|
Cytorhabdovirus
''Cytorhabdovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family ''Rhabdoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. Plants serve as natural hosts. Structure Cytorhabdovirions are enveloped, with bullet shaped and bacilliform geometries. These virions are about 75 nm wide and 180 nm long. Genome Cytorhabdovirus genomes are linear and around 13 kb in length. Life cycle Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the viral G glycoproteins to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the negative stranded RNA virus replication model. Negative stranded RNA virus transcription, using polymerase stuttering is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by budding, and tubule-guided viral movement. Plants serve as the natural host. The virus is transmitted via a vector (insect aphid, leafhopper, planthopper, and insect). Transmission routes are vectors. Taxonomy The following species are recognized: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mononegavirales
''Mononegavirales'' is an order of negative-strand RNA viruses which have nonsegmented genomes. Some common members of the order are Ebola virus, human respiratory syncytial virus, measles virus, mumps virus, Nipah virus, and rabies virus. All of these viruses cause significant disease in humans. Many other important pathogens of nonhuman animals and plants are also in the group. The order includes eleven virus families: '' Artoviridae'', ''Bornaviridae'', ''Filoviridae'', ''Lispiviridae'', ''Mymonaviridae'', ''Nyamiviridae'', ''Paramyxoviridae'', ''Pneumoviridae'', ''Rhabdoviridae'', '' Sunviridae'', and ''Xinmoviridae''. Use of term The order ''Mononegavirales'' (pronounced: ) According to the rules for taxon naming established by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), the name ''Mononegavirales'' is always to be capitalized, italicized, and never abbreviated. The names of the order's physical members ("mononegaviruses" or "mononegavirads") are to be writte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strawberry Crinkle Cytorhabdovirus
''Strawberry crinkle cytorhabdovirus'', commonly called Strawberry crinkle virus (SCV), is a negative sense single stranded RNA virus that threatens strawberry production worldwide. This virus reduces plant rigidity, runner production, fruit size, and production, while causing distortion and crinkling of the leaves. This virus was first described in 1932 in Oregon and California with commercial strawberry varieties, and later became an issue around the world, including North America, South America, Europe, South Africa, New Zealand, Australia, and Japan. Of the family Rhabdoviridae, it is a large family of viruses that affects plants, vertebrates, and invertebrates. Specifically, this virus infects strawberry plants of the genus ''Fragaria'' and is transmitted through two aphid vectors that feed on strawberries, ''Chaetosiphon fragaefolii'' and '' C. jacobi''. When SCV is combined with other aphid-transmitted strawberry viruses, such as mottle, mild yellow-edge, vein banding, or pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lettuce Necrotic Yellows Cytorhabdovirus
''Lettuce necrotic yellows cytorhabdovirus'' (LNYV) is a plant virus belonging to the virus order ''Mononegavirales'', family ''Rhabdoviridae'' and genus ''Cytorhabdovirus''. It was first identified in Australia in the plant species ''Lactuca sativa'' in 1963 by Stubbs et al. Since then it has been identified in many other plant species including ''Datura stramonium'' and '' Nicotiana glutinosa''. The virus is transmitted by the insect vector '' Hyperomyzus lactucae'' the insect can become infected by feeding on an infected plant. It then acts as a reservoir for the virus A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ... in which it can multiply. The virus is also transmitted congenitally to its progeny References Stubbs, L.L. and Grogan, R.G. (1963). Aust. J. agric. Res. 14: 439 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
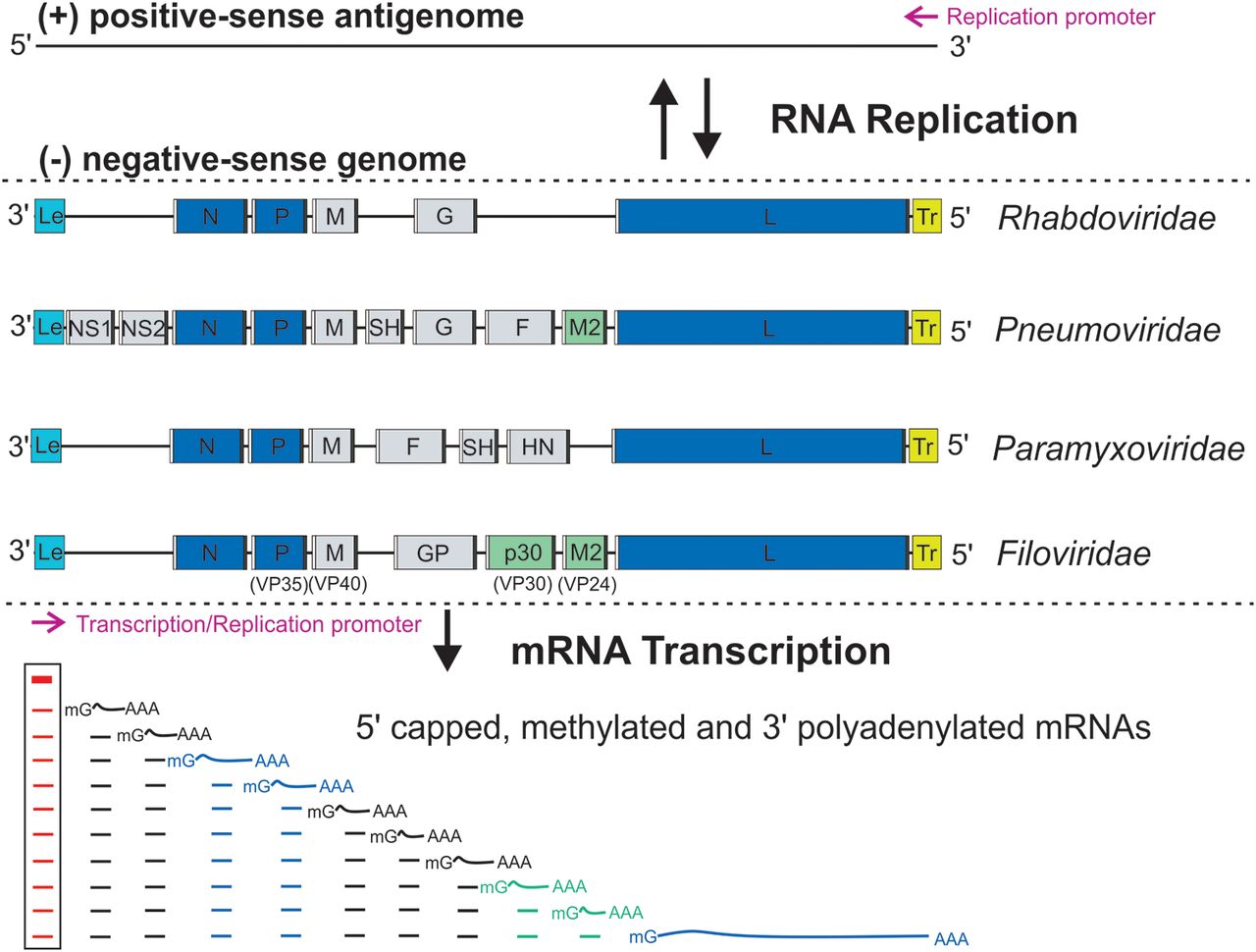
Rhabdoviridae
''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member viruses include rabies encephalitis caused by the rabies virus, and flu-like symptoms in humans caused by vesiculoviruses. The name is derived from Ancient Greek , meaning rod, referring to the shape of the viral particles. The family has 40 genera, most assigned to three subfamilies. Structure The individual virus particles (virions) of rhabdoviruses are composed of RNA, protein, carbohydrate and lipid. They have complex bacilliform or bullet-like shapes. All these viruses have structural similarities and have been classified as a single family. The virions are about 75 nm wide and 180 nm long. Rhabdoviruses are enveloped and have helical nucleocapsids and their genomes are linear, around 11–15 kb in length. Rhabdoviruses c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Cereal Mosaic Cytorhabdovirus
''Northern cereal mosaic cytorhabdovirus'' (NCMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Rhabdoviridae ''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member virus ...''. External linksICTVdB - The Universal Virus Database: Northern cereal mosaic virus Viral plant pathogens and diseases Cytorhabdoviruses {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley Yellow Striate Mosaic Cytorhabdovirus
''Barley yellow striate mosaic cytorhabdovirus'' (BYSMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Rhabdoviridae ''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member virus ...''. External linksICTVdB - The Universal Virus Database: Barley yellow striate mosaic virus Cytorhabdoviruses Viral plant pathogens and diseases {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broccoli Necrotic Yellows Cytorhabdovirus
''Broccoli necrotic yellows cytorhabdovirus'' (BNYV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Rhabdoviridae ''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member virus ...''. External linksICTVdB - The Universal Virus Database: Broccoli necrotic yellows virus Cytorhabdoviruses Viral plant pathogens and diseases {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strawberry Cytorhabdovirus 1
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus ''Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely appreciated for its characteristic aroma, bright red color, juicy texture, and sweetness. It is consumed in large quantities, either fresh or in such prepared foods as jam, juice, pies, ice cream, milkshakes, and chocolates. Artificial strawberry flavorings and aromas are also widely used in products such as candy, soap, lip gloss, perfume, and many others. The garden strawberry was first bred in Brittany, France, in the 1750s via a cross of ''Fragaria virginiana'' from eastern North America and ''Fragaria chiloensis'', which was brought from Chile by Amédée-François Frézier in 1714. Cultivars of ''Fragaria'' × ''ananassa'' have replaced, in commercial production, the woodland strawberry (''Fragaria vesca''), which was the first strawber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomato Yellow Mottle-associated Cytorhabdovirus
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , from which the English word ''tomato'' derived. Its domestication and use as a cultivated food may have originated with the indigenous peoples of Mexico. The Aztecs used tomatoes in their cooking at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and after the Spanish encountered the tomato for the first time after their contact with the Aztecs, they brought the plant to Europe, in a widespread transfer of plants known as the Columbian exchange. From there, the tomato was introduced to other parts of the European-colonized world during the 16th century. Tomatoes are a significant source of umami flavor. They are consumed in diverse ways: raw or cooked, and in many dishes, sauces, salads, and drinks. While tomatoes are fruits—bota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichosanthes Cytorhabdovirus
''Trichosanthes'' is a genus of tropical and subtropical vines. They belong to the cucumber family ( Cucurbitaceae), and are closely related to '' Gymnopetalum''. ''Hodgsonia'', formerly included here, is usually considered a well-distinct genus nowadays. The shoots, tendrils, and leaves of some or possibly all species may be eaten as greens, and at least two species (serpent gourd, ''T. cucumerina'', and pointed gourd, ''T. dioica'') are grown commercially for their fleshy fruits used as vegetables, most popular in South Asia and Southeast Asia. At least two species ('' T. kirilowii'' and '' T. rosthornii'') are grown for use in traditional Chinese medicine, where they are called the name ''gualou'' (). ''Trichosanthes'' is also known as a medicinal as well as poisonous plant in India. The herb has shown an ability to reduce chest congestion by breaking down phlegm and aiding in its removal from the lungs. Selected species * ''Trichosanthes baviensis'' Gagnepain * ''Trichosanth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifolium Pratense Cytorhabdovirus A
Clover or trefoil are common names for plants of the genus ''Trifolium'' (from Latin ''tres'' 'three' + ''folium'' 'leaf'), consisting of about 300 species of flowering plants in the legume or pea family Fabaceae originating in Europe. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution with highest diversity in the temperate Northern Hemisphere, but many species also occur in South America and Africa, including at high altitudes on mountains in the tropics. They are small annual, biennial, or short-lived perennial herbaceous plants, typically growing up to 30 cm tall. The leaves are trifoliate (rarely quatrefoiled; see four-leaf clover), monofoil, bifoil, cinquefoil, hexafoil, septfoil, etcetera, with stipules adnate to the leaf-stalk, and heads or dense spikes of small red, purple, white, or yellow flowers; the small, few-seeded pods are enclosed in the calyx. Other closely related genera often called clovers include ''Melilotus'' (sweet clover) and ''Medicago'' (alfalfa or Calvary clove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |