|
Daphnis Et Alcimadure
(in Occitan classical norm, ''Dafnís e Alcimadura'', or according to the original libretto spelling, ''Daphnis e Alcimaduro'') is an opera by the Baroque violinist, conductor and composer Jean-Joseph Cassanéa de Mondonville to a libretto in the Occitan language, written by the composer himself and loosely inspired by La Fontaine's fable bearing the same title. It takes the form of a pastorale in three acts and was later endowed with a prologue in French entitled ''Les jeux floraux'', to a libretto by Claude-Henri de Fusée de Voisenon.Pitou, p. 137. Pitou is the sole source stating that the prologue was not performed in the context of the premiere. History, criticism and interpretation The opera was first staged on 24 October and 5 November 1754 at the Palace of Fontainebleau and performed before King Louis XV of France and his court. It was quite successful and the last act duet was repeated as an encore. Its public premiere was held by the Paris Opéra at the Théâtre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
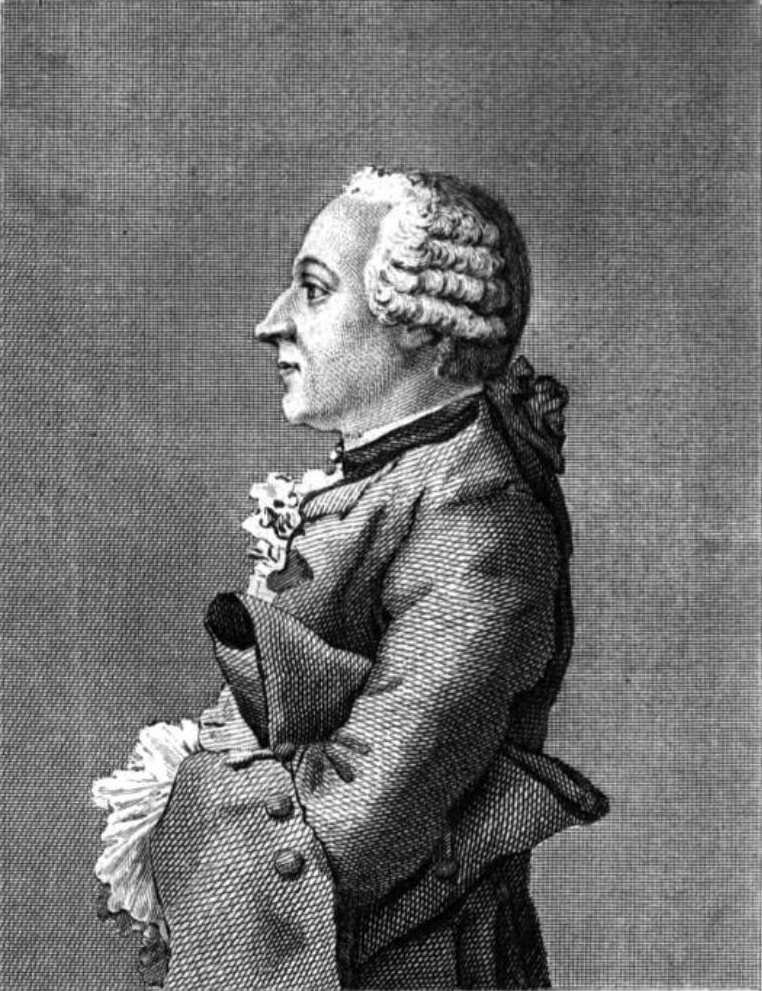
Jean-Joseph Cassanéa De Mondonville
Jean-Joseph de Mondonville (, 25 December 1711 (baptised) – 8 October 1772), also known as Jean-Joseph Cassanéa de Mondonville, was a French violinist and composer. He was a younger contemporary of Jean-Philippe Rameau and enjoyed great success in his day. Pierre-Louis Daquin (son of the composer Louis-Claude Daquin) claimed, "If I couldn't be Rameau, there's no one I would rather be than Mondonville". Life Mondonville was born in Narbonne in Occitania (South France) to an aristocratic family which had fallen on hard times. In 1733, he moved to Paris where he gained the patronage of the king's mistress Madame de Pompadour and won several musical posts, including violinist for the Concert Spirituel. His first opus was a volume of violin sonatas, published in 1733. He became a violinist of the Chapelle royale and chamber and performed in some 100 concerts. Some of his '' grands motets'' were also performed that year, receiving considerable acclaim. He was appointed ''sous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gascon Language
Gascon (; , ) is the name of the vernacular Romance languages, Romance variety spoken mainly in the region of Gascony, France. It is often considered a variety (linguistics), variety of Occitan language, Occitan, although some authors consider it a different language.Cf. Gerhard Rohlfs, Rohlfs, Gerhard. 1970. ''Le Gascon. Études de philologie pyrénéenne'', 2e éd. Tubingen, Max Niemeyer, & Pau, Marrimpouey jeune. Gascon is mostly spoken in Gascony and Béarn (Béarnese dialect) in southwestern France (in parts of the following French ''départements'': Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Hautes-Pyrénées, Landes (department), Landes, Gers, Gironde, Lot-et-Garonne, Haute-Garonne, and Ariège (department), Ariège) and in the Val d'Aran of Catalonia. Aranese language, Aranese, a southern Gascon variety, is spoken in Catalonia alongside Catalan language, Catalan and Spanish. Most people in the region are trilingual in all three languages, causing some influence from Spanish and Catalan. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Campardon
Émile Campardon (18 July 1837 – 23 February 1915) was a French historian, archivist and writer. He was an archivist and head of the judicial section of the Archives nationales de France from 1857 to 1908, and the author of numerous books. At the beginning of the 20th century he published ''Quatrains'' and ''Souvenirs d’un archiviste''. Intended for a circle of friends these extremely rare volumes contain amusing and impertinent portraits of archivists of the 19th century. He is known above all for his four fundamental works on the history of the theatres of Paris: * ''Les Spectacles de la foire'', Paris, Berger-Levrault et Cie, 1877, 2 vols. * ''Les Comédiens de la troupe française'', Paris, H. Champion, 1879. * ''Les Comédiens du roi de la troupe italienne'', Paris, Berger-Levrault et Cie, 1880, 2 vols. * ''L'Académie royale de musique The Paris Opera (, ) is the primary opera and ballet company of France. It was founded in 1669 by Louis XIV as the , and shortly th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comédie-Italienne
Comédie-Italienne or Théâtre-Italien are French names which have been used to refer to Italian-language theatre and opera when performed in France. The earliest recorded visits by Italian players were commedia dell'arte companies employed by the French court under the Italian-born queens Catherine de Medici and Marie de Medici. These troupes also gave public performances in Paris at the theatre of the Hôtel de Bourgogne, probably the earliest public theatre to be built in France. The first official use of the name Comédie-Italienne was in 1680, when it was given to the commedia dell'arte troupe at the Hôtel de Bourgogne, to distinguish it from the French troupe, the Comédie-Française, which was founded that year, and just as the name Théâtre-Français was commonly applied to the latter, Théâtre-Italien was used for the Italians. Over time French phrases, songs, whole scenes, and eventually entire plays were incorporated into the Comédie-Italienne's performances. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comédie Mêlée D'ariettes
The French term ''comédie mêlée d'ariettes'' ('comedy mixed with little songs') was frequently used during the late ''ancien régime'' for certain types of '' opéra comique'' (French opera with spoken dialogue). The term became popular in the mid 18th century following the Querelle des Bouffons, a dispute over the respective merits of French serious opera and Italian ''opera buffa''. At first it was applied to works which parodied Italian ''opera buffa'', in the sense that the words were changed but not the music. One of the earliest examples is the librettist Charles-Simon Favart's '' Le caprice amoureux, ou Ninette à la cour'' (1755), which was a parody of Carlo Goldoni's ''Bertoldo, Bertoldino e Cacasenno'' (1748), a pasticcio with music by Vincenzo Ciampi and others (first performed in Paris in 1753 as ''Bertoldo in corte''). Another common term for such parodies was ''opéra bouffon''.Bartlet 1992. Soon, however, the term ''comédie mêlée d'ariettes'' came to be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
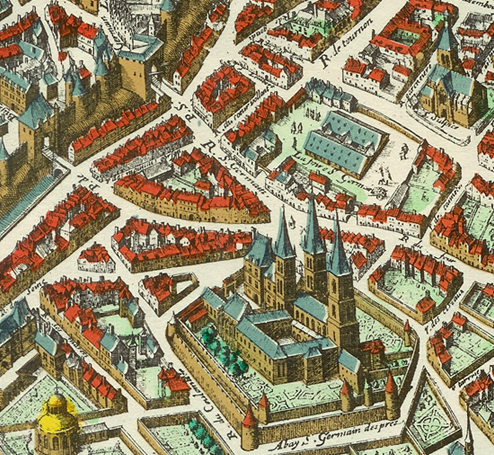
Théâtre De La Foire
Théâtre de la foire is the collective name given to the theatre put on at the annual fairs at Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés, Saint-Germain and Saint-Laurent church, Paris, Saint-Laurent (and for a time, at Saint-Ovide) in Paris. Foire Saint-Germain The earliest references to the annual fair date to 1176. The fairground itself was established in 1482 by Louis XI for the benefit of the Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés and was located near the Abbey on the Rive Gauche, Left Bank southwest of the city center just outside one of the gates of the Wall of Philip II Augustus, Paris, city wall built by Philip II at the beginning of the 13th century. The covered Saint-Germain market today occupies part of the former fairground site with access from the Boulevard Saint-Germain via the Rue de Montfaucon satellite view. The fair generally lasted three to five weeks around Easter. During the 18th century it consistently opened on 3 February and lasted until Palm Sunday. The fair's first a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Joseph Vadé
Jean-Joseph Vadé (17 January 1720 – 4 July 1757) was a French chansonnier and playwright of the 18th century. Biography The son of Jacques Vadé, an innkeeper, Jean-Joseph went with his father to Paris in 1725. His studies suffered from his ebullient and lively character, and he could never learn Latin, but he knew how to correct the weakness of his education by reading the best authors on his own. At twenty, he obtained the position of controller of the '' vingtième'' (income tax) in Soissons, then in Laon, where he was noted for his wit and upbeat verve. In 1743, he left Laon to go to Rouen and became secretary of the Duke of Agenois for two years. Finally, he returned to Paris where his friends helped him find a new job in the office of the ''vingtième''. It was around that time that he became known to the public for his effortless and graceful poems. Occasionally a singer, Vadé participated in the singing society La Dominicale. He had a daughter, Marie Françoise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercure De France
The was originally a French gazette and literary magazine first published in the 17th century, but after several incarnations has evolved as a publisher, and is now part of the Éditions Gallimard publishing group. The gazette was published from 1672 to 1724 (with an interruption in 1674–1677) under the title (sometimes spelled ; 1672–1674) and (1677–1724). The title was changed to in 1724. The gazette was briefly suppressed (under Napoleon) from 1811 to 1815 and ceased publication in 1825. The name was revived in 1890 for both a literary review and (in 1894) a publishing house initially linked with the symbolist movement. Since 1995 has been part of the Éditions Gallimard publishing group. should not be confused with another literary magazine, the (1823–1830). The original ''Mercure galant'' and ''Mercure de France'' The ''Mercure galant'' was founded by the writer Jean Donneau de Visé in 1672. The name refers to the god Mercury, the messenger of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melchior Grimm
Friedrich Melchior, Baron von Grimm (26 September 172319 December 1807) was a German-born French-language journalist, art critic, diplomat and contributor to the ''Encyclopédie ou Dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers''. In 1765 Grimm wrote ''Poème lyrique'', an influential article for the Encyclopédie on lyric and opera librettos. Like Christoph Willibald Gluck and Ranieri de' Calzabigi, Grimm became interested in opera reform. According to Martin Fontius, a German literary theorist, "sooner or later a book entitled ''The Aesthetic Ideas of Grimm'' will have to be written." Early years Grimm was born at Regensburg, the son of Johann Melchior Grimm (1682–1749), a pastor, and Sibylle Margarete Grimm, (''née'' Koch) (1684–1774). He studied at the University of Leipzig, where he came under the influence of Johann Christian Gottsched and of Johann August Ernesti, to whom he was largely indebted for his critical appreciation of classical literatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Querelle Des Bouffons
The ("Quarrel of the Comic Actors"), also known as the ("War of the Comic Actors"), was the name given to a battle of musical philosophies that took place in Paris between 1752 and 1754. The controversy concerned the relative merits of French and Italian opera. It was also known as the ("War of the Corners"), with those favoring French opera in the King's corner, and those favoring Italian opera in the Queen's corner. It was sparked by the reaction of literary Paris to a performance of Giovanni Battista Pergolesi's short intermezzo ''La serva padrona'' at the Académie royale de musique in Paris on 1 August 1752. ''La serva padrona'' was performed by an itinerant Italian troupe of comic actors, known as ''buffoni'' (''bouffons'' in French, hence the name of the quarrel). In the controversy that followed, critics such as Jean-Jacques Rousseau and Friedrich Melchior Grimm, along with other writers associated with the ''Encyclopédie'', praised Italian opera buffa. They attacke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department. Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the Aude between historic trade routes, linking the Atlantic to the Mediterranean Sea and the Massif Central to the Pyrénées. Its strategic importance was quickly recognized by the Romans, who occupied its hilltop until the demise of the Western Roman Empire. In the fifth century, it was taken over by the Visigoths, who founded the city. Within three centuries, it briefly came under Islamic rule. Its strategic location led successive rulers to expand its fortifications until the Treaty of the Pyrenees in 1659. Its citadel, known as the Cité de Carcassonne, is a medieval fortress dating back to the Gallo-Roman period and restored by the theorist and architect Eugène Viollet-le-Duc in 1853. It was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occitania
Occitania ( oc, Occitània , , or ) is the historical region in Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe where the Occitan language, Occitan language was historically spoken and where it is sometimes still used as a second language. This cultural area roughly encompasses the southern third of France (with the exception of the French Basque Country and Northern Catalonia, French Catalonia) as well as part of Spain (Aran Valley), Monaco, and smaller parts of Italy (Occitan Valleys, Guardia Piemontese). Occitania has been recognized as a linguistic and cultural concept since the Middle Ages, but has never been a legal nor a political entity under this name. However, the territory was united in Roman times as the ''Septem Provinciae, Seven Provinces'' ( la, Septem Provinciæ) and in the Early Middle Ages (''Aquitanica'' or the Visigothic Kingdom#Kingdom of Toulouse, Visigothic Kingdom of Toulouse, or the share of Louis the Pious following Thionville ''divisio regnorum'' in 806) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |