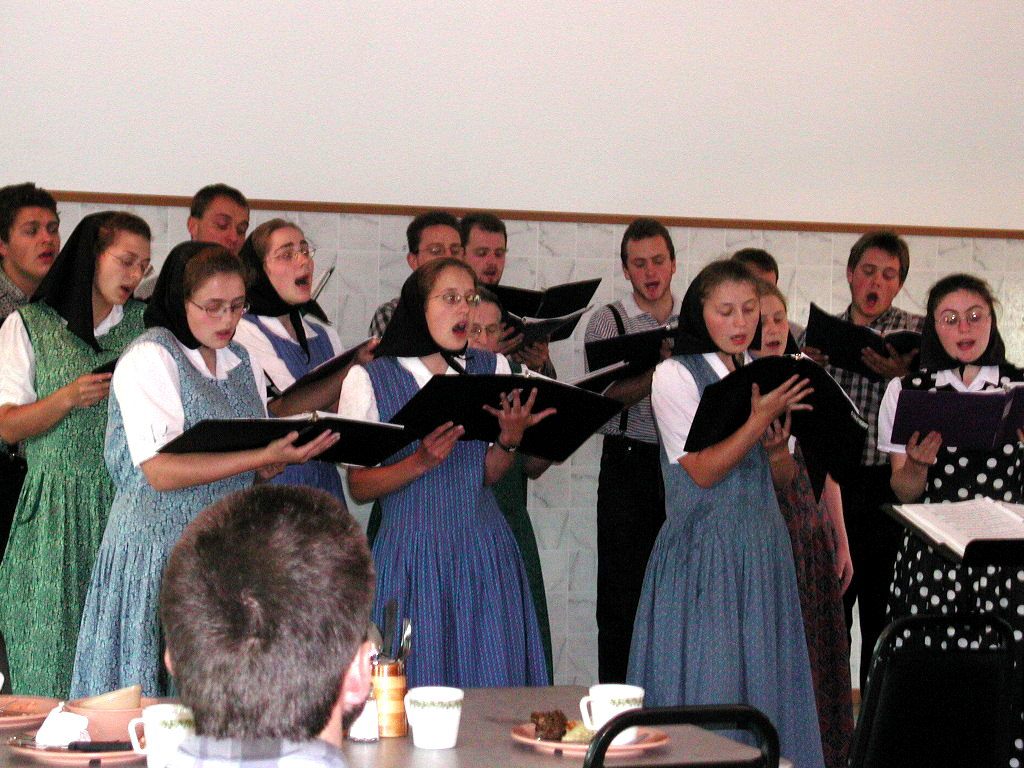|
Dariusleut
The Dariusleut, also Dariusleit, are a branch of the Hutterites that emerged in 1860. History Russian Empire In 1859, Michael Waldner and Jakob Hofer (1830–1900) successfully reestablished a community of goods among some Hutterites in Hutterdorf, Ukraine, then part of the Russian Empire. This group was named Schmiedeleut. In 1860, another group of Hutterites did the same under the leadership of Darius Walter (1835–1903) also in Hutterdorf, Ukraine, but on the opposite side of the village. This group was called Dariusleut, after the first name of its leader. America The Dariusleut left their homes in the Ukraine in June 1874 together with the Schmiedeleut. During the first winter, the Dariusleut lived on government grounds at Silver Lake, South Dakota. In 1875, they founded their first colony on American soil, Wolf Creek Hutterite Colony in South Dakota, the mother colony of the Dariusleut. Shortly after World War I, two Hutterite conscientious objectors, Joseph and M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutterites
Hutterites (german: link=no, Hutterer), also called Hutterian Brethren (German: ), are a communal ethnoreligious group, ethnoreligious branch of Anabaptism, Anabaptists, who, like the Amish and Mennonites, trace their roots to the Radical Reformation of the early 16th century and have formed intentional communities. The founder of the Hutterites, Jacob Hutter, "established the Hutterite colonies on the basis of the Schleitheim Confession, a classic Anabaptist statement of faith" of 1527, and the first communes were formed in 1528. Since the death of Hutter in 1536, the beliefs of the Hutterites, especially those espousing a community of goods and nonresistance, have resulted in hundreds of years of diaspora in many countries. The Hutterites embarked on a series of migrations through central and eastern Europe. Nearly extinct by the 18th century, they migrated to Russian Empire, Russia in 1770 and about a hundred years later to North America. Over the course of 140 years, their p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutterite
Hutterites (german: link=no, Hutterer), also called Hutterian Brethren (German: ), are a communal ethnoreligious group, ethnoreligious branch of Anabaptism, Anabaptists, who, like the Amish and Mennonites, trace their roots to the Radical Reformation of the early 16th century and have formed intentional communities. The founder of the Hutterites, Jacob Hutter, "established the Hutterite colonies on the basis of the Schleitheim Confession, a classic Anabaptist statement of faith" of 1527, and the first communes were formed in 1528. Since the death of Hutter in 1536, the beliefs of the Hutterites, especially those espousing a community of goods and nonresistance, have resulted in hundreds of years of diaspora in many countries. The Hutterites embarked on a series of migrations through central and eastern Europe. Nearly extinct by the 18th century, they migrated to Russian Empire, Russia in 1770 and about a hundred years later to North America. Over the course of 140 years, their p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owa Hutterite Colony
The Christian Community of New Hutterian Brethren at () was a Hutterite colony of the Dariusleut branch in Japan. It was located near village in Nasu District, Tochigi. It existed from 1972 to the end of 2019. The members of the colony were ethnic Japanese. History Background Buddhism, Buddhists have a long tradition of communal living and there are several Buddhist communities in Japan. Therefore, the idea of communal living was not totally uncommon for Japanese Christians. The founders of Colony wanted to establish communal living modeled after the Buddhist commune, but based on Christian principles. In the 1950s, the United Church of Christ, led by , began communal living in . Lacking an organisational model, the Church studied kibbutzim in Israel, but abandoned this model of structure for that of the North American Hutterites, who they established contact with through the Dariusleut Wilson Siding Colony near Lethbridge, Alberta. The Church quickly adopted many aspects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmiedeleut
The Schmiedeleut, also Schmiedeleit, are a branch of the Hutterites that emerged in 1859. It is divided into two subgroups. Name The founder of the Schmiedeleut, Michael Waldner (1834–1889), was a blacksmith and therefore called "Schmied Michel", i.e. "smith Michael". From Waldner's nickname the Schmiedeleut, meaning "smith people", took their name. History Russian Empire In 1857 some Hutterites under the leadership of George Waldner tried to reestablish community of goods in Hutterdorf, Ukraine, then part of the Russian Empire, after having abandoned this custom in 1819 in Radichev, but this first attempt failed. In 1859 Michael Waldner and Jakob Hofer (1830–1900) successfully reestablished a community of goods. America The followers of Michael Waldner, all together 113 people, left their homes in the Ukraine in June 1874 to settle at Bon Homme Hutterite Colony in South Dakota, the mother colony of the Schmiedeleut. During their journey 36 children died of an epidemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John A
Sir John Alexander Macdonald (January 10 or 11, 1815 – June 6, 1891) was the first prime minister of Canada, serving from 1867 to 1873 and from 1878 to 1891. The dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, he had a political career that spanned almost half a century. Macdonald was born in Scotland; when he was a boy his family immigrated to Kingston in the Province of Upper Canada (today in eastern Ontario). As a lawyer, he was involved in several high-profile cases and quickly became prominent in Kingston, which elected him in 1844 to the legislature of the Province of Canada. By 1857, he had become premier under the colony's unstable political system. In 1864, when no party proved capable of governing for long, Macdonald agreed to a proposal from his political rival, George Brown, that the parties unite in a Great Coalition to seek federation and political reform. Macdonald was the leading figure in the subsequent discussions and conferences, which resulted in the Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-American Culture In Montana
German Americans (german: Deutschamerikaner, ) are Americans who have full or partial Germans, German ancestry. With an estimated size of approximately 43 million in 2019, German Americans are the largest of the self-reported ancestry groups by the United States Census Bureau in its American Community Survey. German Americans account for about one third of the total population of people of German ancestry in the world. Very few of the List of states of the German Confederation, German states had colonies in the new world. In the 1670s, the first significant groups of German immigrants arrived in the British America, British colonies, settling primarily in Province of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, Province of New York, New York and Colony of Virginia, Virginia. The Mississippi Company of France moved thousands of Germans from Europe to Louisiana and to the German Coast, Orleans Territory between 1718 and 1750. Immigration ramped up sharply during the 19th century. There is a "Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-Russian Culture In South Dakota
German-Russian or Russian-German (with or without hyphen) may refer to: *Germany–Russia relations (c.f. a "German–Russian treaty") *Germans in the old Russian Empire or present-day Russia **Russia Germans , Russia Germans or Germans from Russia **History of Germans in Russia, Ukraine and the Soviet Union **Baltic Germans **Black Sea Germans **Caucasus Germans (the area is now divided between several countries) **Crimea Germans **Volga Germans ***German Americans#Germans from Russia, Volga Germans in the United States **Volhynian Germans (Germans of Volhynia (Poland and Ukraine)) *Russian-speaking population groups in Germany *Russian Mennonites *Germans from Russia *People with multiple citizenship of Germany and Russia {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-Russian Culture In The United States
German-Russian or Russian-German (with or without hyphen) may refer to: *Germany–Russia relations (c.f. a "German–Russian treaty") *Germans in the old Russian Empire or present-day Russia ** Russia Germans or Germans from Russia ** History of Germans in Russia, Ukraine and the Soviet Union **Baltic Germans **Black Sea Germans **Caucasus Germans (the area is now divided between several countries) **Crimea Germans **Volga Germans *** Volga Germans in the United States **Volhynian Germans (Germans of Volhynia (Poland and Ukraine)) *Russian-speaking population groups in Germany *Russian Mennonites *Germans from Russia The German minority population in Russia, Ukraine, and the Soviet Union stemmed from several sources and arrived in several waves. Since the second half of the 19th century, as a consequence of the Russification policies and compulsory military ... *People with multiple citizenship of Germany and Russia {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
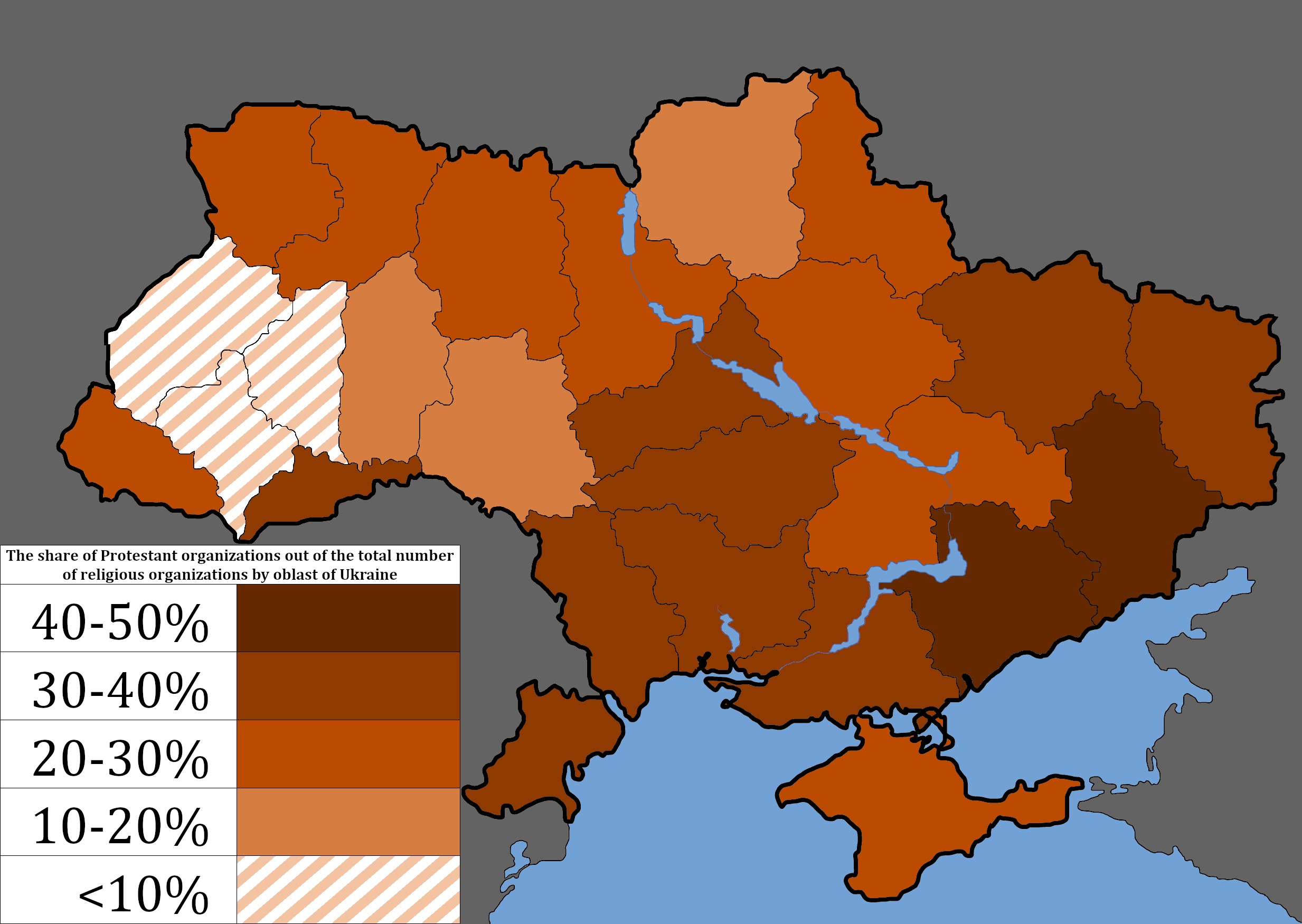
Protestantism In Ukraine
Protestants in Ukraine number about 600,000 to 700,000 (2007), about 2% of the total population. Nearly all traditional Protestant denominations are represented in the country. According to '' Christianity Today'' magazine, Ukraine has become not just the "Bible Belt" of Eastern Europe, but a "hub of evangelical church life, education, and missions".''"Eastern Europe's Evangelical Hub", Christianity Today magazine, January 2008'' At present, the country is a key supplier of missionaries and a center of evangelical training and press printing for all the countries of the former Soviet Union, where the legal environment is not so favourable. Compared to Protestants and Evangelicals in Western Europe and the United States, believers in Ukraine are considered to be more conservative and traditional. For most Western Evangelicals their way of life reflects a form of strict moral asceticism. The earliest Protestants appeared in Ukraine in the 1530s and ’40s. They were preceded by v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnoreligious Groups In Canada
An ethnoreligious group (or an ethno-religious group) is a grouping of people who are unified by a common religious and ethnic background. Furthermore, the term ethno-religious group, along with ethno-regional and ethno-linguistic groups, is a sub-category of ethnicity and is used as evidence of belief in a common culture and ancestry. In a narrower sense, they refer to groups whose religious and ethnic traditions are historically linked. Characteristics The elements that are defined as characteristics of an ethnoreligious group are "social character, historical experience, and theological beliefs". A closing of the community takes place through a strict endogamy, which is specifically for the community and that distinguishes an ethno-religious community, that is, as distinct from any other group. Defining an ethnoreligious group In general, ethnoreligious communities define their ethnic identity not only by ancestral heritage nor simply by religious affiliation but normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European-Canadian Culture In Alberta
European Canadians, or Euro-Canadians, are Canadians who were either born in or can trace their ancestry to the continent of Europe. They form the largest panethnic group within Canada. In the 2021 Canadian census, 19,062,115 Canadians self-identified as having origins from European countries, forming approximately 52.5% of the total Canadian population. Due to changes in the census format, these totals are not directly comparable with previous censuses. Further, as the census permitted a respondent to enter up to six possible ethnic origins in their census questionnaire, this figure includes individual respondents that reported a mixed ancestry of both European and non-European origins. Therefore, it is not possible to accurately assess the total number of European Canadians as a percentage of Canada's total population, or a precise change from previous years. Terminology As with other panethnic groups, Statistics Canada records ethnic ancestry by employing the term "Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabaptist Denominations In North America
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. The term (translation: "Baptizers") is now used, which is considered more impartial. From the perspective of their persecutors, the "Baptizers" baptized for the second time those "who as infants had already been baptized". The denigrative term Anabaptist, given to them by others, signifies rebaptizing and is considered a polemical term, so it has been dropped from use in modern German. However, in the English-speaking world, it is still used to distinguish the Baptizers more clearly from the Baptists, a Protestant sect that developed later in England. Compare their self-designation as "Brethren in Christ" or "Church of God": . is a Protestant Christian movement which traces its origins to the Radical Reformation. The early Anabaptists fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |