|
Dastgah Homayoun
Dastgāh ( fa, دستگاه) is the standard musical system in Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent musical mode in Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mother of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic notes, plus several variable notes used for ornamentation and modulation. Each is a certain modal variety subject to a course of development () that is determined by the pre-established order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists
UNESCO established its Lists of Intangible Cultural Heritage with the aim of ensuring better protection of important intangible cultural heritages worldwide and the awareness of their significance.Compare: This list is published by the Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage, the members of which are elected by State Parties meeting in a General Assembly. Through a compendium of the different oral and intangible treasures of humankind worldwide, the programme aims to draw attention to the importance of safeguarding intangible heritage, which UNESCO has identified as an essential component and as a repository of cultural diversity and of creative expression. The list was established in 2008 when the 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage took effect. the programme compiles two lists. The longer, Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, comprises cultural "practices and expressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgah Segah
Dastgāh ( fa, دستگاه) is the standard musical system in Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent musical mode in Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mother of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic notes, plus several variable notes used for ornamentation and modulation. Each is a certain modal variety subject to a course of development () that is determined by the pre-established order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgah Homayoun
Dastgāh ( fa, دستگاه) is the standard musical system in Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent musical mode in Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mother of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic notes, plus several variable notes used for ornamentation and modulation. Each is a certain modal variety subject to a course of development () that is determined by the pre-established order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgah Chahargah
Dastgāh ( fa, دستگاه) is the standard musical system in Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent musical mode in Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mother of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic notes, plus several variable notes used for ornamentation and modulation. Each is a certain modal variety subject to a course of development () that is determined by the pre-established order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
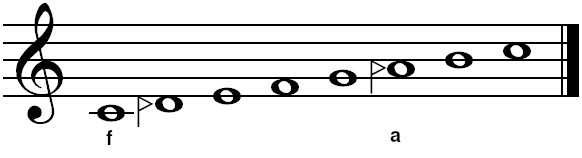
Sori (music)
The sori (Persian:سری) is a symbol that corresponds to a quarter step higher in tone in Persian traditional music. It is written as a ">" sign, crossed by two vertical lines, and can be used like an accidental. In the early 20th century, Iranian master musician Alinaghi Vaziri established this sign for the sori for use in written Persian music using standard western notation. Character representation of this accidental symbol together with Koron encoding (encoded as U+1D1E9 and U+1D1EA) microtones used in modern Iranian classical music added to the Unicode standard in Version 14.0.0. File:Sori used in musical notation.png, Sori used in musical notation See also *Persian traditional music *Dastgah *Quarter tone * koron External links Persian accidentalsin the SMuFL Standard Music Font Layout, or SMuFL, is an open standard for music font mapping. The standard was originally developed by Daniel Spreadbury of Steinberg for its scorewriter software Dorico, but is now deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koron (music)
The koron (Persian: کرن), meaning "less than lower in pitch", is a symbol used in traditional Persian music in order to lower or "flatten" a written note by an interval smaller than a semitone (broadly corresponding to a quarter tone, or specifically a half flat). It is used to alter the pitch of a written note, similar to that of a sharp or a flat. It is written as a line with an open triangular head at the top-right. The koron symbol is positioned in the same manner as other accidentals in Western music, and can even be used in key signatures (see example below). In the early 20th century, Iranian master musician Alinaghi Vaziri established the standard usage of this symbol in written music. It is used for notating many of the microtones found in traditional Persian music. A note so altered can be labeled as the note's letter, followed by "koron" (e.g., "B koron", "D koron", etc.). Character representation of this accidental symbol together with Sori encoding (encoded as U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitches and/or chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, attractions and directionality. In this hierarchy, the single pitch or triadic chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. The root of the tonic chord forms the name given to the key, so in the key of C major, the note C is both the tonic of the scale and the root of the tonic chord (which is C–E–G). Simple folk music songs often start and end with the tonic note. The most common use of the term "is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910". Contemporary classical music from 1910 to the 2000s may practice or avoid any sort of tonality—but harmony in almost all Western popular music remains tonal. Harmony in jazz includes many but not all tonal characteristics of the European common practice period, usually known as "classical music". "All harmonic idioms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koron Sign
{{dab, geo ...
Koron may refer to: * Koron (Cappadocia), now in Turkey * Koron (music), in Persian traditional music See also * Karun, Hormozgan or Korūn, Iran * Koroni or Corone, Greece * Coron (other) * Colon (other) * Colón (other) * Kolon (other) Kolon may refer to: * Kolon Industries, a Korean company * Kolon, Chad, a sub-prefecture of Chad See also * Abba Kolon, a figure in Talmudic mythology * Ali Kolon, 15th-century Songhai king * Colon (other) * Kollon * Kolong (disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological change, form of words and, by extension, the origin and evolution of their semantic meaning across time. It is a subfield of historical linguistics, and draws upon comparative semantics, Morphology_(linguistics), morphology, semiotics, and phonetics. For languages with a long recorded history, written history, etymologists make use of texts, and texts about the language, to gather knowledge about how words were used during earlier periods, how they developed in Semantics, meaning and Phonological change, form, or when and how they Loanword, entered the language. Etymologists also apply the methods of comparative linguistics to reconstruct information about forms that are too old for any direct information to be available. By analyzing related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musicology
Musicology (from Greek μουσική ''mousikē'' 'music' and -λογια ''-logia'', 'domain of study') is the scholarly analysis and research-based study of music. Musicology departments traditionally belong to the humanities, although some music research is scientific in focus (psychological, sociological, acoustical, neurological, computational). Some geographers and anthropologists have an interest in musicology so the social sciences also have an academic interest. A scholar who participates in musical research is a musicologist. Musicology traditionally is divided in three main branches: historical musicology, systematic musicology and ethnomusicology. Historical musicologists mostly study the history of the western classical music tradition, though the study of music history need not be limited to that. Ethnomusicologists draw from anthropology (particularly field research) to understand how and why people make music. Systematic musicology includes music theory, aesthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)



