|
De Bello Africo
''De Bello Africo'' (also ''Bellum Africum''; ''On the African War'') is a Latin work continuing Julius Caesar's accounts of his campaigns, ''De Bello Gallico'' and '' De Bello Civili'', and its sequel by an unknown author ''De Bello Alexandrino''. It details Caesar's campaigns against his Republican enemies in the province of Africa. Authorship ''De Bello Africo'' is preceded by ''De Bello Alexandrino'' and followed by ''De Bello Hispaniensi''. These three works end the Caesarean corpus relating Caesar's Civil War. The historical narratives, though attributed to Caesar, are assumed to have been written by three different anonymous authors around 40 BC. Though normally collected and bound with Caesar's authentic writings, their authorship has been debated since antiquity. One very plausible theory favors Aulus Hirtius as the author of ''De Bello Alexandrino'' (see there for details). But due to considerable differences in style, scholarly consensus has ruled out the author of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bello Alexandrino
''De Bello Alexandrino'' (also ''Bellum Alexandrinum''; ''On the Alexandrine War'') is a Latin work continuing Julius Caesar's commentaries, ''De Bello Gallico'' and '' De Bello Civili''. It details Caesar's campaigns in Alexandria and Asia. Authorship De Bello Alexandrino is followed by De Bello Africo and De Bello Hispaniensi. These three works end the Caesarean corpus relating Caesar's Civil War. Though normally collected and bound with Caesar's authentic writings, their authorship has been debated since antiquity. Suetonius suggests both Oppius and Hirtius as possible authors of De Bello Alexandrino. Alfred Klotz demonstrates in great detail that the style of De Bello Alexandrino is very similar to the style of the eighth and last book of De Bello Gallico, which is very commonly attributed to Hirtius. Thus it seems likely on stylistic grounds that if it was Hirtius who completed the Gallic Wars, it was Hirtius also who wrote De Bello Alexandrino. But if he did so, his knowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bello Hispaniensi
''De Bello Hispaniensi'' (also ''Bellum Hispaniense''; ''On the Hispanic War''; ''On the Spanish War'') is a Latin work continuing Julius Caesar's commentaries, ''De Bello Gallico'' and '' De Bello Civili'', and its sequels by two different unknown authors ''De Bello Alexandrino'' and ''De Bello Africo''. It details Caesar's campaigns on the Iberian Peninsula, ending with the Battle of Munda. Authorship ''De Bello Hispaniensi'' is preceded by ''De Bello Alexandrino'' and ''De Bello Africo''. These three works end the Caesarean corpus relating Caesar's civil war. Though normally collected and bound with Caesar's authentic writings, their authorship has been debated since antiquity. One very plausible theory favors Hirtius as the author of De Bello Alexandrino (see there for details). But due to considerable differences in style, scholarly consensus has ruled out Hirtius or Julius Caesar as the authors of the two last parts. It has been suggested that these were in fact rough d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain and built a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commentarii De Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; en, Commentaries on the Gallic War, italic=yes), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' ( en, Gallic War, italic=yes), is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine years he spent fighting the Celtic and Germanic peoples in Gaul that opposed Roman conquest. The "Gaul" that Caesar refers to is ambiguous, as the term had various connotations in Roman writing and discourse during Caesar's time. Generally, Gaul included all of the regions primarily inhabited by Celts, aside from the province of Gallia Narbonensis (modern-day Provence and Languedoc-Roussillon), which had already been conquered in Caesar's time, therefore encompassing the rest of modern France, Belgium, Western Germany, and parts of Switzerland. As the Roman Republic made inroads deeper into Celtic territory and conquered more land, the definition of "Gaul" shifted. Concu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commentarii De Bello Civili
''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' ''(Commentaries on the Civil War)'', or ''Bellum Civile'', is an account written by Julius Caesar of his war against Gnaeus Pompeius and the Roman Senate. It consists of three books covering the events of 49–48 BC, from shortly before Caesar's invasion of Italy to Pompey's defeat at the Battle of Pharsalus and flight to Egypt. It was preceded by the much longer account of Caesar's campaigns in Gaul and was followed by similar works covering the ensuing wars against the remnants of Pompey's armies in Egypt, North Africa, and Spain. Caesar's authorship of the ''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' is not disputed, while the three later works are believed to have been written by contemporaries of Caesar. Title The Latin title "Commentarii de Bello Civili" is often retained as the title of the book in English translations of the work. The title itself is Latin for "Commentaries on the Civil War". It is sometimes shortened to just "Civil Wars", "About th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa Province
Africa Proconsularis was a Roman province on the northern African coast that was established in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the coast of western Libya along the Gulf of Sirte. The territory was originally inhabited by Berber people, known in Latin as ''Mauri'' indigenous to all of North Africa west of Egypt; in the 9th century BC, Phoenicians built settlements along the Mediterranean Sea to facilitate shipping, of which Carthage rose to dominance in the 8th century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic. It was one of the wealthiest provinces in the western part of the Roman Empire, second only to Italy. Apart from the city of Carthage, other large settlements in the province were Hadrumetum (modern Sousse, Tunisia), capital of Byzacena, and Hippo Regius (modern Annaba, Algeria). History Rome's first province in northern Africa was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
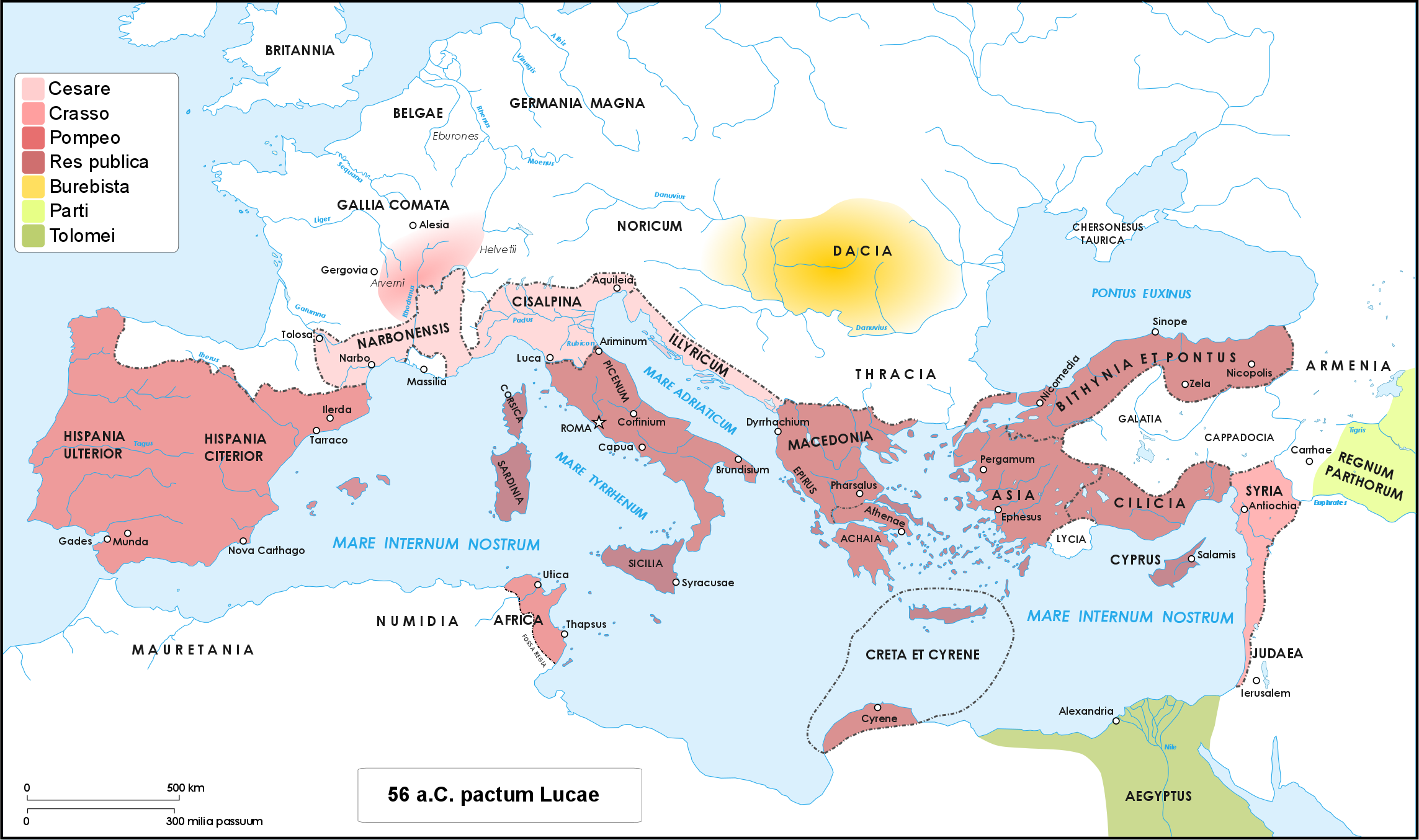
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Hirtius
Aulus Hirtius (; – 43 BC) was consul of the Roman Republic in 43 BC and a writer on military subjects. He was killed during his consulship in battle against Mark Antony at the Battle of Mutina. Biography He was a legate of Julius Caesar's starting around 58 BC and served as an envoy to Pompey in 50. It was reported that Hirtius dined with Caesar, Sallust, Oppius, Balbus and Sulpicius Rufus on the night after Caesar's famous crossing over the Rubicon river into Italy on 10 January 49 BC. During Caesar's Civil War he served in Spain; he may have been a tribune in 48, and in 47 was at Antioch. He was a praetor in 46 and governor of Transalpine Gaul in 45. After Caesar's assassination in March 44, Hirtius was deeply involved in the maneuvering between parties. Having been nominated for that post by Caesar, Hirtius and Pansa became consuls in 43. Initially a supporter of Mark Antony, Hirtius was successfully lobbied by Cicero, who was a personal friend, and switched his allegia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and Latin literature designed to make the text accessible to the broadest possible audience by presenting the original Greek or Latin text on each left-hand page, and a fairly literal translation on the facing page. The General Editor is Jeffrey Henderson, holder of the William Goodwin Aurelio Professorship of Greek Language and Literature at Boston University. History The Loeb Classical Library was conceived and initially funded by the Jewish-German-American banker and philanthropist James Loeb (1867–1933). The first volumes were edited by Thomas Ethelbert Page, W. H. D. Rouse, and Edward Capps, and published by William Heinemann, Ltd. (London) in 1912, already in their distinctive green (for Greek text) and red (for Latin) hardcover bin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The War On Cato
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Histories
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
