|
Danes
Danes ( da, danskere, ) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural. Danes generally regard themselves as a nationality and reserve the word "ethnic" for the description of recent immigrants, sometimes referred to as "new Danes". The contemporary Danish national identity is based on the idea of "Danishness", which is founded on principles formed through historical cultural connections and is typically not based on racial heritage. History Early history Denmark has been inhabited by various Germanic peoples since ancient times, including the Angles, Cimbri, Jutes, Herules, Teutones and others. The first mentions of " Danes" are recorded in the mid-6th century by historians Procopius ( el, δάνοι) and Jordanes (''danī''), who both refer to a tribe related to the Suetidi inhabiting the peninsula of Jutland, the province of Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Germanic Peoples
North Germanic peoples, commonly called Scandinavians, Nordic peoples and in a medieval context Norsemen, were a Germanic peoples, Germanic linguistic group originating from the Scandinavian Peninsula. They are identified by their cultural similarities, common ancestry and common use of the Proto-Norse language from around 200 AD, a language that around 800 AD became the Old Norse language, which in turn later became the North Germanic languages of today. The North Germanic peoples are thought to have emerged as a distinct people in what is now southern Sweden in the early centuries AD. Several North Germanic tribes are mentioned by Classical antiquity, classical writers in antiquity, in particular the Swedes (Germanic tribe), Swedes, Danes (Germanic tribe), Danes, Geats, Gutes and Rugii. During the subsequent Viking Age, seafaring North Germanic adventurers, commonly referred to as Vikings, raided and settled territories throughout Europe and beyond, founding several important po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
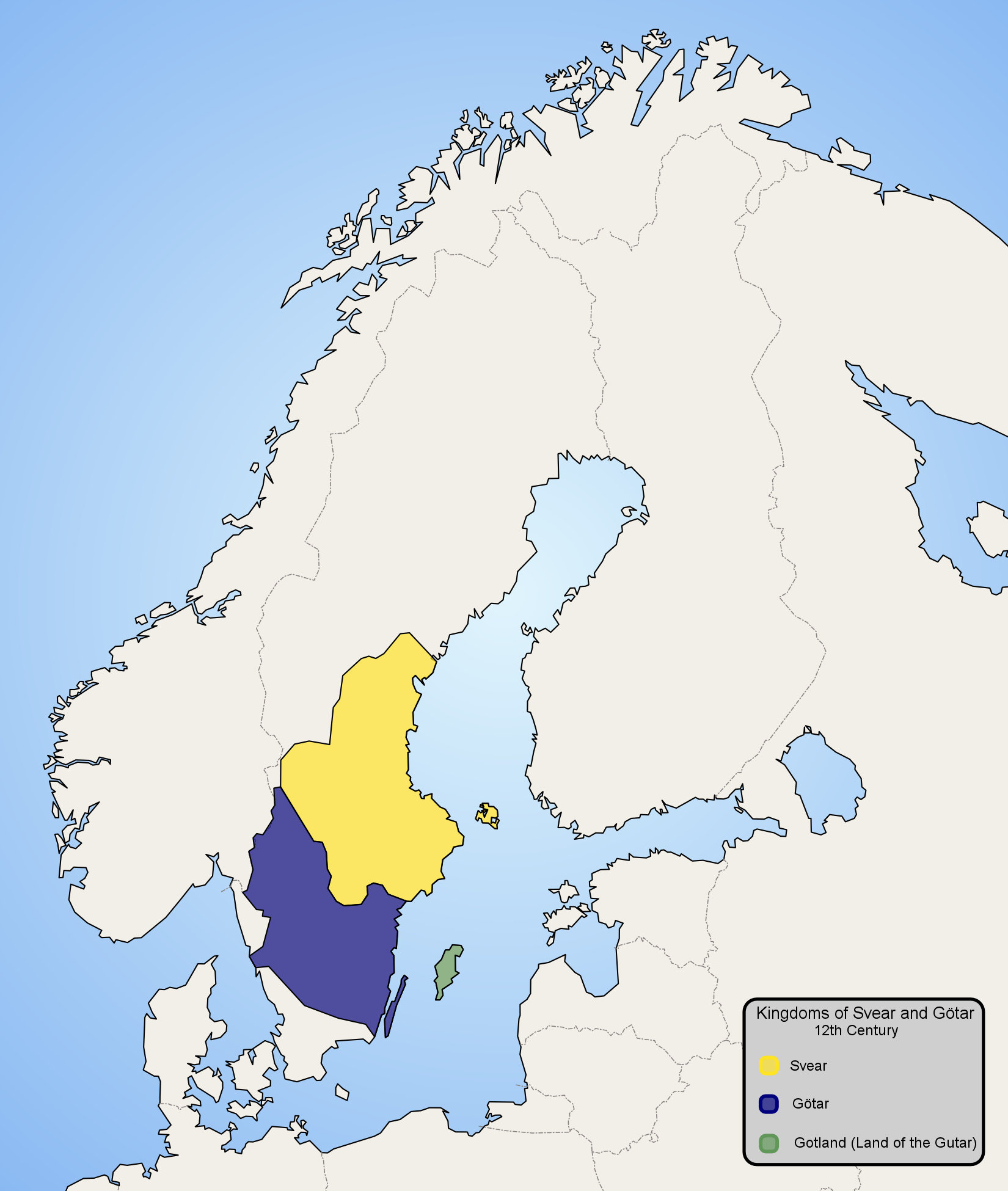
Danes (Germanic Tribe)
The Danes were a North Germanic tribe inhabiting southern Scandinavia, including the area now comprising Denmark proper, and the Scanian provinces of modern-day southern Sweden, during the Nordic Iron Age and the Viking Age. They founded what became the Kingdom of Denmark. The name of their realm is believed to mean " Danish March", viz. "the march of the Danes", in Old Norse, referring to their southern border zone between the Eider and Schlei rivers, known as the Danevirke. Origins The origin of the Danes remains undetermined, but several ancient historical documents and texts refer to them and archaeology has revealed and continues to reveal insights into their culture, beliefs, organization and way of life. The Danes first appear in written history in the 6th century with references in Jordanes' ''Getica'' (551 AD), by Procopius, and by Gregory of Tours. They spoke Old Norse (''dǫnsk tunga''), which the Danes shared with the people in Norway and Sweden and later in Icelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark
) , song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast") , song_type = National and royal anthem , image_map = EU-Denmark.svg , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark , established_title = History of Denmark#Middle ages, Consolidation , established_date = 8th century , established_title2 = Christianization , established_date2 = 965 , established_title3 = , established_date3 = 5 June 1849 , established_title4 = Faroese home rule , established_date4 = 24 March 1948 , established_title5 = European Economic Community, EEC 1973 enlargement of the European Communities, accession , established_date5 = 1 January 1973 , established_title6 = Greenlandic home rule , established_date6 = 1 May 1979 , official_languages = Danish language, Danish , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = German language, GermanGerman is recognised as a protected minority language in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Language
Danish (; , ) is a North Germanic language spoken by about six million people, principally in and around Denmark. Communities of Danish speakers are also found in Greenland, the Faroe Islands, and the northern German region of Southern Schleswig, where it has minority language status. Minor Danish-speaking communities are also found in Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina. Along with the other North Germanic languages, Danish is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples who lived in Scandinavia during the Viking Era. Danish, together with Swedish, derives from the ''East Norse'' dialect group, while the Middle Norwegian language (before the influence of Danish) and Norwegian Bokmål are classified as ''West Norse'' along with Faroese and Icelandic. A more recent classification based on mutual intelligibility separates modern spoken Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish as "mainland (or ''continental'') Scandinavian", while I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of Denmark
The Evangelical-Lutheran Church in Denmark or National Church, sometimes called the Church of Denmark ( da, Folkekirken, literally: "The People's Church" or unofficially da, Den danske folkekirke, literally: "The Danish People's Church"; kl, Ilagiit, literally: "The Congregation"), is the established, state-supported church in Denmark. The supreme secular authority of the church is composed of the reigning monarch and Denmark's Parliament, the Folketing. , 73.2% of the population of Denmark are members,Church membership 1990-2021 Kirkeministeriet though membership is voluntary.Freedom of reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany. The names are derived from the Jutes and the Cimbri, respectively. As with the rest of Denmark, Jutland's terrain is flat, with a slightly elevated ridge down the central parts and relatively hilly terrains in the east. West Jutland is characterised by open lands, heaths, plains, and peat bogs, while East Jutland is more fertile with lakes and lush forests. Southwest Jutland is characterised by the Wadden Sea, a large unique international coastal region stretching through Denmark, Germany, and the Netherlands. Geography Jutland is a peninsula bounded by the North Sea to the west, the Skagerrak to the north, the Kattegat and Baltic Sea to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Denmark
In January 2020, 74.4% of the population of Denmark were registered members of the Church of Denmark (), the officially established church, which is Protestant in classification and Lutheran in orientation.The Church of Denmark is the established church (or state religion) in Denmark and Greenland; the Church of the Faroe Islands became an independent body in 2007. This is down 0.6% compared to the year earlier and 1.2% down compared to two years earlier. Despite the high membership figures, only 3% of the population regularly attend Sunday services, and only 19% of Danes consider religion to be an important part of their life. Religiosity According to a Eurobarometer Poll conducted in 2010, 28% of Danish citizens responded that "they believe there is a God", 47% responded that "they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 24% responded that "they do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God or life force". Another poll, carried out in 2008, found that 25% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herules
The Heruli (or Herules) were an early Germanic peoples, Germanic people. Possibly originating in Scandinavia, the Heruli are first mentioned by Ancient Rome, Roman authors as one of several "Scythians, Scythian" groups raiding Roman provinces in the Balkans and the Aegean Sea, attacking by land, and notably also by sea. During this time they reportedly lived near the Sea of Azov. From the late 4th century AD the Heruli were one of the peoples that were brought into the fold of the Hunnic Confederation of Attila. By 454, after the death of Attila, they established their own kingdom on the Middle Danube, and Heruli also participated in successive conquests of Italy by Odoacer, Theoderic the Great, Narses and probably also the Longobards. However, their independent kingdom was destroyed by the Longobards by the early 6th century AD. A part of this population subsequently became established inside the Roman empire near Belgrade, and continued contributing fighting men to the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedes (Germanic Tribe)
The Swedes ( sv, svear; Old Norse: ''svíar'') (probably from the PIE reflexive pronominal root * s(w)e, "one's own ribesmen/kinsmen;Bandle, Oskar. 2002. The Nordic languages: an international handbook of the history of the North Germanic languages. 2002. P.391 ang, Swēon) were a North Germanic tribe who inhabited Svealand ("land of the Swedes") in central Sweden and one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Geats and Gutes. They had their tribal centre in Gamla Uppsala. The first author who wrote about the tribe is Tacitus, who in his ''Germania'' from 98 CE mentions the ''Suiones''. They are possibly first mentioned locally by the Kylver Stone in the 4th century. Jordanes, in the 6th century, mentions ''Suehans'' and ''Suetidi''. ''Beowulf'' mentions the Swedes around 1000 A.D. According to early sources such as the sagas, especially ''Heimskringla'', the Swedes were a powerful tribe whose kings claimed descendence from the god Freyr. During the Viking Age t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nations, along with the Angles and the Saxons: There is no consensus amongst historians of the origins on the Jutes. However, there is some archaeological evidence to support a theory that they originated from the eponymous Jutland Peninsula (then called ''Iutum'' in Latin) and to have populated parts of the North Frisian coast. Based on contemporary sources, it appears that they were a tribe of admixed Gutones, Cimbri, Teutons and Charudes, also called ''Eudoses'', ''Eotenas'', ''Iutae'' and ''Euthiones''. The Jutes invaded and settled in southern Britain in the later fifth century during the Migration Period, as part of a larger wave of Germanic settlement into Britain. Settlement in southern Britain During the period after the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jelling Stones
The Jelling stones ( da, Jellingstenene) are massive carved runestones from the 10th century, found at the town of Jelling in Denmark. The older of the two Jelling stones was raised by King Gorm the Old in memory of his wife Thyra. The larger of the two stones was raised by King Gorm's son, Harald Bluetooth, in memory of his parents, celebrating his conquest of Denmark and Norway, and his conversion of the Danes to Christianity. The runic inscriptions on these stones are considered the best known in Denmark. In 1994, the stones, in addition to the burial mounds and small church nearby, were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List as an unparalleled example of both pagan and Christian Nordic culture. Significance The stones are strongly identified with the creation of Denmark as a nation state. Both inscriptions mention the name "Danmark" (in the form of accusative "tanmaurk" () on the large stone, and genitive "tanmarkar" (pronounced ) on the small stone). The larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, Weapons and Ornaments: Germanic Material Culture in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400-750. BRILL, 2001, p.42. Later the term was associated with Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire. Although the Frankish name does not appear until the 3rd century, at least some of the original Frankish tribes had long been known to the Romans under their own names, both as allies providing soldiers, and as e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |