|
Dart (missile)
Darts are airborne ranged weapons. They are designed to fly such that a sharp, often weighted point will strike first. They can be distinguished from javelins by the presence of fletching (feathers on the tail) and a shaft that is shorter and/or more flexible. Darts can be propelled by hand or with the aid of a hand-held implement such as a blowgun. They can be distinguished from arrows because they are not used with a bow. Darts have been used since pre-history. The plumbatae were lead-weighted darts thrown by infantrymen in Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Darts can be propelled by a number of means. The atlatl uses leverage to increase the velocity of the dart, the kestros increases the range of propelled darts using a sling, and the exhalation of a person's breath through a blowgun propels small stone points or poisoned needles with pneumatic force. In the modern era, darts have been used for recreation; in lawn darts and the game of darts. History Pre-history Some of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, iron, steel, or bronze. The most common design for hunting or combat spears since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, lozenge, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature barbs or serrated edges. The word '' spear'' comes from the Old English '' spere'', from the Proto-Germanic ''speri'', from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*sper-'' "spear, pole". Spears can be divided into two broad categories: those designed for thrusting as a melee weapon and those designed for throwing as a ranged weapon (usually referred to as javelins or darts). The spear has been used throughout human history both as a hunting and fishing tool and as a weapon. Along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolerance (engineering)
Engineering tolerance is the permissible limit or limits of variation in: # a physical dimension; # a measured value or physical property of a material, manufactured object, system, or service; # other measured values (such as temperature, humidity, etc.); # in engineering and safety, a physical distance or space (tolerance), as in a truck (lorry), train or boat under a bridge as well as a train in a tunnel (see structure gauge and loading gauge); # in mechanical engineering, the space between a bolt and a nut or a hole, etc. Dimensions, properties, or conditions may have some variation without significantly affecting functioning of systems, machines, structures, etc. A variation beyond the tolerance (for example, a temperature that is too hot or too cold) is said to be noncompliant, rejected, or exceeding the tolerance. Considerations when setting tolerances A primary concern is to determine how wide the tolerances may be without affecting other factors or the outcome of a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amentum
An ''amentum'' (Greek ''ἀγκύλη'') was a leather strap attached to a javelin used in ancient Greek athletics, hunting, and warfare, which helped to increase the range and the stability of the javelin in flight. Stability in flight was important because it allowed the javelin to land on its point, which was the only way the throw could be accurately recorded in competition or be useful against a live target. An amentum also increased the effective length of the throwing arm, as does a spear-thrower, and so enhanced speed. It is very similar to the Swiss arrow. Throwing technique The javelin was held at ear level and released after a short run. The amentum was looped over the first two fingers of the throwing hand so as to slip off when the throw was made. In competition throwing for distance, including the Ancient Olympic pentathlon at Olympia, Greece, a blunt javelin would be launched at about 45 degrees, but in war or the chase, a sharp weapon was thrown much closer to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
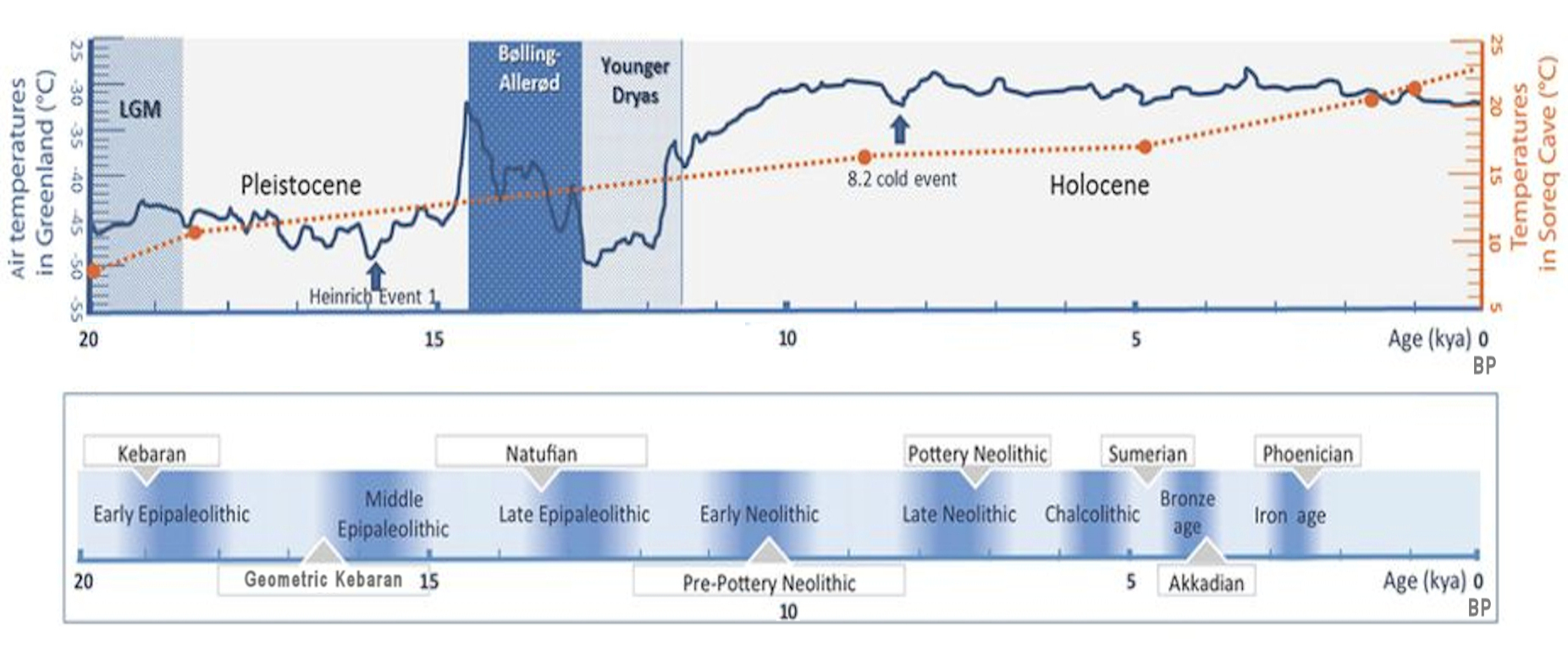
Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are sometimes confused or used as synonyms. More often, they are distinct, referring to approximately the same period of time in different geographic areas. Epipaleolithic always includes this period in the Levant and, often, the rest of the Near East. It sometimes includes parts of Southeast Europe, where Mesolithic is much more commonly used. Mesolithic very rarely includes the Levant or the Near East; in Europe, Epipalaeolithic is used, though not very often, to refer to the early Mesolithic. The Epipalaeolithic has been defined as the "final Upper Palaeolithic industries occurring at the end of the final glaciation which appear to merge technologically into the Mesolithic". The period is generally dated from BP to 10,000 BP in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Re Militari
''De re militari'' (Latin "Concerning Military Matters"), also ''Epitoma rei militaris'', is a treatise by the Late Latin writer Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus about Roman warfare and military principles as a presentation of the methods and practices in use during the height of the Roman Empire and responsible for its power. The extant text dates to the 5th century. Vegetius emphasized things such as training of soldiers as a disciplined force, orderly strategy, maintenance of supply lines and logistics, quality leadership and use of tactics and even deceit to ensure advantage over the opposition. He was concerned about selection of good soldiers and recommended hard training of at least four months before the soldier was accepted into the ranks. The leader of the army (''dux'') had to take care of the men under his command and keep himself informed about the movements of the enemy to gain advantage in the battle. ''De re militari'' became a military guide in the Middle Ages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus
Publius (or Flavius) Vegetius Renatus, known as Vegetius (), was a writer of the Later Roman Empire (late 4th century). Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what is contained in his two surviving works: ''Epitoma rei militaris'' (also referred to as '' De re militari''), and the lesser-known ''Digesta Artis Mulomedicinae'', a guide to veterinary medicine. He identifies himself in the opening of his work ''Epitoma rei militaris'' as a Christian. Dating of work The latest event alluded to in his ''Epitoma rei militaris'' is the death of the Emperor Gratian (383); the earliest attestation of the work is a ''subscriptio'' by Flavius Eutropius, writing in Constantinople in 450, which appears in one of two families of manuscripts, suggesting that a division of the manuscript tradition had already occurred. Despite Eutropius' location in Constantinople, the scholarly consensus is that Vegetius wrote in the Western Roman Empire.Walter Goffart. The date and purposes of Vegetius' D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plumbatae
''Plumbatae'' or ''martiobarbuli'' were lead-weighted darts carried by infantrymen in Antiquity and the Middle Ages. History The first examples seem to have been carried by the Ancient Greeks from about 500 BC onwards, but the best-known users were the late Roman and Eastern Roman armies. The earliest and best written source for these weapons refers to a period around 300 AD, though the document was composed around 390–450 AD. A second source, also from the late 4th century, is an anonymous treatise titled ''De rebus bellicis'', which briefly discusses (so far archaeologically unattested) spiked ''plumbatae'' (''plumbata tribolata''), but which is also the only source that shows an image of what a ''plumbata'' looked like. The image shows what looks like a short arrow with a weight attached to the shaft. Although only later copies of the original manuscript exist, this is confirmed by the remains which have so far turned up in the archaeological record. A third source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woomera (spear-thrower)
A woomera is a wooden Australian Aboriginal spear-throwing device. Similar to an atlatl, it serves as an extension of the human arm, enabling a spear to travel at a greater speed and force than possible with only the arm. Name The word "woomera" comes from the Dharug language of the Eora people of the Sydney basin. The name was adopted for the town of Woomera, South Australia, founded in 1947 as the home of the Anglo-Australian Long Range Weapons Establishment, also known as the "Woomera Rocket Range" and now called RAAF Woomera Range Complex. Description The woomera is in length. One end is wide and possessing a hollow, curved cross-section not unlike an airfoil, while the other is more pointed and has a hook. Some woomera were traditionally decorated with incised or painted designs that indicated belonging to a particular linguistic group that it may be returned to if found abandoned. Use Records show that the implement began to be used about 5,000 years ago, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl, Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, city-state of the Mexica or Tenochca; Texcoco (altepetl), Texcoco; and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco (altepetl), Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahuas, Nahua polities or peoples of central Pre-Columbian Mexico, Mexico in the preh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear-thrower
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface which allows the user to store energy during the throw. It may consist of a shaft with a cup or a spur at the end that supports and propels the butt of the spear. It's usually about as long as the user's arm or forearm. The user holds the spear-thrower in one hand, gripping near the end farthest from the cup. The user puts the butt end of the spear, or dart, in the cup, or grabs the spur with the end of the spear. The spear is much longer than the thrower. The user holds the spear parallel to the spear-thrower and going in the other direction. The user can hold the spear, with the index and thumb, with the same hand as the thrower, with the other fingers. The user reaches back with the spear pointed at the target. Then they make an overhand throwing motion with the thrower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law of motion. After some other definitions, Newton states in his first law of motion: The word "perseveres" is a direct translation from Newton's Latin. Other, less forceful terms such as "to continue" or "to remain" are commonly found in modern textbooks. The modern use follows from some changes in Newton's original mechanics (as stated in the ''Principia'') made by Euler, d'Alembert, and other Cartesians. The term inertia comes from the Latin word ''iners'', meaning idle, sluggish. The term inertia may also refer to the resistance of any physical object to a change in its velocity. This includes changes to the object's speed or direction of motion. An aspect of this property is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
