|
Dachsen
Dachsen is a municipality in the district of Andelfingen in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland. History Dachsen is first mentioned in 876 as ''Tahsheim''. Geography Dachsen has an area of . Of this area, 52.8% is used for agricultural purposes, while 13% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 25.3% is settled (buildings or roads) and the remainder (8.9%) is non-productive (rivers, glaciers or mountains). The municipality is a linear village (built along a single street) on a terrace near the Rhine knee near Laufen-Uhwiesen. Currently it is part of the agglomeration of Schaffhausen, even though it is in the canton of Zürich. Demographics Dachsen has a population (as of ) of . , 11.4% of the population was made up of foreign nationals. Over the last 10 years the population has grown at a rate of 34%. Most of the population () speaks German (95.1%), with Italian being second most common (1.6%) and French being third (0.7%). In the 2007 election the most popular party was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dachsen Railway Station
{{switzerland-railstation-stub ...
Dachsen is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Zurich and municipality of Dachsen. It is located on the Rheinfall line and is served by Zurich S-Bahn lines S12 and S33. References External links *Dachsen station on Swiss Federal Railway's web site Dachsen Dachsen Dachsen is a municipality in the district of Andelfingen in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland. History Dachsen is first mentioned in 876 as ''Tahsheim''. Geography Dachsen has an area of . Of this area, 52.8% is used for agricultural purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andelfingen (district)
Andelfingen District is one of the twelve districts of the German language, German-speaking canton of Zurich, Switzerland. It corresponds to the Zürcher Weinland, bounded by the Rhine to the north and west, by the canton of Thurgau to the east, by Winterthur to the south and by the Irchel to the southwest. Municipalities Andelfingen contains a total of twenty-two Municipalities of Switzerland, municipalities: Mergers *1872: Secession from Adlikon bei Andelfingen, Adlikon → Humlikon *1878: Renaming of ''Dorlikon'' → Thalheim an der Thur *1879: Secession from Trüllikon → Truttikon *1970: Renaming of ''Grossandelfingen'' → Andelfingen, Switzerland, Andelfingen *2013: Merger between ''„Obere Hueb“'' from the Municipality of Buch am Irchel → Neftenbach *2019: Merger between Oberstammheim, Unterstammheim and Waltalingen → Stammheim, Zurich, Stammheim See also *Municipalities of the canton of Zürich References {{DEFAULTSORT:Andelfingen (District) Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S33 (ZVV)
The S33 is a regional railway line of the S-Bahn Zürich on the Zürcher Verkehrsverbund (ZVV), Zürich transportation network, and is one of the network's lines connecting the cantons of Zürich and Schaffhausen. Route * The line runs from the northwest of the canton of Zürich from Winterthur and heads for Schaffhausen. At both terminal stations, connections to InterCity and InterRegio trains as well as other S-Bahn services exist. Stations * Winterthur * Hettlingen * Henggart * Andelfingen * Marthalen * Dachsen * Schloss Laufen am Rheinfall * Neuhausen * Schaffhausen Rolling stock S33 services are operated by RABe 511 units, except for weekday services to Schaffhausen which are run by Re 450 class locomotives pushing or pulling double-deck passenger carriages. Until 2018, the S33 services were operated by THURBO rolling stock (Stadler GTW units). Scheduling The train frequency is usually hourly and the trip takes 33 minutes. The S33 runs hourly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laufen-Uhwiesen
Laufen-Uhwiesen is a municipality in the district of Andelfingen in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland. History Laufen-Uhwiesen is first mentioned in 858 as ''ad Laufin''. In 1290 it was mentioned as ''ze Uwisan''. Geography Laufen-Uhwiesen has an area of . Of this area, 40.1% is used for agricultural purposes, while 44.4% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 11.7% is settled (buildings or roads) and the remainder (3.8%) is non-productive (rivers, glaciers or mountains). The municipality is located on the edge of the Schaffhausen Agglomeration, though it is in the canton of Zürich. It includes the village of Uhwiesen, which is located on a terrace of the Cholfirst elevation, the village of Laufen with Laufen Castle on the Rhine Falls, and the hamlet of Nohl on the right bank of the Rhine. Until 1840, it was part of the municipality of Flurlingen. Demographics Laufen-Uhwiesen has a population (as of ) of . , 9.3% of the population was made up of foreign nationals. Over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinau, Switzerland
Rheinau is a municipality in the district of Andelfingen in the Canton of Zürich in Switzerland. It is located at a bend of the Rhine River which forms the Swiss-German border in this area. A bridge links Rheinau to Altenburg, part of the municipality of Jestetten, Baden-Württemberg state. Geography Rheinau has an area of . Of this area, 26.8% is used for agricultural purposes, while 54.8% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 11.3% is settled (buildings or roads) and the remainder (7.2%) is non-productive (rivers, glaciers or mountains). Rheinau Abbey Rheinau Abbey was founded in 778 and grew until it was abandoned during the Protestant Reformation in 1529. It was re-established in 1532 and was a center of the Counter-reformation. In 1862 the cantonal council decreed the dissolution of the abbey. Following the dissolution of the abbey, in 1867 a cantonal hospital and nursing home were set up in the buildings. Later, a cantonal psychiatric clinic that developed here ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-Bahn Zürich
The S-Bahn is the name of hybrid urban- suburban rail systems serving a metropolitan region in German-speaking countries. Some of the larger S-Bahn systems provide service similar to rapid transit systems, while smaller ones often resemble commuter or even regional rail. The term derives from ''Schnellbahn'', ''Stadtbahn'' or ''Stadtschnellbahn''. Similar systems in Switzerland are known as S-Bahn as well. In Belgium it is known as S-Trein (Flemish) or Train S (French). In Belgium there are S-Trains in the five largest cities: Brussels, Antwerp, Liège, Ghent and Charleroi. In Denmark, they are known as S-tog , in the Czech Republic as Esko or S-lines. Characteristics There is no complete definition of an S-Bahn system. S-Bahn are, where they exist, the most local type of railway stopping at all existing stations inside and around a city, while other mainline trains only call at major stations. They are slower than mainline railways but usually serve as fast crosstown serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
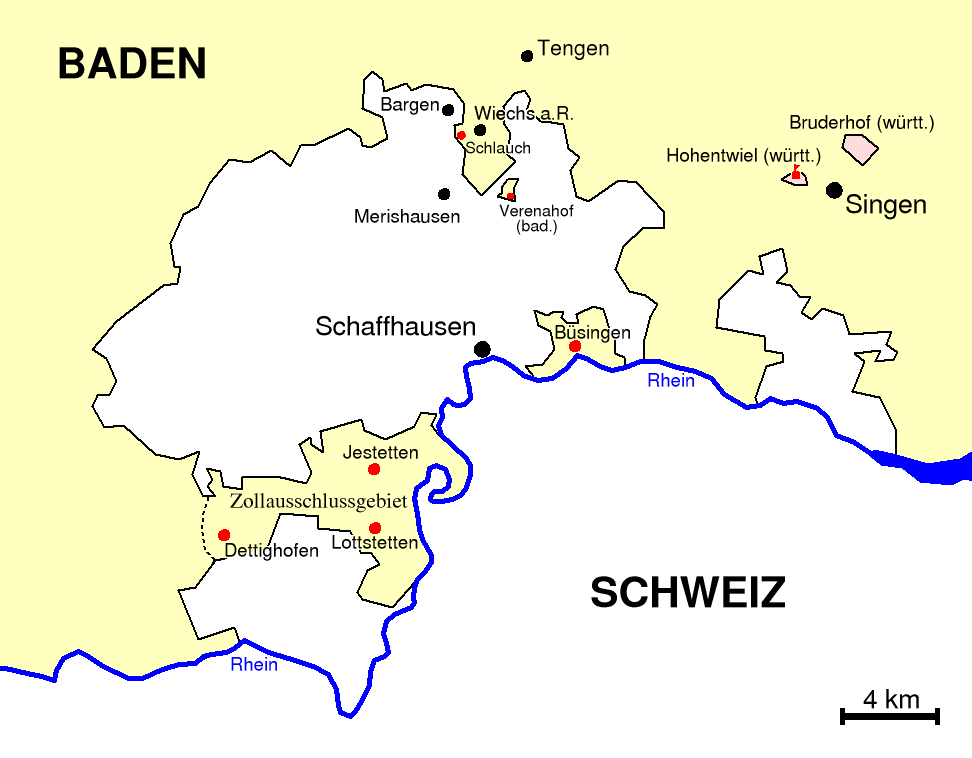
Jestetten
Jestetten is a municipality in the district of Waldshut in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. History In 1806 Jestetten became part of Baden. From 1840 until 1935, the territory of Jestetten together with Altenburg, Lottstetten and what was then Dettighofen, was part of the region which formed a customs exclusion zone and was not part of the German customs area. Inhabitants were able to offer their produce to the rest of Germany as well as to Switzerland. This situation brought about a higher standard of living and prosperity compared to the rest of Germany. Geography The border crossing into Switzerland is located to the east of town along Schaffhauserstraße leading to Neuhausen am Rheinfall. Another border crossing in the municipality is located south west of town along Osterfingerstraße, towards the villager of Osterfingen in Wilchingen municipality, Schaffhausen canton. Transport Jestetten railway station is situated on the Swiss Federal Railway's cross-border Eglisau-Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Sector Of The Economy
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the secondary sector (manufacturing). The tertiary sector consists of the provision of Service (economics), services instead of Product (business), end products. Services (also known as "Intangible good, intangible goods") include attention, advice, access, experience and affective labor. The information economy, production of information has been long regarded as a service, but some economists now attribute it to a fourth sector, called the quaternary sector. The tertiary sector involves the provision of services to other businesses as well as to final consumers. Services may involve the transport, distribution (economics), distribution and sale of goods from a producer to a consumer, as may happen in wholesaler, wholesaling and retailer, retaili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Sector Of The Economy
In macroeconomics, the secondary sector of the economy is an economic sector in the three-sector theory that describes the role of manufacturing. It encompasses industries that produce a finished, usable product or are involved in construction. This sector generally takes the output of the primary sector (i.e. raw materials) and creates finished goods suitable for sale to domestic businesses or consumers and for export (via distribution through the tertiary sector). Many of these industries consume large quantities of energy, require factories and use machinery; they are often classified as light or heavy based on such quantities. This also produces waste materials and waste heat that may cause environmental problems or pollution (see negative externalities). Examples include textile production, car manufacturing, and handicraft. Manufacturing is an important activity in promoting economic growth and development. Nations that export manufactured products tend to generate highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Sector Of The Economy
The primary sector of the economy includes any industry involved in the extraction and production of raw materials, such as farming, logging, fishing, forestry and mining. The primary sector tends to make up a larger portion of the economy in developing countries than it does in developed countries. For example, in 2018, agriculture, forestry, and fishing comprised more than 15% of GDP in sub-Saharan Africa but less than 1% of GDP in North America. In developed countries the primary sector has become more technologically advanced, enabling for example the mechanization of farming, as compared with lower-tech methods in poorer countries. More developed economies may invest additional capital in primary means of production: for example, in the United States corn belt, combine harvesters pick the corn, and sprayers spray large amounts of insecticides, herbicides and fungicides, producing a higher yield than is possible using less capital-intensive techniques. These technologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fachhochschule
A ''Fachhochschule'' (; plural ''Fachhochschulen''), abbreviated FH, is a university of applied sciences (UAS), in other words a German tertiary education institution that provides professional education in many applied sciences and applied arts, such as engineering, technology, business, architecture, design, and industrial design. ''Fachhochschulen'' were first founded in Germany and were later adopted in Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Cyprus, and Greece. An increasing number of ''Fachhochschulen'' are abbreviated as ''Hochschule'', the generic term in Germany for institutions awarding academic degrees in higher education, or expanded as ''Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften (HAW)'', the German translation of "universities of applied sciences", which are primarily designed with a focus on teaching professional skills. Swiss law calls ''Fachhochschulen'' and universities "separate but equal". Due to the Bologna process, universities and ''Fachhochschulen'' award l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education In Switzerland
The education system in Switzerland is very diverse, because the constitution of Switzerland delegates the authority for the school system mainly to the cantons. The Swiss constitution sets the foundations, namely that primary school is obligatory for every child and is free in state schools and that the confederation can run or support universities. The minimum age for primary school is about six years in all cantons but Obwalden, where it is five years and three months. After primary schools, the pupils split up according to their abilities and intentions of career paths. Roughly 25% of all students attend lower and upper secondary schools leading, normally after 12 school years in total to the federal recognized matura or an academic Baccalaureate which grants access to all universities. The other students split in two or more school-types, depending on the canton, differing in the balance between theoretical and practical education. It is obligatory for all children to atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |