|
David Relman
David Arnold Relman is an American microbiologist and the Thomas C. and Joan M. Merigan Professor in Medicine, and in Microbiology & Immunology at the Stanford University School of Medicine. His research focuses on the human microbiome and microbial ecosystem—for which he was a pioneer in the use of modern molecular methods, as well as on pathogen discovery and the genomics of host response. Education Relman was born in Boston, raised in Lexington, MA, and then moved to Philadelphia where he attended Germantown Friends School. He was an undergraduate at MIT and graduated in 1977. He attended medical school at the Harvard Medical School and received an M.D. degree, magna cum laude in 1982. He did his internship, residency, and a clinical infectious diseases fellowship year at Massachusetts General Hospital. He completed his infectious diseases and microbiology research training as a postdoctoral fellow with Stanley Falkow at Stanford University. He began his independent career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th-List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the country. The city boundaries encompass an area of about and a population of 675,647 2020 U.S. Census, as of 2020. It is the seat of Suffolk County, Massachusetts, Suffolk County (although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999). The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country. A broader combined statistical area (CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postdoctoral Fellow
A postdoctoral fellow, postdoctoral researcher, or simply postdoc, is a person professionally conducting research after the completion of their doctoral studies (typically a PhD). The ultimate goal of a postdoctoral research position is to pursue additional research, training, or teaching in order to have better skills to pursue a career in academia, research, or any other field. Postdocs often, but not always, have a temporary academic appointment, sometimes in preparation for an academic faculty position. They continue their studies or carry out research and further increase expertise in a specialist subject, including integrating a team and acquiring novel skills and research methods. Postdoctoral research is often considered essential while advancing the scholarly mission of the host institution; it is expected to produce relevant publications in peer-reviewed academic journals or conferences. In some countries, postdoctoral research may lead to further formal qualification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Academy Of Microbiology
The American Society for Microbiology (ASM), originally the Society of American Bacteriologists, is a professional organization for scientists who study viruses, bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa as well as other aspects of microbiology. It was founded in 1899. The Society publishes a variety of scientific journals, textbooks, and other educational materials related to microbiology and infectious diseases. ASM organizes annual meetings, as well as workshops and professional development opportunities for its members. History ASM was founded in 1899 under the name the "Society of American Bacteriologists." In December 1960, it was renamed the "American Society for Microbiology." Mission ASM's mission is "to promote and advance the microbial sciences." The society seeks to accomplish this mission through: * Publishing highly-cited publications * Running multi-disciplinary meetings * Deploying resources and expertise around the world * Advocating for scientific research * Fosteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosecurity
Biosecurity refers to measures aimed at preventing the introduction and/or spread of harmful organisms (e.g. viruses, bacteria, etc.) to animals and plants in order to minimize the risk of transmission of infectious disease. In agriculture, these measures are aimed at protecting food crops and livestock from pests, invasive species, and other organisms not conducive to the welfare of the human population. The term includes biological threats to people, including those from pandemic diseases and bioterrorism. The definition has sometimes been broadened to embrace other concepts, and it is used for different purposes in different contexts. The COVID-19 pandemic is a recent example of a threat for which biosecurity measures have been needed in all countries of the world. Background and terminology The term "biosecurity" has been defined differently by various disciplines. The term was first used by the agricultural and environmental communities to describe preventative measures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeman Spogli Institute For International Studies
Stanford University has many centers and institutes dedicated to the study of various specific topics. These centers and institutes may be within a department, within a school but across departments, an independent laboratory, institute or center reporting directly to the dean of research and outside any school, or semi-independent of the university itself. Independent laboratories, institutes and centers These report directly to the vice-provost and dean of research and are outside any school though any faculty involved in them must belong to a department in one of the schools. These include Bio-X and Spectrum in the area of Biological and Life Sciences; Precourt Institute for Energy and Woods Institute for the Environment in the Environmental Sciences area; the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences (CASBS), the Center for the Study of Language and Information (CSLI) (see below), Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies (FSI) (see below), Human-Sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whipple's Disease
Whipple's disease is a rare systemic infectious disease caused by the bacterium '' Tropheryma whipplei''. First described by George Hoyt Whipple in 1907 and commonly considered as a gastrointestinal disorder, Whipple's disease primarily causes malabsorption, but may affect any part of the human body, including the heart, brain, joints, skin, lungs and the eyes. Weight loss, diarrhea, joint pain, and arthritis are common presenting symptoms, but the presentation can be highly variable in certain individuals, and about 15% of patients do not have the standard signs and symptoms. Whipple's disease is significantly more common in men, with 87% of patients diagnosed being male. When recognized and treated, Whipple's disease can usually be cured with long-term antibiotic therapy, but if the disease is left undiagnosed or untreated, it can ultimately be fatal. Signs and symptoms The most common symptoms are diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss, and joint pains. The joint pains may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillary Angiomatosis
Bacillary angiomatosis (BA) is a form of angiomatosis associated with bacteria of the genus ''Bartonella''. Symptoms Cutaneous BA is characterised by the presence of lesions on or under the skin. Appearing in numbers from one to hundreds, these lesions may take several forms: * papules or nodules which are red, globular and non-blanching, with a vascular appearance * purplish nodules sufficiently similar to Kaposi's sarcoma that a biopsy may be required to verify which of the two it is * a purplish lichenoid plaque * a subcutaneous nodule which may have ulceration, similar to a bacterial abscess While cutaneous BA is the most common form, it can also affect several other parts of the body, such as the brain, bone, bone marrow, lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, spleen, and liver. Symptoms vary depending on which parts of the body are affected; for example, those whose livers are affected may have an enlarged liver and fever, while those with osseous BA exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Amplification
Gene amplification refers to a number of natural and artificial processes by which the number of copies of a gene is increased "without a proportional increase in other genes". Artificial DNA amplification In research or diagnosis DNA amplification can be conducted through methods such as: * Polymerase chain reaction, an easy, cheap, and reliable way to repeatedly replicate a focused segment of DNA by polymerizing nucleotides, a concept which is applicable to numerous fields in modern biology and related sciences. * Ligase chain reaction, a method that amplifies the nucleic acid used as the probe. For each of the two DNA strands, two partial probes are ligated to form the actual one; thus, LCR uses two enzymes: a DNA polymerase (used for initial template amplification and then inactivated) and a thermostable DNA ligase. * Transcription-mediated amplification, an isothermal, single-tube nucleic acid amplification system utilizing two enzymes, RNA polymerase and reverse transcri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Subunit RRNA
Small subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid (SSU rRNA) is the smaller of the two major RNA components of the ribosome. Associated with a number of ribosomal proteins, the SSU rRNA forms the small subunit of the ribosome. It is encoded by SSU- rDNA. Characteristics Use in phylogenetics SSU rRNA sequences are widely used for determining evolutionary relationships among organisms, since they are of ancient origin and are found in all known forms of life. See also *LSU rRNA Large subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid (LSU rRNA) is the largest of the two major RNA components of the ribosome. Associated with a number of ribosomal proteins, the LSU rRNA forms the large subunit of the ribosome. The LSU rRNA acts as a ribo ...: the large subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid. References {{Ribosome subunits Ribosomal RNA Protein biosynthesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
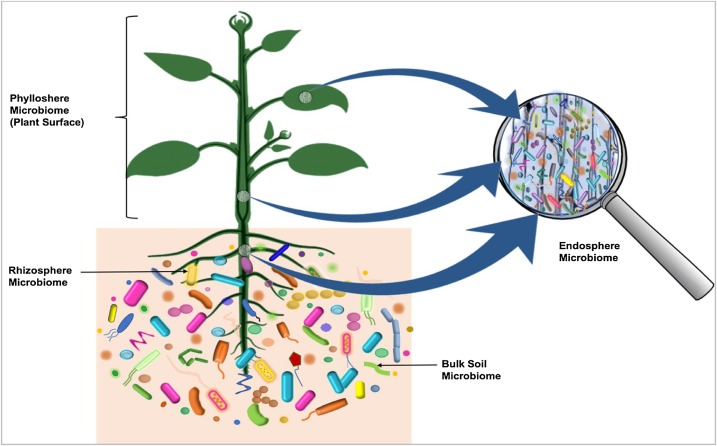
Microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or within the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product ( short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pathos'' 'suffering, disease' and γένεσις ''genesis'' 'creation'. Description Types of pathogenesis include microbial infection, inflammation, malignancy and tissue breakdown. For example, bacterial pathogenesis is the process by which bacteria cause infectious illness. Most diseases are caused by multiple processes. For example, certain cancers arise from dysfunction of the immune system (skin tumors and lymphoma after a renal transplant, which requires immunosuppression), Streptococcus pneumoniae is spread through contact with respiratory secretions, such as saliva, mucus, or cough droplets from an infected person and colonizes the upper respiratory tract and begins to multiply. The pathogenic mechanisms of a disease (or con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |