|
Daphnia Pulicaria
''Daphnia pulicaria'' is a species of freshwater crustaceans found within the genus of ''Daphnia,'' which are often called "water fleas," and they are commonly used as model organisms for scientific research Like other species of ''Daphnia'', they reproduce via cyclic parthenogenesis. ''D. pulicaria'' are filter-feeders with a diet primarily consisting of algae, including ''Ankistrodesmus falcatus,'' and they can be found in deep lakes located in temperate climates. Furthermore, ''D. pulicaria'' are ecologically important herbivorous zooplankton, which help control algal populations and are a source of food for some fish. ''D. pulicaria'' are closely related to ''Daphnia pulex'', and numerous studies have investigated the nature and strength of this relationship because these species can produce ''Daphnia pulex-pulicaria'' hybrids. In recent years, ''D. pulicaria'' along with other ''Daphnia'' species have been negatively affected by invasive predators, such as ''Bythotrephes longi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Alfred Forbes
Stephen Alfred Forbes (May 29, 1844 – March 13, 1930) was the first chief of the Illinois Natural History Survey, a founder of aquatic ecosystem science and a dominant figure in the rise of American ecology. His publications are striking for their merger of extensive field observations with conceptual insights. Forbes believed that ecological knowledge was fundamental for human well being. Forbes was important to the development of ecological theory. He was acknowledged by the National Academy of Sciences as "the founder of the science of ecology in the United States". While already famous as an economic entomologist, Forbes undertook studies of massive fish mortality in Lake Mendota, Wisconsin. He showed the connection of algae blooms and lake physics to fish kills, and embarked on a remarkable research program into lake ecology and river ecology. Many of his insights about lake ecology were collected in an influential paper, "The Lake as a Microcosm". Notable for both conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
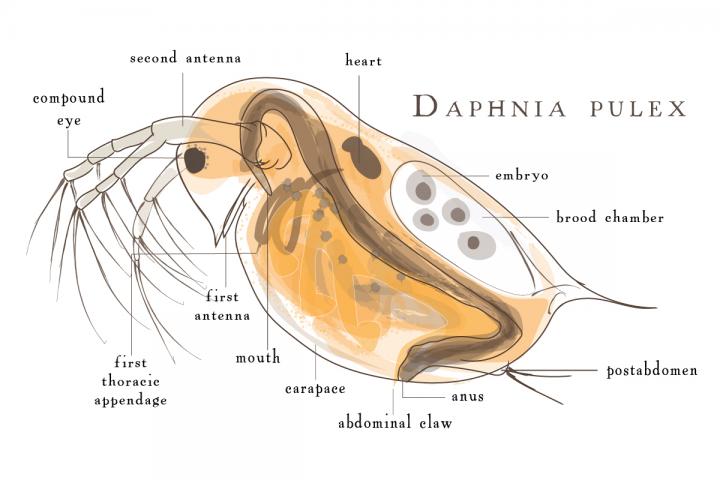
Daphnia Pulex
''Daphnia pulex'' is the most common species of water flea. It has a cosmopolitan distribution: the species is found throughout the Americas, Europe, and Australia. It is a model species, and was the first crustacean to have its genome sequenced. Description ''D. pulex'' is an arthropod whose body segments are difficult to distinguish. It can only be recognised by its appendages (only ever one pair per segment), and by studying its internal anatomy. The head is distinct and is made up of six segments, which are fused together even as an embryo. It bears the mouthparts, and two pairs of antennae, the second pair of which is enlarged into powerful organs used for swimming. No clear division is seen between the thorax and abdomen, which collectively bear five pairs of appendages. The shell surrounding the animal extends posteriorly into a spine. Like most other ''Daphnia'' species, ''D. pulex'' reproduces by cyclical parthenogenesis, alternating between sexual and asexual reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephippia
Ephippia (singular: ephippium) are winter or dry-season eggs of the various species of small crustacean in the order Cladocera (within the Branchiopoda); they are provided with an extra shell layer, which preserves and protects the resting stages inside from harsh environmental conditions until the more favorable times, such as spring, when the reproductive cycle is able to take place once again. Ephippia are part of the back of a mother carrying them until they are fully developed. After molting, the ephippium stays in the water, or in the soil of dried puddles, small ponds, and vernal pools. The resting stages are often called eggs, but are in fact embryos with arrested development. Ephippia can rest for many years before the embryo resumes development upon an appropriate hatching stimulus. See also * ''Bythotrephes longimanus'' (invasive species) * ''Cercopagis pengoi'' (invasive species) * ''Daphnia ** ''Daphnia longispina'' ** ''Daphnia lumholtzi'' (invasive species) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Described In 1893
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Crustaceans
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include non- salty mineral-rich waters such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranean rivers and lakes. Fresh water is the water resource that is of the most and immediate use to humans. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of higher plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to survive. Fresh water is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladocera
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms). Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more undescribed. The oldest fossils of diplostracans date to the Jurassic, though their modern morphology suggests that they originated substantially earlier, during the Paleozoic. Some have also adapted to a life in the ocean, the only members of Branchiopoda to do so, even if several anostracans live in hypersaline lakes. Most are long, with a down-turned head with a single median compound eye, and a carapace covering the apparently unsegmented thorax and abdomen. Most species show cyclical parthenogenesis, where asexual reproduction is occasionally supplemented by sexual reproduction, which produces resting eggs that allow the species to survive harsh conditions and disperse to distant habitats. Description They are mostly long, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |