|
Cynfarch
Cynfarch Oer ('Cynfarch the Dismal', also known as Cunomarcus or Cynfarch ap Meirchion) was probably a 6th-century king of the Sub-Roman realm of Rheged, believed to be located in north-west England and south-west Scotland. Next to nothing is known about Cynfarch. He appears in the Old Welsh pedigrees of the Brythonic ' Men of the North' as the son of the equally obscure Meirchion Gul (Marcianus ''the Lean'') and father of the better documented Urien Rheged. The epithet An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, di ... "Oer" is literally translated as 'cold', but may be understood in unflattering terms as 'Cynfarch the unwelcoming'. Cynfach was however, well remembered by his own descendents who were referred to as the 'Cynferchyn' in his honour. References {{DEFAULTSORT: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
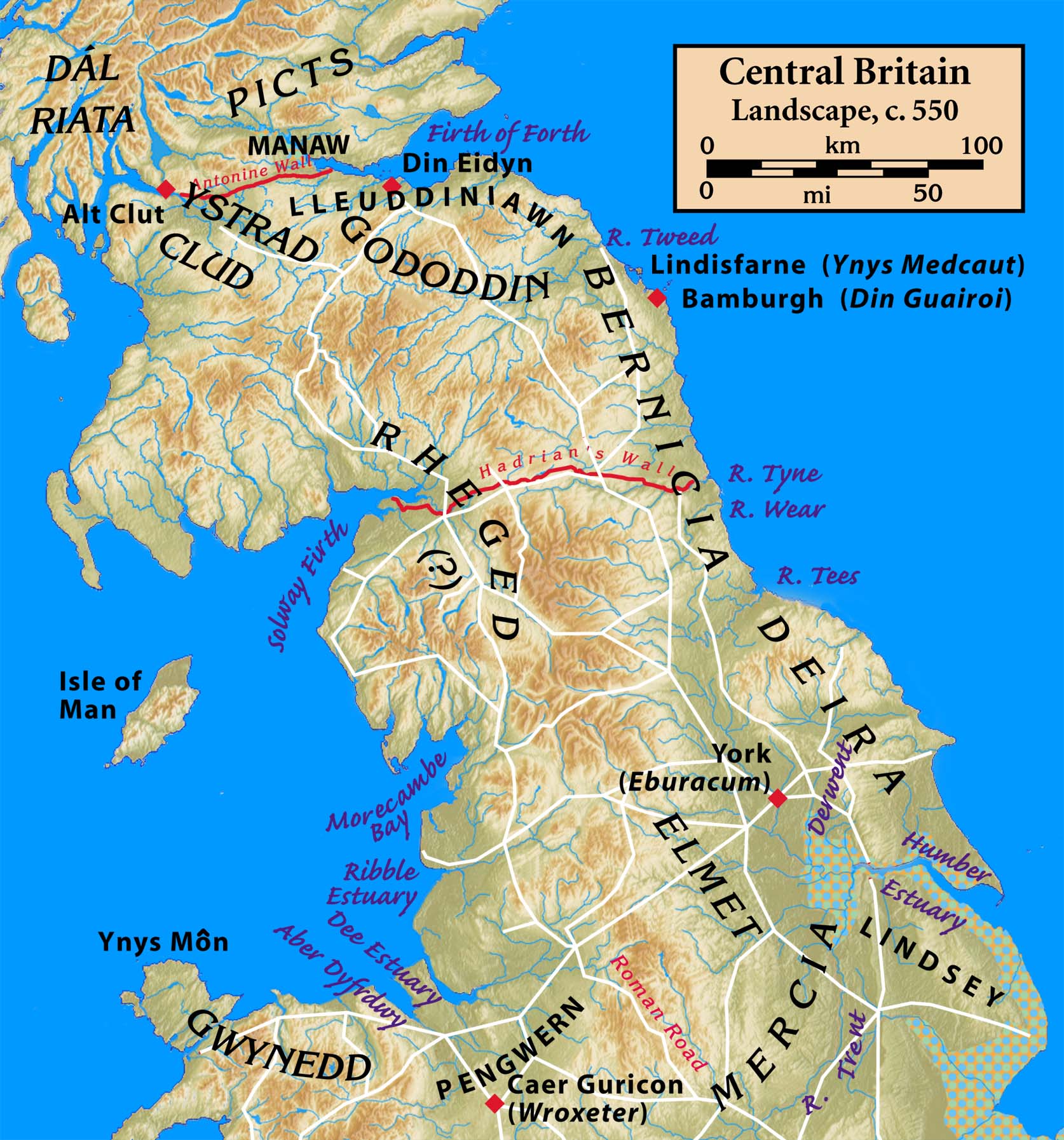
Rheged
Rheged () was one of the kingdoms of the ''Hen Ogledd'' ("Old North"), the Brittonic-speaking region of what is now Northern England and southern Scotland, during the post-Roman era and Early Middle Ages. It is recorded in several poetic and bardic sources, although its borders are not described in any of them. A recent archaeological discovery suggests that its stronghold was located in what is now Galloway in Scotland rather than, as was previously speculated, being in Cumbria. Rheged possibly extended into Lancashire and other parts of northern England. In some sources, Rheged is intimately associated with the king Urien Rheged and his family. Its inhabitants spoke Cumbric, a Brittonic dialect closely related to Old Welsh. Etymology The origin of the name ''Rheged'' has been described as "problematic". One Brittonic-language solution is that the name may be a compound of ''rö-'', a prefix meaning "great", and ''cę:d'' meaning "wood, forest" (c.f. Welsh ''coed'') although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meirchion Gul
{{more citations needed, date=September 2018Meirchion Gul was probably a late 5th-century king of Rheged, a Brythonic realm in the area of Sub-Roman Britain known as the ''Hen Ogledd'' (in the North of England and Southern Scotland today). Next to nothing is known about Meirchion, although his epithet means ''the Lean''. He appears in the Middle Welsh genealogical text ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' as the son of the equally obscure Gwrwst Lledlwm, a grandson of Coel Hen, and grandfather of renowned Urien Rheged. He is assumed, like Urien, to have ruled Rheged, including Catterick. His two sons appear at the head of two later dynasties. Cynfarch Oer was Urien's father. Another son, Elidyr Lydanwyn (''the Stout and Handsome''), was the ruler of Rheged, according to the Gwynedd version of Hywel Dda's 'Welsh laws'. He was the father of Llywarch Hen Llywarch Hen (, "Llywarch the Old"; c. 534 – c. 608), was a prince and poet of the Brythonic kingdom of Rheged, a ruling family in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urien Rheged
Urien (; ), often referred to as Urien Rheged or Uriens, was a late 6th-century king of Rheged, an early British kingdom of the Hen Ogledd (today's northern England and southern Scotland) of the House of Rheged. His power and his victories, including the battles of Gwen Ystrad and Alt Clut Ford, are celebrated in the praise poems to him by Taliesin, preserved in the ''Book of Taliesin''. In Arthurian legend, he inspired the character of King Urien of either Garlot (Garloth) or Gore (Gorre). His most famous son Owain mab Urien similarly turned into the character of Ywain. Life According to the genealogies, Urien was the son of Cynfarch Oer, son of Meirchion Gul, son of Gorwst, son of Cenau, son of Coel Hen (King Cole), the first recorded post-Roman military leader in the area of Hadrian's Wall. He fought against the rulers of the Anglian kingdom of Bernicia (modern Northumbria). An Anglian noble, Ida, had occupied Metcauld around the middle of the 6th century and begun to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain is the period of late antiquity in Great Britain between the end of Roman rule and the Anglo-Saxon settlement. The term was originally used to describe archaeological remains found in 5th- and 6th-century AD sites that hinted at the decay of locally made wares from a previous higher standard under the Roman Empire. It is now used to describe the period that commenced with the evacuation of Roman troops to Gaul by Constantine III in 407 and to have concluded with the Battle of Deorham in 577. Meaning of terms The period of sub-Roman Britain traditionally covers the history of the area which subsequently became England from the end of Roman imperial rule, traditionally dated to be in 410, to the arrival of Saint Augustine in 597. The date taken for the end of this period is arbitrary in that the sub-Roman culture continued in northern England until the merger of Rheged (the kingdom of the Brigantes) with Northumbria by dynastic marriage in 633, and longer i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Welsh Language
Old Welsh ( cy, Hen Gymraeg) is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, has been called "Primitive"Koch, p. 1757. or "Archaic Welsh". Texts The oldest surviving text entirely in Old Welsh is understood to be that on a gravestone now in Tywyn – the Cadfan Stone – thought to date from the 7th century, although more recent scholarship dates it in the 9th century. A key body of Old Welsh text also survives in glosses and marginalia from around 900 in the Juvencus Manuscript and in . Some examples of medieval Welsh poems and prose additionally originate from this period, but are found in later manuscripts; ''Y Gododdin,'' for example, is preserved in Middle Welsh. A text in Latin and Old Welsh in the ''Lichfield Gospels'' called the "Surrexit Memorandum" is thought to have been written in the early 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brython
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, Cornish and Bretons (among others). They spoke the Common Brittonic language, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages. The earliest written evidence for the Britons is from Greco-Roman writers and dates to the Iron Age.Koch, pp. 291–292. Celtic Britain was made up of many tribes and kingdoms, associated with various hillforts. The Britons followed an Ancient Celtic religion overseen by druids. Some of the southern tribes had strong links with mainland Europe, especially Gaul and Belgica, and minted their own coins. The Roman Empire conquered most of Britain in the 1st century, creating the province of Britannia. The Romans invaded northern Britain, but the Britons and Caledonians in the north remai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hen Ogledd
Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the historical region which is now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages. Its population spoke a variety of the Brittonic language known as Cumbric which is closely related to, if not a dialect of Old Welsh. The people of Wales and the Hen Ogledd considered themselves to be one people, and both were referred to as Cymry ('fellow-countrymen') from the Brittonic word ''combrogi.'' The Hen Ogledd was distinct from the parts of North Britain inhabited by the Picts, Anglo-Saxons, and Scoti. The major kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd were Elmet, Gododdin, Rheged, and the Kingdom of Strathclyde. Smaller kingdoms included Aeron and Calchfynydd. Eidyn, Lleuddiniawn, and Manaw Gododdin were evidently parts of Gododdin. The Angle kingdoms of Deira and Bernicia both had Brittonic-derived names, suggesting they may have been Brittonic kingdoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithet
An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, divinities, objects, and binomial nomenclature. It can also be a descriptive title: for example, Pallas Athena, Phoebus Apollo, Alfred the Great, Suleiman the Magnificent, and Władysław I the Elbow-high. Many English monarchs have traditional epithets: some of the best known are Edward the Confessor, William the Conqueror, Richard the Lionheart, Æthelred the Unready, John Lackland and Bloody Mary. The word ''epithet'' can also refer to an abusive, defamatory, or derogatory phrase. This use as a euphemism is criticized by Martin Manser and other proponents of linguistic prescription. H. W. Fowler complained that "epithet is suffering a vulgarization that is giving it an abusive imputation." Linguistics Epithets are sometimes at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchs Of Rheged
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually a monarch either personally inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the crown'') or is selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may proclaim themself monarch, which may be backed and legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisite adult age to rule. Monarchs' actual powers vary from one monarchy to another and in different eras; on one extreme, they may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century English Monarchs
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |