|
Daulat (painter)
Muhammad Daulat (or Dawlat) was a leading artist in Mughal painting, active on imperial commissions between about 1595 and 1635–1640, during the reigns of Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan. He began his career painting large narrative scenes, then specialized in portraits, but later in his career seems to have specialized in highly ornate borders to miniatures. Life and career His father, L'al, served in the imperial court, very likely as one of the many artists in the imperial workshop. Daulat trained there and was active as a painter by the mid-1590s, remaining for the whole of his career. His brother Daud (Da'ud) was also an artist, who is usually referred to in inscriptions and art history as "Daud, brother of Daulat". Like Govardhan, the other main portrait specialist of the period, and ultimately a finer artist than Daulat, he was influenced by Basawan. Important manuscript projects he contributed to in the 1590s include the British Library ''Akbarnama'' (MS Or. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daulat Self-portrait
{{disambiguation, given name ...
Daulat may refer to: *Daulat (painter), Mughal painter * ''Daulat'' (1949 film) * ''Daulat'' (1982 film) * ''Daulat'' (2020 film) *Daulat Beg Oldi, Indian military base in Ladakh People with the given name *Daulat Khan Lodi, 16th-century governor of Lahore *Daulat Rao Sindhia, Maharaja of Gwalior (d. 1827) See also * al-Dawla The Arabic title ''al-Dawla'' (, often rendered ''ad-Dawla'', ''ad-Daulah'', ''ud-Daulah'', etc.) means 'dynasty' or 'state', (in modern usage, 'government') and appears in many laqab, honorific and regnal titles in the Islamic world. Invented i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colophon (publishing)
In publishing, a colophon () is a brief statement containing information about the publication of a book such as an "imprint" (the place of publication, the publisher, and the date of publication). A colophon may include the device (logo) of a printer or publisher. Colophons are traditionally printed at the ends of books (see History below for the origin of the word), but sometimes the same information appears elsewhere (when it may still be referred to as colophon) and many modern (post-1800) books bear this information on the title page or on the verso of the title-leaf, which is sometimes called a "biblio-page" or (when bearing copyright data) the " copyright-page". History The term ''colophon'' derives from the Late Latin ''colophōn'', from the Greek κολοφών (meaning "summit" or "finishing touch"). The term colophon was used in 1729 as the bibliographic explication at the end of the book by the English printer Samuel Palmer in his ''The General History of Printing, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Indian Painters
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Painters
Mughal or Moghul may refer to: Related to the Mughal Empire * Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries * Mughal dynasty * Mughal emperors * Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia * Mughal architecture * Mughlai cuisine * Mughal painting Other uses * Moghulistan in Central Asia ** Moghol people * Moghul, Iran, a village * Mirza Mughal (1817–1857), a Mughal prince * Fiyaz Mughal, founder of Tell MAMA Tell MAMA (Measuring Anti-Muslim Attacks) is a national project which records and measures anti-Muslim incidents in the United Kingdom. It is modelled on the Jewish Community Security Trust (CST) and like the CST it also provides support for vi ... See also * Mogul (other) * Mughal-e-Azam (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuart Cary Welch
Stuart Cary Welch Jr. (2 April 1928 – 13 August 2008) was an American scholar and curator of Indian and Islamic art. Life and career Welch was born to a prominent family in Buffalo, New York. His maternal grandfather, Norman Edward Mack, was publisher of The Buffalo Times. He began collecting drawings by Indian artists as a boy. He earned a bachelor's degree in fine arts from Harvard University in 1950, then did graduate work there in classical art. Because they offered no Indian or Islamic art courses at the time, he became an autodidact. His first paid position at Harvard was in 1956, as honorary assistant keeper of Islamic Art at the Fogg Museum. He later developed one of the first curricula for Islamic and Indian art. He was curator of Islamic and Later Indian art at the Harvard Art Museum, and from 1979 to 1987, he was also special consultant for the department of Islamic art at the Metropolitan Museum of Art.Raynor, Vivien (December 21, 1979). Art People; Expert on In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Mandsaur of Madhya Pradesh and some parts of Gujarat. For centuries, the region was ruled by Rajputs. The princely state of Udaipur emerged as an administrative unit during the period of British East India Company governance in India and remained until the end of the British Raj era. The Mewar region lies between the Aravali Range to the northwest, Ajmer to the north, Gujarat and the Vagad region of Rajasthan to the south, the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh state to the south and the Hadoti region of Rajasthan to the east. Etymology The word "Mewar" is vernacular form of "Medapata" ( IAST: Medapāṭa), the ancient name of the region. The earliest epigraph that mentions the word "Medapata" is a 996–997 CE (1053 VS) inscription discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amar Singh I
Maharana Amar Singh I, the Maharana of Mewar (March 16, 1559 – January 26, 1620), was the eldest son and successor of Maharana Pratap of Mewar. He was the 16th Rana of Mewar dynasty of Sisodia Rajputs and ruler of Mewar from January 19, 1597 till his death on January 26, 1620. His capital was Udaipur. Birth and coronation Amar Singh was the eldest son of Maharana Pratap. He was born in Chittor on 16 March 1559 to Maharana Pratap and Maharani Ajabde Punwar, the same year, when foundation of Udaipur was laid by his grandfather, Udai Singh II. Amar Singh succeeded Maharana Pratap upon his death on 19 January 1597. Reign In start of his reign, Amar Singh implemented internal reforms. He defined the order of precedence for his chiefs, and their privileges. He also rehabilitated people, who were displaced due to Mughal invasions, settled them in many villages, including Kelwa, Muroli and Rampura. He appointed Hari Das Jhala as the commander of his standing army and made larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishandas
Bishandas was a 17th-century Mughal painter at the court of the Mughal emperor Jahangir (1569–1627), specializing in portraits. Jahangir praised him as "unrivalled in the art of portraiture". Though little is known of Bishandas’ life, his name suggests he was a Hindu, like several others in the imperial workshop. In 1613 he was sent on a diplomatic mission to Persia, to paint the portraits of Shah Abbas I of Persia (1571–1629) and other leading Persian figures. Here he was so successful that he remained until 1620, and on his return Jahangir gave him an elephant. File:Recto- "Portrait of Raja Suraj Singh Rathor", verso- Page of Calligraphy. Folio from the Shah Jahan Album MET DT200625 (cropped).jpg, Portrait of Raja Suraj Singh of Jodhpur, Jahangir's brother in law. File:Bishan Das. Shaikh Phul in His Hermitage, ca 1610, Bharat Kala Bhavan, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi -.jpg, Shaikh Phul in His Hermitage, c. 1610 File:Bishan Das. The Birth of Prince, ca 1610-15, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu'l Hasan
Abu'l-Hasan (or Abu al-Hasan) (1589 – c. 1630), from Delhi, India, was a Mughal painter of miniatures during the reign of Jahangir. Biography Abu al-Hasan was the son of Aqa Reza of Herat in Safavid Iran, a city with an artistic tradition. Aqa Reza was established as an artist and took up employment with Jahangir (r. 1605 –1627) before the latter's accession to the throne of the Mughal empire. When Abu al-Hasan began producing art, the emperor, Jahangir, appreciated the skills of the boy. In 1599, Abu al-Hasan moved with Jahangir to his newly founded court in Allahabad. The emperor considered Abu al-Hasan to be particularly special to him and under his care. This is because although Abu al-Hasan's artwork was similar in many ways to his father's with Dutch and English influence, it was considered to be of a higher quality similar to that of older masters in the field. Jahangir said of Abu al-Hasan that he had no equal and for the work done on the frontispiece for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most populous city in Iran and Western Asia, and has the second-largest metropolitan area in the Middle East, after Cairo. It is ranked 24th in the world by metropolitan area population. In the Classical era, part of the territory of present-day Tehran was occupied by Rhages, a prominent Median city destroyed in the medieval Arab, Turkic, and Mongol invasions. Modern Ray is an urban area absorbed into the metropolitan area of Greater Tehran. Tehran was first chosen as the capital of Iran by Agha Mohammad Khan of the Qajar dynasty in 1786, because of its proximity to Iran's territories in the Caucasus, then separated from Iran in the Russo-Iranian Wars, to avoid the vying factions of the previously ruling Iranian dynasties. The capital has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
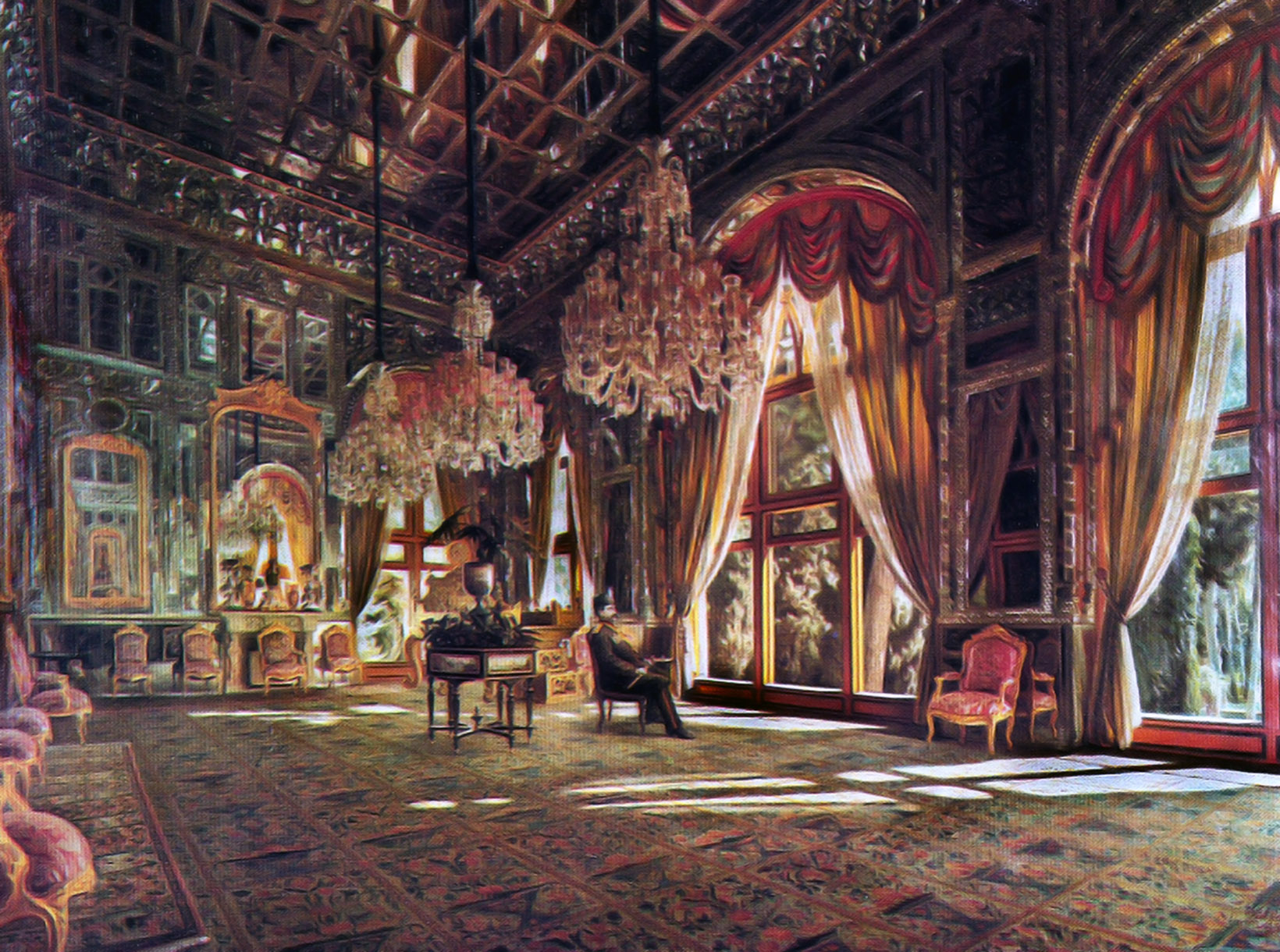
Golestan Palace
The Golestan Palace ( fa, کاخ گلستان, ''Kākh-e Golestān''), also transliterated as the Gulistan Palace and sometimes translated as the Rose Garden Palace from Persian language, was built in the 16th century, renovated in the 18th century and finally rebuilt in 1865. It is the former official royal Qajar complex in Tehran. One of the oldest historic monuments in the city of Tehran, and of world heritage status, the Golestan Palace belongs to a group of royal buildings that were once enclosed within the mud-thatched walls of Tehran's arg ("citadel"). It consists of gardens, royal buildings, and collections of Iranian crafts and European presents from the 18th and 19th centuries. History Tehran's arg ("citadel") was built during the reign of Tahmasp I (r. 1524–1576) of the Safavid dynasty (1502–1736), and was later renovated by Karim Khan of the Zand dynasty (r. 1750–1779). Agha Mohammad Khan of the Qajar dynasty (1742–1797) chose Tehran as his capital. The arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |