|
DNAG Logo
DnaG is a bacterial DNA primase and is encoded by the ''dnaG'' gene. The enzyme DnaG, and any other DNA primase, synthesizes short strands of RNA known as oligonucleotides during DNA replication. These oligonucleotides are known as primers because they act as a starting point for DNA synthesis. DnaG catalyzes the synthesis of oligonucleotides that are 10 to 60 nucleotides (the fundamental unit of DNA and RNA) long, however most of the oligonucleotides synthesized are 11 nucleotides. These RNA oligonucleotides serve as primers, or starting points, for DNA synthesis by bacterial DNA polymerase III (Pol III). DnaG is important in bacterial DNA replication because DNA polymerase cannot initiate the synthesis of a DNA strand, but can only add nucleotides to a preexisting strand. DnaG synthesizes a single RNA primer at the origin of replication. This primer serves to prime leading strand DNA synthesis. For the other parental strand, the lagging strand, DnaG synthesizes an RNA prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, ''M. tuberculosis'' can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fastness, Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen stain, Ziehl–Neelsen, or Fluorescence, fluorescent stains such as Auramine O, auramine are used instead to identify ''M. tuberculosis'' with a microscope. The physiology of ''M. tuberculosis'' is highly aerobic organism, aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the Mantoux test, tuberculin skin test, Acid-Fast Stain, acid-fast stain, Microbiological cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
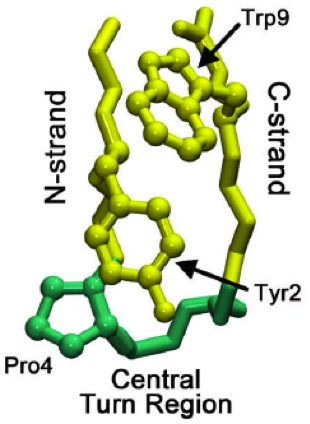
Beta Hairpin
The beta hairpin (sometimes also called beta-ribbon or beta-beta unit) is a simple protein structural motif involving two beta strands that look like a hairpin. The motif consists of two strands that are adjacent in primary structure, oriented in an antiparallel direction (the N-terminus of one sheet is adjacent to the C-terminus of the next), and linked by a short loop of two to five amino acids. Beta hairpins can occur in isolation or as part of a series of hydrogen bonded strands that collectively comprise a beta sheet. Researchers such as Francisco Blanco ''et al.'' have used protein NMR to show that beta-hairpins can be formed from isolated short peptides in aqueous solution, suggesting that hairpins could form nucleation sites for protein folding. Classification Beta hairpins were originally categorized solely by the number of amino acid residues in their loop sequences, such that they were named one-residue, two-residue, etc. This system, however, is somewhat ambiguous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) in order to stabilize the fold. It was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from the African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'') transcription factor IIIA. However, it has been found to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures in eukaryotic cells. ''Xenopus laevis'' TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein followed soon thereafter by the Krüppel factor in ''Drosophila''. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins. Proteins that contain zinc fingers (zinc finger proteins) are classified into several different structural families. Unlike many other clearly defined supersecondary structures such as Greek keys or β hairpins, there are a number of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DnaG Zinc Binding Domain
DnaG is a bacterial DNA primase and is encoded by the ''dnaG'' gene. The enzyme DnaG, and any other DNA primase, synthesizes short strands of RNA known as oligonucleotides during DNA replication. These oligonucleotides are known as primers because they act as a starting point for DNA synthesis. DnaG catalyzes the synthesis of oligonucleotides that are 10 to 60 nucleotides (the fundamental unit of DNA and RNA) long, however most of the oligonucleotides synthesized are 11 nucleotides. These RNA oligonucleotides serve as primers, or starting points, for DNA synthesis by bacterial DNA polymerase III (Pol III). DnaG is important in bacterial DNA replication because DNA polymerase cannot initiate the synthesis of a DNA strand, but can only add nucleotides to a preexisting strand. DnaG synthesizes a single RNA primer at the origin of replication. This primer serves to prime leading strand DNA synthesis. For the other parental strand, the lagging strand, DnaG synthesizes an RNA prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides. RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protein coding, i.e. messenger RNA (mRNA); or n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalyze the chemical reaction : deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNAn pyrophosphate + DNAn+1. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. In this way, genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Pyrophosphatase
Inorganic pyrophosphatase (or inorganic diphosphatase, PPase) is an enzyme () that catalyzes the conversion of one ion of pyrophosphate to two phosphate ions. This is a highly exergonic reaction, and therefore can be coupled to unfavorable biochemical transformations in order to drive these transformations to completion. The functionality of this enzyme plays a critical role in lipid metabolism (including lipid synthesis and degradation), calcium absorption and bone formation, and DNA synthesis, as well as other biochemical transformations. Two types of inorganic diphosphatase, very different in terms of both amino acid sequence and structure, have been characterised to date: soluble and transmembrane proton-pumping pyrophosphatases (sPPases and H(+)-PPases, respectively). sPPases are ubiquitous proteins that hydrolyse pyrophosphate to release heat, whereas H+-PPases, so far unidentified in animal and fungal cells, couple the energy of PPi hydrolysis to proton movement across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehydration Synthesis
In chemistry, a dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes, the reverse of a hydration reaction. Dehydration reactions in organic chemistry Esterification The classic example of a dehydration reaction is the Fischer esterification, which involves treating a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to give an ester :RCO2H + R′OH RCO2R′ + H2O Often such reactions require the presence of a dehydrating agent, i.e. a substance that reacts with water. Etherification Two monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, can be joined together (to form saccharose) using dehydration synthesis. The new molecule, consisting of two monosaccharides, is called a disaccharide. Nitrile formation Nitriles are often prepared by dehydration of primary amides. :RC(O)NH2 → RCN + H2O Ketene formation Ketene is produced by heating acetic acid and trapping the product: :CH3CO2H → CH2=C= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replication Fork
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoside Triphosphate
A nucleoside triphosphate is a nucleoside containing a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose), with three phosphate groups bound to the sugar. They are the molecular precursors of both DNA and RNA, which are chains of nucleotides made through the processes of DNA replication and transcription. Nucleoside triphosphates also serve as a source of energy for cellular reactions and are involved in signalling pathways. Nucleoside triphosphates cannot be absorbed well, so they are typically synthesized within the cell. Synthesis pathways differ depending on the specific nucleoside triphosphate being made, but given the many important roles of nucleoside triphosphates, synthesis is tightly regulated in all cases. Nucleoside analogues may also be used to treat viral infections. For example, azidothymidine (AZT) is a nucleoside analogue used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. Naming The term nucleoside refers to a nitrogenous base linked to a 5-carbon suga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |