|
Dardanus (Sacchini)
''Dardanus'' is an opera by Antonio Sacchini. It takes the form of a tragédie lyrique in four acts (later revised to a three-act version). It was first performed at Versailles on 18 September 1784, and subsequently at the Paris Opera on 30 November of the same year. The French-language libretto was adapted by Nicolas-François Guillard from that by Charles-Antoine Leclerc de La Bruère, which had already been set to music by Jean-Philippe Rameau in his earlier opera of the same name. History Guillard's adaptation blends both 1739 and 1744 versions of Rameau's opera, but is based principally upon the second one. Although "the title-page of the printed score reads only 'paroles de M. Guillard', n factmost of the text is by La Bruère". Guillard's interventions mainly consisted in " mittingthe Prologue, lteringthe order of events in Act 3, and skilfully ompressingActs 4 and 5".Grove The librettist "justified his redoing the subject ... y explainingthat his aim was to tighten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tragédie En Musique
Tragédie en musique (, ''musical tragedy''), also known as tragédie lyrique (, ''lyric tragedy''), is a genre of French opera introduced by Jean-Baptiste Lully and used by his followers until the second half of the eighteenth century. Operas in this genre are usually based on stories from Classical mythology or the Italian romantic epics of Tasso and Ariosto. The stories may not necessarily have a tragic ending – in fact, most do not – but the works' atmospheres are suffused throughout with an affect of nobility and stateliness. The standard ''tragédie en musique'' has five acts. Earlier works in the genre were preceded by an allegorical prologue and, during the lifetime of Louis XIV, these generally celebrated the king's noble qualities and his prowess in war. Each of the five acts usually follows a basic pattern, opening with an aria in which one of the main characters expresses their feelings, followed by dialogue in recitative interspersed with short arias (''petits airs'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Grove Dictionary Of Opera
''The New Grove Dictionary of Opera'' is an encyclopedia of opera, considered to be one of the best general reference sources on the subject. It is the largest work on opera in English, and in its printed form, amounts to 5,448 pages in four volumes. First published in 1992 by Macmillan Reference, London, it was edited by Stanley Sadie with contributions from over 1,300 scholars. There are 11,000 articles in total, covering over 2,900 composers and 1800 operas. Appendices including an index of role names and an index of incipits of arias, ensembles, and opera pieces. The dictionary is available online, together with ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians''. References *William Salaman, "Review: The New Grove Dictionary of Opera", ''British Journal of Music Education'' (1999), 16: 97-110 Cambridge University Pres*John Simon, "Review: The New Grove Dictionary of Opera, 4 vols.", ''National Review'', April 26, 199* * *Charles Rosen, "Review: The New Grove Dictionary of O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Larrivée
Henri Larrivée (9 January 1737 – 7 August 1802) was a French opera singer. He was born in Lyon. His voice range was ''basse-taille'' (equivalent to baritone).Dratwicki, p. 85 According to Fétis, Larrivée was working as an apprentice to a wigmaker when the head of the Paris Opéra, Rebel, noticed his talent for singing and hired him as a chorus member. He made his first solo appearance as a high priest in a 1755 revival of Rameau's ''Castor et Pollux''. He was particularly associated with the works of Christoph Willibald Gluck, helping Gluck establish his "reform operas" in France. He found Gluck's rival, Niccolò Piccinni, less congenial but still worked with him on the premieres of operas including '' Roland'' (1778).Rushton p. 269 After already getting a pension in 1779, he retired from the ''Académie Royale de Musique'' in 1786 and devoted most of the time he had left to live to tour around with his two daughters, Camille (later known as Mme Delaval) and Henriette, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass-baritone
A bass-baritone is a high-lying bass or low-lying "classical" baritone voice type which shares certain qualities with the true baritone voice. The term arose in the late 19th century to describe the particular type of voice required to sing three Wagnerian roles: the title role in ''Der fliegende Holländer'', Wotan/Der Wanderer in the ''Ring Cycle'' and Hans Sachs in '' Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg''. Wagner labelled these roles as ''Hoher Bass'' ("high bass")—see fach for more details. The bass-baritone voice is distinguished by two attributes. First, it must be capable of singing comfortably in a baritonal tessitura. Secondly, however, it needs to have the ripely resonant lower range typically associated with the bass voice. For example, the role of Wotan in ''Die Walküre'' covers the range from F2 (the F at the bottom of the bass clef) to F4 (the F above middle C), but only infrequently descends beyond C3 (the C below middle C). Bass-baritones are typically divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
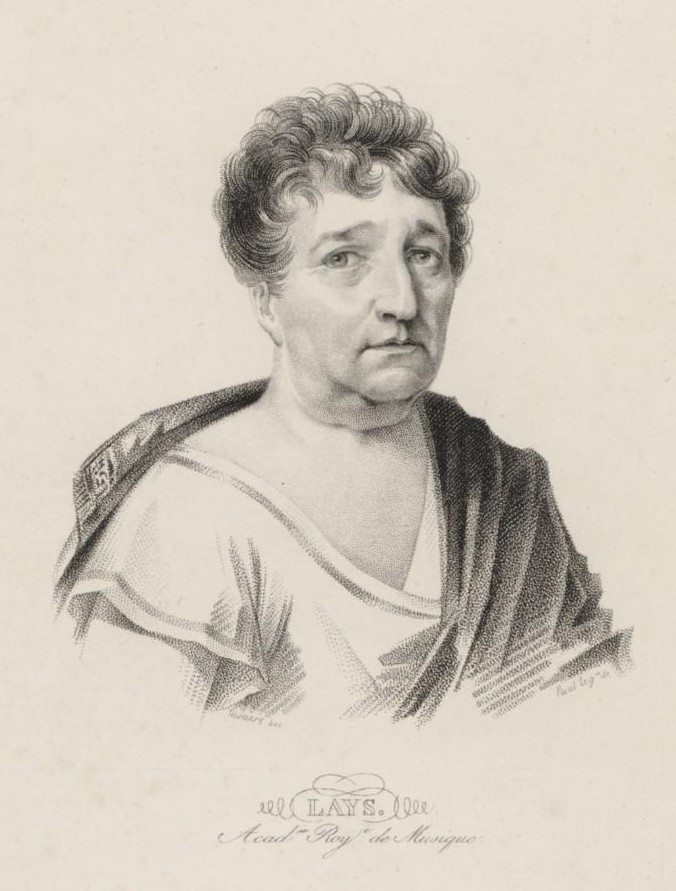
François Lays
François Lay, better known under the stage name Lays (14 February 1758 – 30 March 1831), was a French baritone and tenor opera singer. Originally destined for a career in the church, Lays was recruited by the Paris Opéra in 1779. He soon became a leading member of the company, in spite of quarrels with the management. Lays enthusiastically welcomed the French Revolution and became involved in politics with the encouragement of his friend Bertrand Barère. Barère's downfall led to Lays being imprisoned briefly, but he soon won back the public and secured the patronage of Napoleon, at whose coronation and second wedding he sang. This association with the Emperor caused him trouble when the Bourbon monarchy was restored and Lays's final years were darkened by disputes over his pension, mounting debts, the death of his only son and his wife's illness. After a career spanning more than four decades, he died in poverty. Lays was famous for the beauty of his voice. One of the Op� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baritone
A baritone is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the bass and the tenor voice-types. The term originates from the Greek (), meaning "heavy sounding". Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second F below middle C to the F above middle C (i.e. F2–F4) in choral music, and from the second A below middle C to the A above middle C (A2 to A4) in operatic music, but the range can extend at either end. Subtypes of baritone include the baryton-Martin baritone (light baritone), lyric baritone, ''Kavalierbariton'', Verdi baritone, dramatic baritone, ''baryton-noble'' baritone, and the bass-baritone. History The first use of the term "baritone" emerged as ''baritonans'', late in the 15th century, usually in French sacred polyphonic music. At this early stage it was frequently used as the lowest of the voices (including the bass), but in 17th-century Italy the term was all-encompassing and used to describe the averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bari-tenor
Baritenor (also rendered in English language sources as bari-tenor or baritenore) is a portmanteau (blend) of the words "baritone" and "tenor." It is used to describe both baritone and tenor voices. In ''Webster's Third New International Dictionary'' it is defined as "a baritone singing voice with virtually a tenor range." However, the term was defined in several late 19th century and early 20th century music dictionaries, such as ''The American History and Encyclopedia of Music'', as "a low tenor voice, almost barytone sic.html"_;"title="'sic">'sic''" _In_opera Baritenor_(or_its_Italian_language.html" "title="sic">'sic''.html" ;"title="sic.html" ;"title="'sic">'sic''">sic.html" ;"title="'sic">'sic''" In opera Baritenor (or its Italian language">Italian form, ''baritenore'') is still used today to describe a type of tenor voice which came to particular prominence in Rossini's operas. It is characterized by a dark, weighty lower octave and a ringing upper one but with sufficient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haute-contre
The haute-contre (plural hautes-contre) was the primary French operatic tenor voice, predominant in French Baroque and Classical opera, from the middle of the seventeenth century until the latter part of the eighteenth century. History This voice was predominantly used in male solo roles, typically heroic and amatory ones, but also in comic parts, even ''en travesti'' (see apropos the portrait reproduced below and representing Pierre Jélyotte made up for the female title role of Rameau's ''Platée''). Lully wrote 8 out of 14 leading male roles for the voice; Charpentier, who was an haute-contre himself, composed extensively for the voice-part, as did Rameau and, later, Gluck. The leading ''hautes-contre'' of the ''Académie Royale de Musique'' that created the main roles of Lully's operas, at the end of the seventeenth century, were Bernard Clédière (who started off as a ''taille'', a lower Tenor voice type) and Louis Gaulard Dumesny. Notable ''hautes-contre'' of the eighteent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenor
A tenor is a type of classical music, classical male singing human voice, voice whose vocal range lies between the countertenor and baritone voice types. It is the highest male chest voice type. The tenor's vocal range extends up to C5. The low extreme for tenors is widely defined to be B2, though some roles include an A2 (two As below middle C). At the highest extreme, some tenors can sing up to the second F above middle C (F5). The tenor voice type is generally divided into the ''leggero'' tenor, lyric tenor, spinto tenor, dramatic tenor, heldentenor, and tenor buffo or . History The name "tenor" derives from the Latin word ''wikt:teneo#Latin, tenere'', which means "to hold". As Fallows, Jander, Forbes, Steane, Harris and Waldman note in the "Tenor" article at ''Grove Music Online'': In polyphony between about 1250 and 1500, the [tenor was the] structurally fundamental (or 'holding') voice, vocal or instrumental; by the 15th century it came to signify the male voice that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soprano
A soprano () is a type of classical female singing voice and has the highest vocal range of all voice types. The soprano's vocal range (using scientific pitch notation) is from approximately middle C (C4) = 261 Hz to "high A" (A5) = 880 Hz in choral music, or to "soprano C" (C6, two octaves above middle C) = 1046 Hz or higher in operatic music. In four-part chorale style harmony, the soprano takes the highest part, which often encompasses the melody. The soprano voice type is generally divided into the coloratura, soubrette, lyric, spinto, and dramatic soprano. Etymology The word "soprano" comes from the Italian word '' sopra'' (above, over, on top of),"Soprano" '' |
Maria Antonia Of Austria
Maria Antonia Josepha Benedicta Rosalia Petronella of Austria (18 January 1669 – 24 December 1692) was an Electress of Bavaria as the wife of Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria. She was the eldest daughter and only surviving child of Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I and his first wife Margaret Theresa of Spain. She was the heir to the Spanish throne after her maternal uncle Charles II of Spain from 1673 until her death. Life Early life Archduchess Maria Antonia of Austria was born on 18 January 1669 in Vienna, Archduchy of Austria, Holy Roman Empire. She was the second child of Emperor Leopold I (1640–1705) and his wife Margaret Theresa of Spain (1651–1673). Her only older sibling had already died by the time she was born. She had 2 younger siblings, both of whom died in infancy, and twelve half-siblings, eight of whom lived into adulthood. Maria Antonia had the highest coefficient of inbreeding in the House of Habsburg, 0.3053: her father was her mother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XVI Of France
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was executed by guillotine. He was the son of Louis, Dauphin of France, son and heir-apparent of King Louis XV, and Maria Josepha of Saxony. When his father died in 1765, he became the new Dauphin. Upon his grandfather's death on 10 May 1774, he became King of France and Navarre, reigning as such until 4 September 1791, when he received the title of King of the French, continuing to reign as such until the monarchy was abolished on 21 September 1792. The first part of his reign was marked by attempts to reform the French government in accordance with Enlightenment ideas. These included efforts to abolish serfdom, remove the ''taille'' (land tax) and the ''corvée'' (labour tax), and increase tolerance toward non-Catholics as well as abolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |