims to provide a basis on which color definitions in fields from fashion and printing to botany and geology can be systematized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OSA-UCS
In colorimetry the OSA-UCS (Optical Society of America Uniform Color Space) is a color space first published in 1947 and developed by the Optical Society of America’s Committee on Uniform Color Scales. Previously created color order systems, such as the Munsell color system, failed to represent perceptual uniformity in all directions. The committee decided that, in order to accurately represent uniform color differences in each direction, a new shape of three dimensional Cartesian geometry would need to be used. History and development The development of the OSA-UCS took place during many years, from 1947-1977. Not long after the first mathematical color model was developed by the CIE, David MacAdam showed that when selecting a color on the CIE chromaticity diagram, it could not be guaranteed that colors of the same perceived color difference around this color were at the same color distance with respect to the reference color. More simply, the Euclidean distance between an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
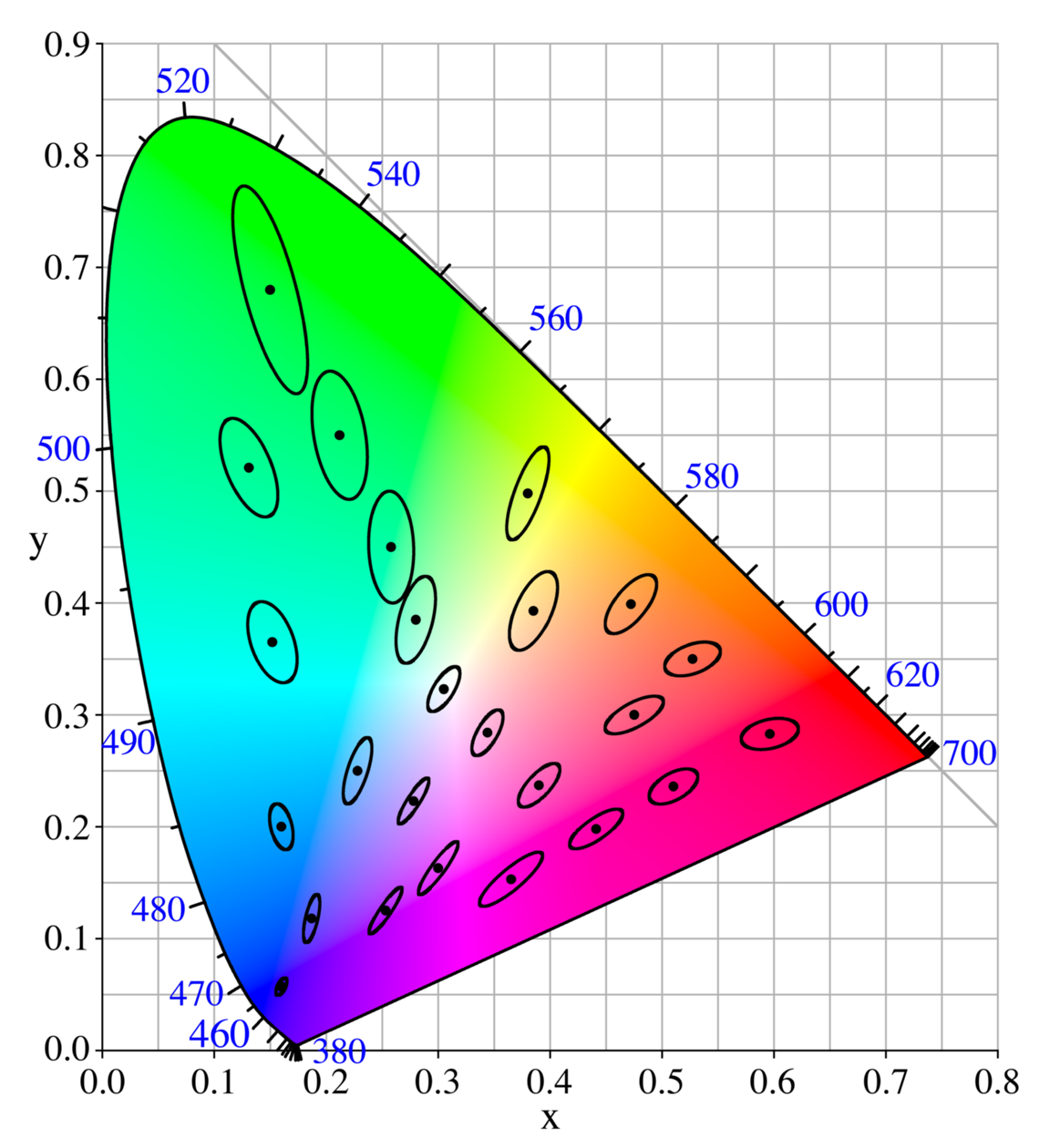
David MacAdam
David Lewis MacAdam (July 1, 1910 – March 9, 1998) was an American physicist and color scientist who made important contributions to color science and technology in the fields of colorimetry, color discrimination, color photography and television, and color order. Education MacAdam grew up in Upper Darby outside of Philadelphia, graduating from Upper Darby High School in 1928, attended Lehigh University, and in 1936 received a PhD in physics from MIT. Under Prof. Arthur C. Hardy, he originated the first course in color measurement and assisted Hardy in the preparation of “Handbook of Colorimetry,” published in 1936. Career Upon graduation MacAdam joined the Research Laboratories of the Eastman Kodak company in Rochester, NY, from where he retired as a Senior Research Associate in 1975. Subsequently, he was named Adjunct Professor at the University of Rochester, Institute of Optics where he remained active until 1995. At Eastman Kodak, among many other things, he helped t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |