|
DPA-713
DPA-713 or ''N'',''N''-diethyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5,7-dimethylpyrazolo[1,5-''a'']pyrimidine-3-acetamide is a selective ligand for the translocator protein (TSPO). The binding affinity of DPA-713 for TSPO is reported as ''K''i = 4.7 ± 0.2 nM. DPA-713 has been radiolabelled with carbon-11 as a potential radiotracer for imaging the TSPO using positron emission tomography (PET). Radiation dosimetry and biodistribution of [11C]DPA-713 have been assessed in healthy volunteers, indicating that [11C]DPA-713 is a suitable radiotracer for imaging the TSPO in humans. See also * DPA-714 References {{Translocator protein modulators Pyrazolopyrimidines TSPO ligands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translocator Protein
Translocator protein (TSPO) is an 18 kDa protein mainly found on the outer mitochondrial membrane. It was first described as peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR), a secondary binding site for diazepam, but subsequent research has found the receptor to be expressed throughout the body and brain. In humans, the translocator protein is encoded by the ''TSPO'' gene. It belongs to a family of tryptophan-rich sensory proteins. Regarding intramitochondrial cholesterol transport, TSPO has been proposed to interact with StAR (steroidogenic acute regulatory protein) to transport cholesterol into mitochondria, though evidence is mixed. Function In animals, TSPO (PBR) is a mitochondrial protein usually located in the outer mitochondrial membrane and characterised by its ability to bind a variety of benzodiazepine-like drugs, as well as to dicarboxylic tetrapyrrole intermediates of the haem biosynthetic pathway. TSPO has many proposed functions depending on the tissue. The most studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DPA-714
DPA-714 or ''N'',''N''-diethyl-2-[4-(2-fluoroethoxy)phenyl]-5,7-dimethylpyrazolo[1,5-''a'']pyrimidine-3-acetamide is a selective ligand for the translocator protein (TSPO) currently under evaluation for several clinical applications. For this reason, a practical, multigram synthetic route for its preparation has been described. The binding affinity of DPA-714 for TSPO is reported as ''K''i = 7.0 ± 0.4 nM. [18F]DPA-714 is currently under investigation as a potential radiopharmaceutical for imaging TSPO in living systems using positron emission tomography (PET). DPA-714, along with other members of the DPA class of TSPO ligands, has been shown to decrease microglial activation and increase neuronal survival in a quinolinic acid rat model of excitotoxic neurodegeneration, suggesting potential neuroprotective effects. See also * DPA-713 References {{Translocator protein modulators Pyrazolopyrimidines TSPO ligands Fluoroethyl ethers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding Affinity
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition of ligan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon-11
Carbon (6C) has 15 known isotopes, from to , of which and are stable. The longest-lived radioisotope is , with a half-life of years. This is also the only carbon radioisotope found in nature—trace quantities are formed cosmogenically by the reaction + → + . The most stable artificial radioisotope is , which has a half-life of . All other radioisotopes have half-lives under 20 seconds, most less than 200 milliseconds. The least stable isotope is , with a half-life of . List of isotopes , - , , style="text-align:right" , 6 , style="text-align:right" , 2 , , [] , proton emission, 2p , Subsequently decays by double proton emission to for a net reaction of → + 4 , 0+ , , , - , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 6 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 3 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , β+ () , , rowspan=3, 3/2− , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , - , β+α () , Immediately decays by proton emission to for a net reaction of � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiotracer
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. Radiolabeling or radiotracing is thus the radioactive form of isotopic labeling. In biological contexts, use of radioisotope tracers are sometimes called radioisotope feeding experiments. Radioisotopes of hydrogen, carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, and iodine have been used extensively to trace the path of biochemical reactions. A radioactive tracer can also be used to track the distribution of a substance within a natural system such as a cell or tissue, or as a flow tracer to track fluid flow. Radioactive tracers are also used to determine the location of fractures created by hydraulic fracturing in natural gas production.Reis, John C. (1976). ''Environmental Control in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
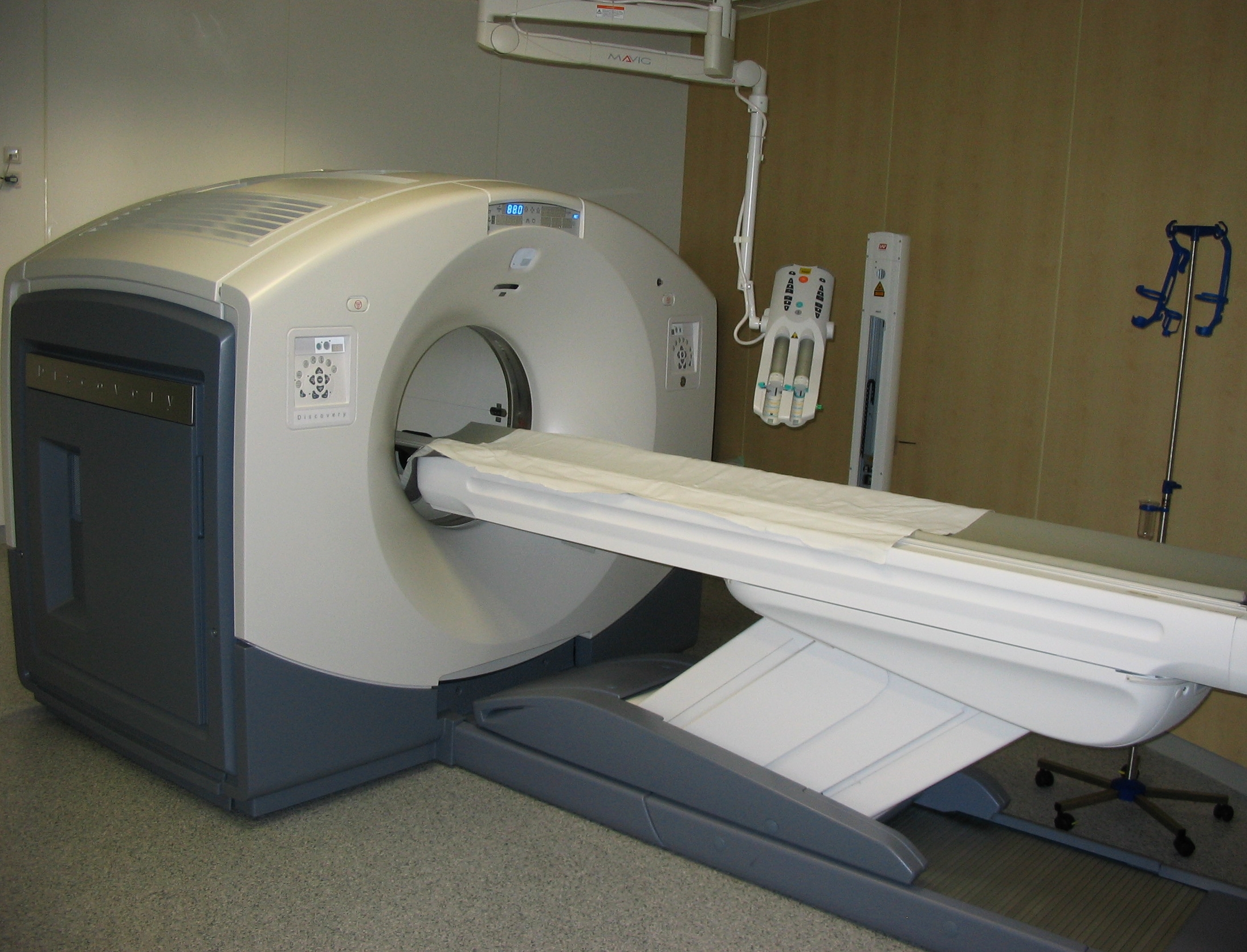
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18F-FDG, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, Sodium fluoride#Medical imaging, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and Isotopes of oxygen#Oxygen-15, oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common medical imaging, imaging technique, a Scintigraphy#Process, medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical, radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrazolopyrimidines
Pyrazolopyrimidines are a series of isomeric heterocyclic chemical compounds with the molecular formula C6H5N3. They form the central core of a variety of more complex chemical compounds including some pharmaceuticals and pesticides. Pharmaceuticals One isomer of pyrazolopyrimidines, known as pyrazolo ,5-''a''yrimidine, is the basis for a class of sedative and anxiolytic drugs related (in terms of their effect) to benzodiazepines. Most of the drugs from this class marketed to date are intended to induce sleep, and are prescribed for people suffering insomnia, however some newer compounds produce anxiolytic effects with relatively little sedation, and are being developed for use as non-sedating anti-anxiety drugs. They include: * Zaleplon - hypnotic (trade name Sonata) * Indiplon - hypnotic * Ocinaplon - anxiolytic * Lorediplon - hypnotic As they are not chemically related to the benzodiazepines despite their similar effect, such drugs—as well as the imidazopyridines and cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |