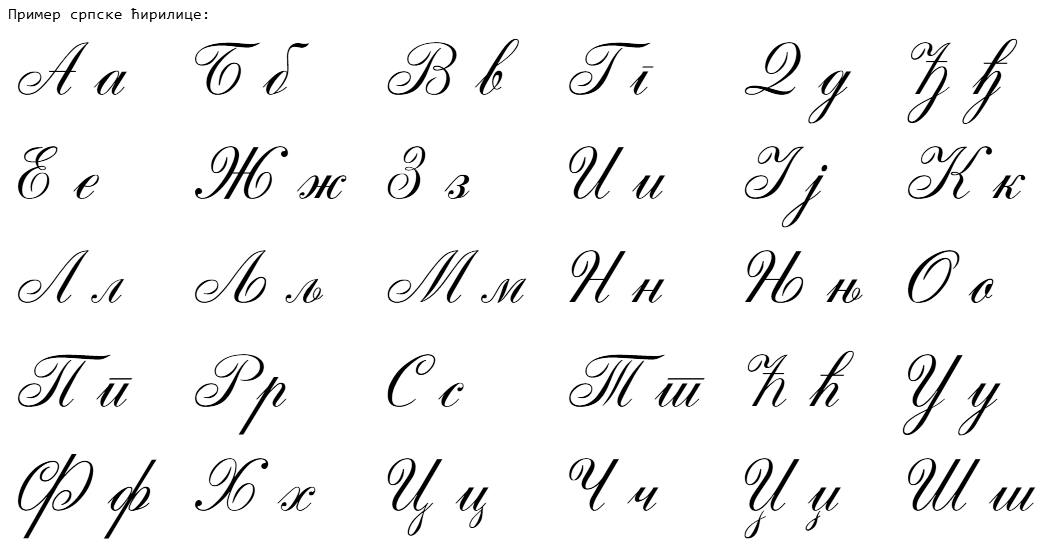|
DKOI
DKOI (russian: ДКОИ, Двоичный Код Обработки Информации, "Binary Code for Information Processing") is an EBCDIC encoding for Russian Cyrillic. It is a Telegraphy-based encoding used in ES EVM mainframes. ''Вострикова З. П.'' Программирование на языке ассемблера ЕС ЭВМ. — М.: Наука, 1981. — С. 291. It has been defined by several standards: GOST 19768-74 / ST SEV 358-76, ST SEV 358-88 / GOST 19768-93, CSN 36 9103. DKOI K1 In DKOI K1 (ДКОИ К1), each Cyrillic letter is given its own code point. Characters are shown with their equivalent Unicode codes. The dollar sign may be placed in code point 0x5B; in that case the currency sign is in code point 0xE1. DKOI K2 In DKOI K2 (ДКОИ К2), some Cyrillic letters (А, В, Е, К, М, Н, О, Р, С, Т, Х, а, е, о, р, с, у, х) are merged with visually identical Latin letters (A, B, E, K, M, H, O, P, C, T, X, a, e, o, p, c, y, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Page 880
DKOI (russian: ДКОИ, Двоичный Код Обработки Информации, "Binary Code for Information Processing") is an EBCDIC encoding for Russian Cyrillic. It is a Telegraphy-based encoding used in ES EVM mainframes. ''Вострикова З. П.'' Программирование на языке ассемблера ЕС ЭВМ. — М.: Наука, 1981. — С. 291. It has been defined by several standards: GOST 19768-74 / ST SEV 358-76, ST SEV 358-88 / GOST 19768-93, CSN 36 9103. DKOI K1 In DKOI K1 (ДКОИ К1), each Cyrillic letter is given its own code point. Characters are shown with their equivalent Unicode codes. The dollar sign may be placed in code point 0x5B; in that case the currency sign is in code point 0xE1. DKOI K2 In DKOI K2 (ДКОИ К2), some Cyrillic letters (А, В, Е, К, М, Н, О, Р, С, Т, Х, а, е, о, р, с, у, х) are merged with visually identical Latin letters (A, B, E, K, M, H, O, P, C, T, X, a, e, o, p, c, y, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EBCDIC
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC; ) is an eight-bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems. It descended from the code used with punched cards and the corresponding six-bit binary-coded decimal code used with most of IBM's computer peripherals of the late 1950s and early 1960s. It is supported by various non-IBM platforms, such as Fujitsu-Siemens' BS2000/OSD, OS-IV, MSP, and MSP-EX, the SDS Sigma series, Unisys VS/9, Unisys MCP and ICL VME. History EBCDIC was devised in 1963 and 1964 by IBM and was announced with the release of the IBM System/360 line of mainframe computers. It is an eight-bit character encoding, developed separately from the seven-bit ASCII encoding scheme. It was created to extend the existing Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) Interchange Code, or BCDIC, which itself was devised as an efficient means of encoding the two ''zone'' and ''number'' punches on punched cards into six bits. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphen-minus
The hyphen-minus is the most commonly used type of hyphen, widely used in digital documents. It is the only character that looks like a minus sign or a dash in many character sets such as ASCII or on most keyboards, so it is also used as such. The name "hyphen-minus" derives from the original ASCII standard, where it was called "hyphen(minus)". The character is referred to as a "hyphen", a "minus sign", or a "dash" according to the context where it is being used. Description In early monospaced font typewriters and character encodings, a single key/code was almost always used for hyphen, minus, various dashes, and strikethrough, since they all have a roughly similar appearance. The current Unicode Standard specifies distinct characters for a number of different dashes, an unambiguous minus sign ("Unicode minus") at code point U+2212, and various types of hyphen including the unambiguous "Unicode hyphen" at U+2010 and the hyphen-minus at U+002D. When a hyphen is called for, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Cyrillic
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian, the other being Gaj's Latin alphabet. Karadžić based his alphabet on the previous Slavonic-Serbian script, following the principle of "write as you speak and read as it is written", removing obsolete letters and letters representing iotified vowels, introducing from the Latin alphabet instead, and adding several consonant letters for sounds specific to Serbian phonology. During the same period, linguists led by Ljudevit Gaj adapted the Latin alphabet, in use in western South Slavic areas, using the same principles. As a result of this joint effort, Serbian Cyrillic and Gaj's Latin alphabets for Serbian-Croatian have a complete one-to-one congruence, with the Latin digraphs Lj, Nj, and Dž counting as single letters. Karadžić's Cyril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overline
An overline, overscore, or overbar, is a typographical feature of a horizontal line drawn immediately above the text. In old mathematical notation, an overline was called a '' vinculum'', a notation for grouping symbols which is expressed in modern notation by parentheses, though it persists for symbols under a radical sign. The original use in Ancient Greek was to indicate compositions of Greek letters as Greek numerals. In Latin, it indicates Roman numerals multiplied by a thousand and it forms medieval abbreviations (sigla). Marking one or more words with a continuous line above the characters is sometimes called ''overstriking'', though overstriking generally refers to printing one character on top of an already-printed character. An overline, that is, a single line above a chunk of text, should not be confused with the macron, a diacritical mark placed above (or sometimes below) ''individual'' letters. The macron is narrower than the character box. Uses Medicine In most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negation
In logic, negation, also called the logical complement, is an operation that takes a proposition P to another proposition "not P", written \neg P, \mathord P or \overline. It is interpreted intuitively as being true when P is false, and false when P is true. Negation is thus a unary logical connective. It may be applied as an operation on notions, propositions, truth values, or semantic values more generally. In classical logic, negation is normally identified with the truth function that takes ''truth'' to ''falsity'' (and vice versa). In intuitionistic logic, according to the Brouwer–Heyting–Kolmogorov interpretation, the negation of a proposition P is the proposition whose proofs are the refutations of P. Definition ''Classical negation'' is an operation on one logical value, typically the value of a proposition, that produces a value of ''true'' when its operand is false, and a value of ''false'' when its operand is true. Thus if statement is true, then \neg P (pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Page 500
Code page 37 (CCSID 37; label ), known as "USA/Canada - CECP", is an EBCDIC code page used on IBM mainframes. It encodes the ISO/IEC 8859-1 repertoire of graphic characters. Code page 37 is one of the most-used and best-supported EBCDIC code pages. It is used as the default z/OS code page in the United States and other English speaking countries. It is considered the "required" EBCDIC code page for the United States, and also used in Australia, New Zealand, the Netherlands, Portugal and Brazil, and on ESA/390 systems in Canada, but not on Canadian AS/400 systems, which use Code page 500 instead. It is one of four EBCDIC code pages (alongside 500, 875 and 1026) with mapping data supplied by Microsoft to the Unicode Consortium, and one of seven (alongside 273, 424, 500, 875, 1026 and 1140) supported by Python as standard. Character set Code page 37 exists in two versions: a "base character set" or "DP94" version (GCSGID 101 with CPGID 37, or CCSID 8229), containing only 94 gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eight Ones
EO, or Eight Ones, is an 8-bit EBCDIC character code represented as all ones (binary 1111 1111, hexadecimal FF). It is used for synchronisation purposes, such as a time and media filler. When translated from the EBCDIC character set to code pages with a C1 control code set, it is typically mapped to hexadecimal code 9F, in order to provide a unique character mapping in both directions. See also *0xFF *Delete character The delete control character (also called DEL or rubout) is the last character in the ASCII repertoire, with the code 127. It is supposed to do nothing and was designed to erase incorrect characters on paper tape. It is denoted as in caret notat ... References {{compsci-stub Control characters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brace (punctuation)
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'right' bracket or, alternatively, an "opening bracket" or "closing bracket", respectively, depending on the directionality of the context. Specific forms of the mark include parentheses (also called "rounded brackets"), square brackets, curly brackets (also called 'braces'), and angle brackets (also called 'chevrons'), as well as various less common pairs of symbols. As well as signifying the overall class of punctuation, the word "bracket" is commonly used to refer to a specific form of bracket, which varies from region to region. In most English-speaking countries, an unqualified word "bracket" refers to the parenthesis (round bracket); in the United States, the square bracket. Various forms of brackets are used in mathematics, with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equals Sign
The equals sign (British English, Unicode) or equal sign (American English), also known as the equality sign, is the mathematical symbol , which is used to indicate equality in some well-defined sense. In an equation, it is placed between two expressions that have the same value, or for which one studies the conditions under which they have the same value. In Unicode and ASCII, it has the code point U+003D. It was invented in 1557 by Robert Recorde. History The etymology of the word "equal" is from the Latin word "''æqualis",'' as meaning "uniform", "identical", or "equal", from ''aequus'' ("level", "even", or "just"). The symbol, now universally accepted in mathematics for equality, was first recorded by Welsh mathematician Robert Recorde in ''The Whetstone of Witte'' (1557). The original form of the symbol was much wider than the present form. In his book Recorde explains his design of the "Gemowe lines" (meaning ''twin'' lines, from the Latin '' gemellus'')See also g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostrophe
The apostrophe ( or ) is a punctuation mark, and sometimes a diacritical mark, in languages that use the Latin alphabet and some other alphabets. In English, the apostrophe is used for two basic purposes: * The marking of the omission of one or more letters, e.g. the contraction of "do not" to "don't". * The marking of possessive case of nouns (as in "the eagle's feathers", "in one month's time", "at your parents' ome). The word "apostrophe" comes ultimately from Greek (, ' he accent ofturning away or elision'), through Latin and French. For use in computer systems, Unicode has code points for three different forms of apostrophe. Usage in English Historical development The apostrophe was first used by Pietro Bembo in his edition of '' De Aetna'' (1496). It was introduced into English in the 16th century in imitation of French practice. French practice Introduced by Geoffroy Tory (1529), the apostrophe was used in place of a vowel letter to indicate elision (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Sign
The symbol is known variously in English-speaking regions as the number sign, hash, or pound sign. The symbol has historically been used for a wide range of purposes including the designation of an ordinal number and as a Typographic ligature, ligatured abbreviation for Pound (mass), pounds avoirdupois – having been derived from the now-rare . Since 2007, widespread usage of the symbol to introduce metadata tags on social media platforms has led to such tags being known as "hashtags", and from that, the symbol itself is sometimes called a hashtag. The symbol is distinguished from similar symbols by its combination of level horizontal strokes and right-tilting vertical strokes. History It is believed that the symbol traces its origins to the symbol , an abbreviation of the Roman term ''Roman pound, libra pondo'', which translates as "pound weight". This abbreviation was printed with a dedicated Ligature (writing), ligature type element, with a horizontal line across, so t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |