|
D-alanine 2-hydroxymethyltransferase
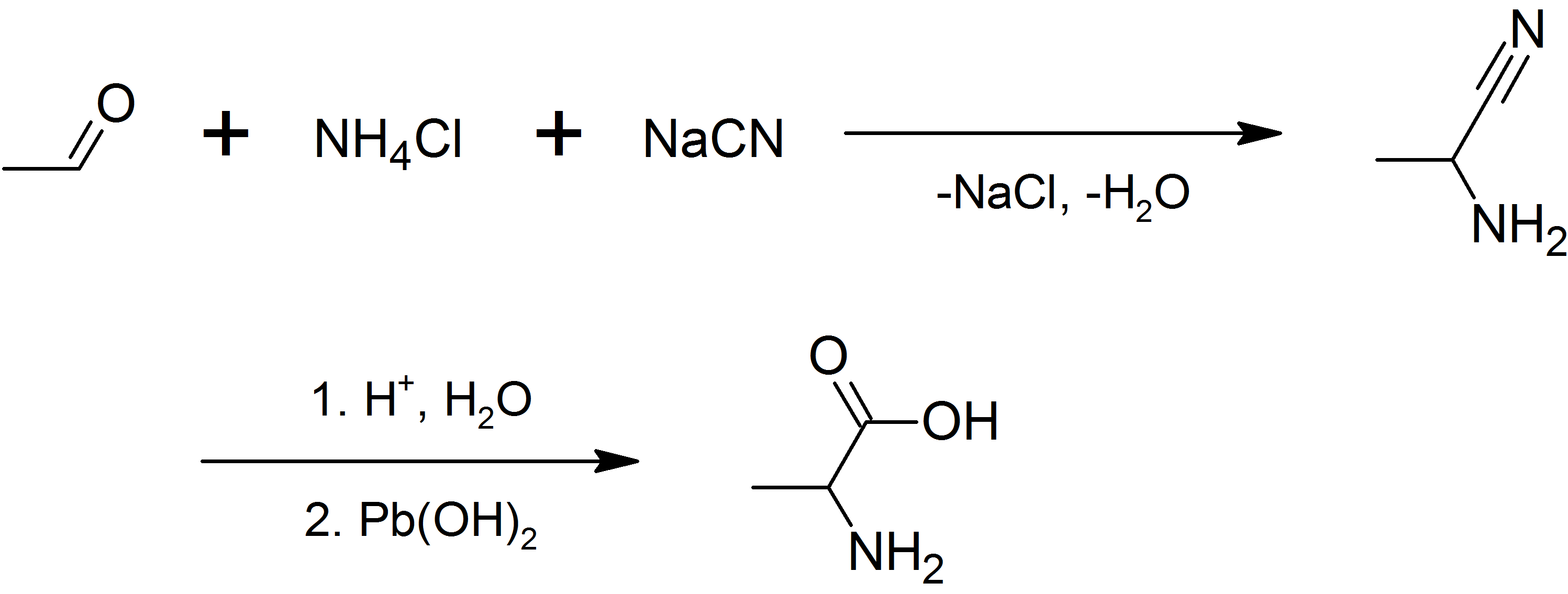
In enzymology, a D-alanine 2-hydroxymethyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + D-alanine + H2O \rightleftharpoons tetrahydrofolate + 2-methylserine The 3 substrates of this enzyme are 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate, D-alanine Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side c ..., and H2O, whereas its two products are tetrahydrofolate and 2-methylserine. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases that transfer one-carbon groups, specifically the hydroxymethyl-, formyl- and related transferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate:D-alanine 2-hydroxymethyltransferase. This enzyme is also called 2-methylserine hydroxymethyltransferase. This enzyme participates in one ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biochemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate (N5,N10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5,10-CH2-THF) is cofactor in several biochemical reactions. It exists in nature as the diastereoisomer R5,10-methylene-THF. As an intermediate in one-carbon metabolism, 5,10-CH2-THF interconverts to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, 5-formyltetrahydrofolate, and methenyltetrahydrofolate. It is substrate for the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) It is mainly produced by the reaction of tetrahydrofolate with serine, catalyzed by the enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Selected functions Formaldehyde detoxification Methylenetetrahydrofolate is an intermediate in the detoxification of formaldehyde. Pyrimidine biosynthesis It is the one-carbon donor for thymidylate synthase, for methylation of 2-deoxy-uridine-5-monophosphate ( dUMP) to 2-deoxy-thymidine-5-monophosphate (dTMP). The coenzyme is necessary for the biosynthesis of thymidine and is the C1-donor in the reactions catalyzed by TS and thymidyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side chain. Consequently, its IUPAC systematic name is 2-aminopropanoic acid, and it is classified as a nonpolar, aliphatic α-amino acid. Under biological conditions, it exists in its zwitterionic form with its amine group protonated (as −NH3+) and its carboxyl group deprotonated (as −CO2−). It is non-essential to humans as it can be synthesised metabolically and does not need to be present in the diet. It is encoded by all codons starting with GC (GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG). The L-isomer of alanine (left-handed) is the one that is incorporated into proteins. L-alanine is second only to leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-alanine, occurs in pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (chemistry)
Products are the species formed from chemical reactions. During a chemical reaction, reactants are transformed into products after passing through a high energy transition state. This process results in the consumption of the reactants. It can be a spontaneous reaction or mediated by catalysts which lower the energy of the transition state, and by solvents which provide the chemical environment necessary for the reaction to take place. When represented in chemical equations, products are by convention drawn on the right-hand side, even in the case of reversible reactions. The properties of products such as their energies help determine several characteristics of a chemical reaction, such as whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic. Additionally, the properties of a product can make it easier to extract and purify following a chemical reaction, especially if the product has a different state of matter than the reactants. Spontaneous reaction : R \rightarrow P *Where R is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofolate
Tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA), or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative. Metabolism Human synthesis Tetrahydrofolic acid is produced from dihydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase. This reaction is inhibited by methotrexate. It is converted into 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate by serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Bacterial synthesis Many bacteria use dihydropteroate synthetase to produce dihydropteroate, a molecule without function in humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide antibiotics, which compete with the PABA precursor. Functions Tetrahydrofolic acid is a cofactor in many reactions, especially in the synthesis (or anabolism) of amino acids and nucleic acids. In addition, it serves as a carrier molecule for single-carbon moieties, that is, groups containing one carbon atom e.g. methyl, methylene, methenyl, formyl, or formimino. When combined with one such single-carbon moiety as in 10-formyltetrahydrofolate, it acts as a donor of a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transferase
A transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life's most important processes. Transferases are involved in myriad reactions in the cell. Three examples of these reactions are the activity of coenzyme A (CoA) transferase, which transfers thiol esters, the action of N-acetyltransferase, which is part of the pathway that metabolizes tryptophan, and the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), which converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA. Transferases are also utilized during translation. In this case, an amino acid chain is the functional group transferred by a peptidyl transferase. The transfer involves the removal of the growing amino acid chain from the tRNA molecule in the A-site of the ribosome and its subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |