|
DES Challenges
The DES Challenges were a series of brute force attack contests created by RSA Security to highlight the lack of security provided by the Data Encryption Standard. The Contests The first challenge began in 1997 and was solved in 96 days by the DESCHALL Project. DES Challenge II-1 was solved by distributed.net in 39 days in early 1998. The plaintext message being solved for was "The secret message is: Many hands make light work." DES Challenge II-2 was solved in just 56 hours in July 1998, by the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), with their purpose-built Deep Crack machine. EFF won $10,000 for their success, although their machine cost $250,000 to build. The contest demonstrated how quickly a rich corporation or government agency, having built a similar machine, could decrypt ciphertext encrypted with DES. The text was revealed to be "The secret message is: It's time for those 128-, 192-, and 256-bit keys." DES Challenge III was a joint effort between distributed.net and D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brute Force Attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack consists of an attacker submitting many passwords or passphrases with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. The attacker systematically checks all possible passwords and passphrases until the correct one is found. Alternatively, the attacker can attempt to guess the Key (cryptography), key which is typically created from the password using a key derivation function. This is known as an exhaustive key search. A brute-force attack is a cryptanalytic attack that can, in theory, be used to attempt to decrypt any encrypted data (except for data encrypted in an information-theoretically secure manner). Such an attack might be used when it is not possible to take advantage of other weaknesses in an encryption system (if any exist) that would make the task easier. When password-guessing, this method is very fast when used to check all short passwords, but for longer passwords other methods such as the dictionary attack are used because a br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSA Security
RSA Security LLC, formerly RSA Security, Inc. and doing business as RSA, is an American computer and network security company with a focus on encryption and encryption standards. RSA was named after the initials of its co-founders, Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman, after whom the RSA public key cryptography algorithm was also named. Among its products is the SecurID authentication token. The BSAFE cryptography libraries were also initially owned by RSA. RSA is known for incorporating backdoors developed by the NSA in its products. It also organizes the annual RSA Conference, an information security conference. Founded as an independent company in 1982, RSA Security was acquired by EMC Corporation in 2006 for US$2.1 billion and operated as a division within EMC. When EMC was acquired by Dell Technologies in 2016, RSA became part of the Dell Technologies family of brands. On 10 March 2020, Dell Technologies announced that they will be selling RSA Security to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Encryption Standard
The Data Encryption Standard (DES ) is a symmetric-key algorithm for the encryption of digital data. Although its short key length of 56 bits makes it too insecure for modern applications, it has been highly influential in the advancement of cryptography. Developed in the early 1970s at IBM and based on an earlier design by Horst Feistel, the algorithm was submitted to the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) following the agency's invitation to propose a candidate for the protection of sensitive, unclassified electronic government data. In 1976, after consultation with the National Security Agency (NSA), the NBS selected a slightly modified version (strengthened against differential cryptanalysis, but weakened against brute-force attacks), which was published as an official Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) for the United States in 1977. The publication of an NSA-approved encryption standard led to its quick international adoption and widespread academic scrutiny. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DESCHALL Project
DESCHALL, short for DES Challenge, was the first group to publicly break a message which used the Data Encryption Standard (DES), becoming the $10,000 winner of the first of the set of DES Challenges proposed by RSA Security in 1997. It was established by a group of computer scientists led by Rocke Verser assisted by Justin Dolske and Matt Curtin and involved thousands of volunteers who ran software in the background on their own machines, connected by the Internet. They announced their success on June 18, only 96 days after the challenge was announced on January 28. Background To search the 72 quadrillion possible keys of a 56-bit DES key using conventional computers was considered impractical even in the 1990s. Rocke Verser already had an efficient algorithm that ran on a standard PC and had the idea of involving the spare time on hundreds of other such machines that were connected to the internet. So they set up a server on a 486-based PS/2 PC with 56MB of memory and announc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory * Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space * Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra * Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Frontier Foundation
The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) is an international non-profit digital rights group based in San Francisco, California. The foundation was formed on 10 July 1990 by John Gilmore, John Perry Barlow and Mitch Kapor to promote Internet civil liberties. The EFF provides funds for legal defense in court, presents '' amicus curiae'' briefs, defends individuals and new technologies from what it considers abusive legal threats, works to expose government malfeasance, provides guidance to the government and courts, organizes political action and mass mailings, supports some new technologies which it believes preserve personal freedoms and online civil liberties, maintains a database and web sites of related news and information, monitors and challenges potential legislation that it believes would infringe on personal liberties and fair use and solicits a list of what it considers abusive patents with intentions to defeat those that it considers without merit. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
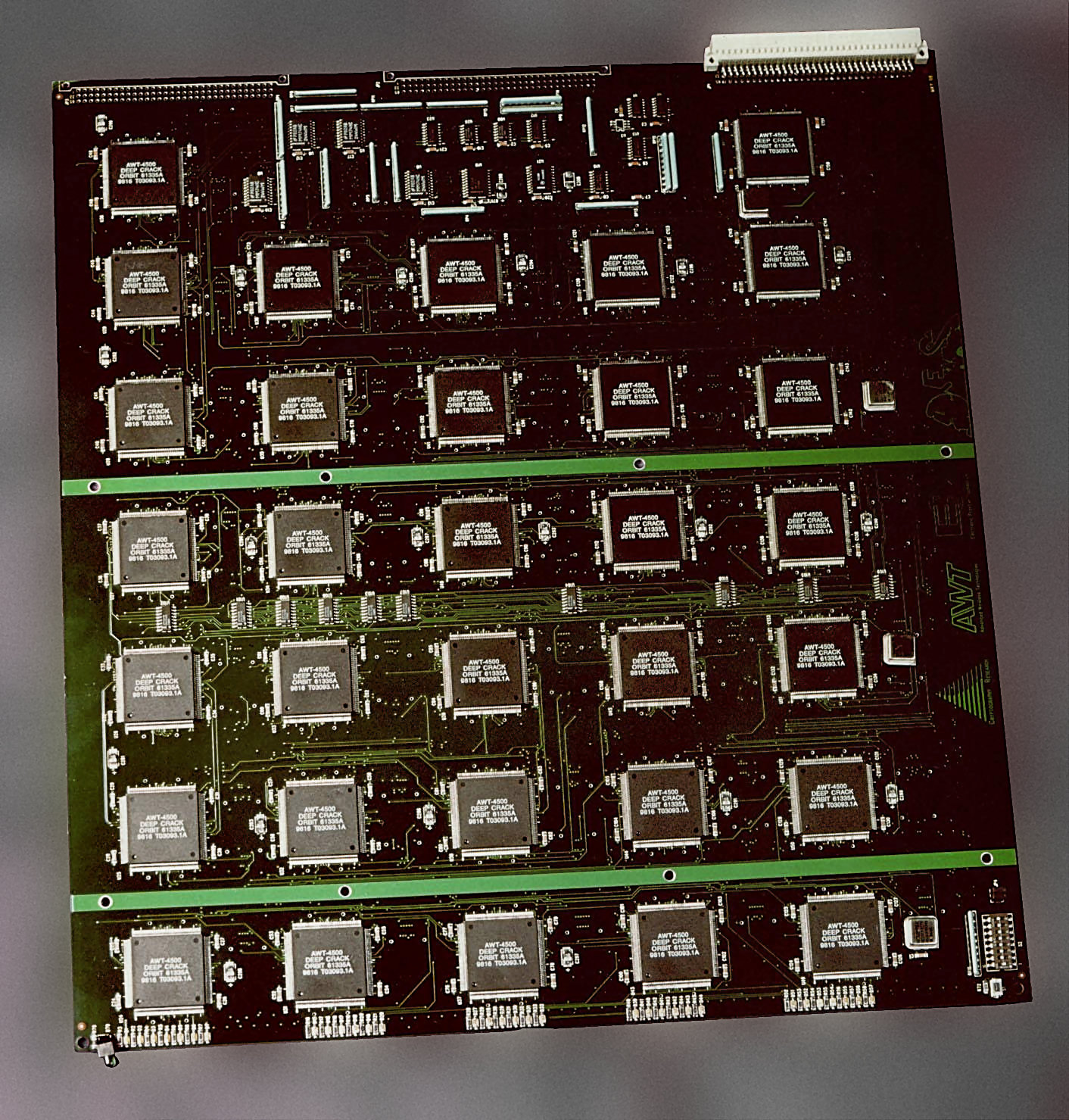
EFF DES Cracker
In cryptography, the EFF DES cracker (nicknamed "Deep Crack") is a machine built by the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) in 1998, to perform a brute force search of the Data Encryption Standard (DES) cipher's key space – that is, to decrypt an encrypted message by trying every possible key. The aim in doing this was to prove that the key size of DES was not sufficient to be secure. Background DES uses a 56-bit key, meaning that there are 256 possible keys under which a message can be encrypted. This is exactly 72,057,594,037,927,936, or approximately 72 quadrillion possible keys. One of the major criticisms of DES, when proposed in 1975, was that the key size was too short. Martin Hellman and Whitfield Diffie of Stanford University estimated that a machine fast enough to test that many keys in a day would have cost about $20 million in 1976, an affordable sum to national intelligence agencies such as the US National Security Agency. Subsequent advances in the price/per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Bureau Of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, the FBI is also a member of the U.S. Intelligence Community and reports to both the Attorney General and the Director of National Intelligence. A leading U.S. counterterrorism, counterintelligence, and criminal investigative organization, the FBI has jurisdiction over violations of more than 200 categories of federal crimes. Although many of the FBI's functions are unique, its activities in support of national security are comparable to those of the British MI5 and NCA; the New Zealand GCSB and the Russian FSB. Unlike the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), which has no law enforcement authority and is focused on intelligence collection abroad, the FBI is primarily a domestic agency, maintaining 56 field offices in major cities t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical science laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified in 1789, granted these powers to the new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Encryption Standard
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael (), is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001. AES is a variant of the Rijndael block cipher developed by two Belgian cryptographers, Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen, who submitted a proposal to NIST during the AES selection process. Rijndael is a family of ciphers with different key and block sizes. For AES, NIST selected three members of the Rijndael family, each with a block size of 128 bits, but three different key lengths: 128, 192 and 256 bits. AES has been adopted by the U.S. government. It supersedes the Data Encryption Standard (DES), which was published in 1977. The algorithm described by AES is a symmetric-key algorithm, meaning the same key is used for both encrypting and decrypting the data. In the United States, AES was announced by the NIST as U.S. FIPS PUB 197 (FIPS 197) on Nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple DES
In cryptography, Triple DES (3DES or TDES), officially the Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA or Triple DEA), is a symmetric-key block cipher, which applies the DES cipher algorithm three times to each data block. The Data Encryption Standard's (DES) 56-bit key is no longer considered adequate in the face of modern cryptanalytic techniques and supercomputing power. A CVE released in 2016, CVE-2016-2183' disclosed a major security vulnerability in DES and 3DES encryption algorithms. This CVE, combined with the inadequate key size of DES and 3DES, NIST has deprecated DES and 3DES for ''new'' applications in 2017, and for ''all'' applications by the end of 2023. It has been replaced with the more secure, more robust AES. While the government and industry standards abbreviate the algorithm's name as TDES (Triple DES) and TDEA (Triple Data Encryption Algorithm), RFC 1851 referred to it as 3DES from the time it first promulgated the idea, and this namesake has since come into wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Round_Function.png)