|
Dastgāh
Dastgāh ( fa, دستگاه) is the standard musical system in Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent musical mode in Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mother of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic notes, plus several variable notes used for ornamentation and modulation. Each is a certain modal variety subject to a course of development () that is determined by the pre-established order o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgāh-e Šur
Dastgāh-e Šur ( fa, دستگاه شور; az, Şur) is one of the seven ''Dastgāh''s of Persian Music (Classically, Persian Music is organized into seven ''Dastgāhs'' and five '' Āvāz''es, however from a merely technical point of view, one can consider them as an ensemble of 12 ''Dastgāh''s). Introduction ''Šur'' is in some respects the most important of the ''Dastgāh''s. It contains a large body of pieces, and in its domain belong four important '' Āvāz''es: '' Dašti'', '' Abuatā'', '' Bayāt-e Tork'' and '' Afšāri''. A great many folk tunes, from different parts of Persia, are founded on the modal schemes of ''Šur'' or its derivative ''Dastgāh''s and ''Guše''s. The melodic formation in ''Šur'' is conceived within the modal structure shown below for ''Šur D'' : :: The characteristics of this mode are: # The tetrachord above the finalis (marked with "F") is the focal point of melodic activity. # The finalis is the most emphasized tone. # The 4th above is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgah Segah
Dastgāh ( fa, دستگاه) is the standard musical system in Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent musical mode in Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mother of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic notes, plus several variable notes used for ornamentation and modulation. Each is a certain modal variety subject to a course of development () that is determined by the pre-established order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgah Homayoun
Dastgāh ( fa, دستگاه) is the standard musical system in Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent musical mode in Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mother of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic notes, plus several variable notes used for ornamentation and modulation. Each is a certain modal variety subject to a course of development () that is determined by the pre-established order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgah Chahargah
Dastgāh ( fa, دستگاه) is the standard musical system in Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent musical mode in Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mother of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic notes, plus several variable notes used for ornamentation and modulation. Each is a certain modal variety subject to a course of development () that is determined by the pre-established order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgāh-e Māhur
Dastgāh-e Māhūr or Dastgaah-e Maahur ( fa, دستگاه ماهور) is one of the seven ''Dastgāh''s of Persian Music (Classically, Persian Music is organized into seven ''Dastgāhs'' and five '' Āvāz''es, however from a merely technical point of view, one can consider them as an ensemble of 12 ''Dastgāh''s). Introduction The intervallic structure of the mode of ''Māhur'' partly parallels that of the major mode in western classic music. Yet, because of the other elements which go into the making of Persian modes, probably no melody in the major mode can be said to be in the mode of ''Māhur''. A far closer analogue from an intervallic standpoint is the Obikhod scale (widespread in Russian medieval Znamenny chant and folk song) and the Jewish Adonai malakh mode. The modal structure of ''Māhur'' is shown below for ''Māhur C'' : :: The characteristics of this mode are: # The range is unusually wide, a minor 10th. # The finalis (marked "Ā,F") has a central position; it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirza Abdollah
Mirza Abdollah, also known as Agha Mirza Abdollah Farahani ( fa, میرزا عبدالله فراهانی) (1843–1918), was a tar and setar player. He is among the most significant musicians in Iran's history. Born in Shiraz, he and his younger brother Mirza Hossein Gholi started learning music from their father Ali Akbar Farahani who was a well-known musician. He is best known for his radif for tar and setar and for his fruitful music lessons. Abolhasan Saba, Esmaeil Ghahremani and Ali-Naqi Vaziri were among his students. Mírzá 'Abdu'lláh was one of the most influential masters of Persian classical music. Because of his desire to collect and assemble a large repertoire of traditional pieces, and because of his generosity of spirit, and his willingness to teach others, the particular rendition of Persian music he collected has become the most widely known and the most practiced among contemporary Persian musicians. His association with the Bahá'í faith, and mystica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
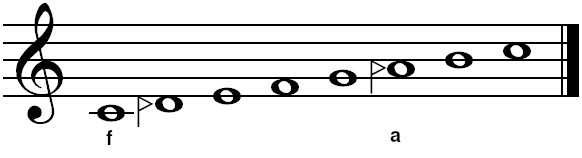
Sori (music)
The sori (Persian:سری) is a symbol that corresponds to a quarter step higher in tone in Persian traditional music. It is written as a ">" sign, crossed by two vertical lines, and can be used like an accidental. In the early 20th century, Iranian master musician Alinaghi Vaziri established this sign for the sori for use in written Persian music using standard western notation. Character representation of this accidental symbol together with Koron encoding (encoded as U+1D1E9 and U+1D1EA) microtones used in modern Iranian classical music added to the Unicode standard in Version 14.0.0. File:Sori used in musical notation.png, Sori used in musical notation See also *Persian traditional music *Dastgah *Quarter tone * koron External links Persian accidentalsin the SMuFL Standard Music Font Layout, or SMuFL, is an open standard for music font mapping. The standard was originally developed by Daniel Spreadbury of Steinberg for its scorewriter software Dorico, but is now deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koron (music)
The koron (Persian: کرن), meaning "less than lower in pitch", is a symbol used in traditional Persian music in order to lower or "flatten" a written note by an interval smaller than a semitone (broadly corresponding to a quarter tone, or specifically a half flat). It is used to alter the pitch of a written note, similar to that of a sharp or a flat. It is written as a line with an open triangular head at the top-right. The koron symbol is positioned in the same manner as other accidentals in Western music, and can even be used in key signatures (see example below). In the early 20th century, Iranian master musician Alinaghi Vaziri established the standard usage of this symbol in written music. It is used for notating many of the microtones found in traditional Persian music. A note so altered can be labeled as the note's letter, followed by "koron" (e.g., "B koron", "D koron", etc.). Character representation of this accidental symbol together with Sori encoding (encoded as U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitches and/or chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, attractions and directionality. In this hierarchy, the single pitch or triadic chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. The root of the tonic chord forms the name given to the key, so in the key of C major, the note C is both the tonic of the scale and the root of the tonic chord (which is C–E–G). Simple folk music songs often start and end with the tonic note. The most common use of the term "is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910". Contemporary classical music from 1910 to the 2000s may practice or avoid any sort of tonality—but harmony in almost all Western popular music remains tonal. Harmony in jazz includes many but not all tonal characteristics of the European common practice period, usually known as "classical music". "All harmonic idioms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koron Sign
{{dab, geo ...
Koron may refer to: * Koron (Cappadocia), now in Turkey * Koron (music), in Persian traditional music See also * Karun, Hormozgan or Korūn, Iran * Koroni or Corone, Greece * Coron (other) * Colon (other) * Colón (other) * Kolon (other) Kolon may refer to: * Kolon Industries, a Korean company * Kolon, Chad, a sub-prefecture of Chad See also * Abba Kolon, a figure in Talmudic mythology * Ali Kolon, 15th-century Songhai king * Colon (other) * Kollon * Kolong (disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |