|
Current Injection Technique
The current injection technique is a technique developed to reduce the turn-OFF switching transient of power bipolar semiconductor devices. It was developed and published by Dr S. Eio of Staffordshire University (United Kingdom) in 2007. Background The Turn-OFF switching transient of silicon-based power bipolar semiconductor devices, caused by stored charge in the device during the forward conduction state, limits switching speed of the device, which in turn limits the efficiency of the application it is used within. Different techniques, such as carrier lifetime control, injection efficiency and buffer layer devices, have been used to minimize turn-OFF switching transient, but all result in a trade-off between the ON-state loss and switching speed. Details of the Technique The current injection technique examined in Dr Eio's publications optimize the switching transient of power diodes, thyristors and insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) without the need of changing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staffordshire University
, mottoeng = Dare to know , type = Public , endowment = £70 million (2015) , administrative_staff = 1,375 , chancellor = Francis Fitzherbert, 15th Baron Stafford , vice_chancellor = Professor Martin Jones , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Staffordshire (Stafford; Stoke-on-Trent; Lichfield; London , state = Shropshire (Shrewsbury) , country = England, United Kingdom , campus = Urban and rural , colours=Red and white , website = , affiliations = Staffordshire University is a public research university in Staffordshire, England. It has one main campus based in the city of Stoke-on-Trent and four other campuses; in Stafford, Lichfield, Shrewsbury and London. History In 1901, industrialist Alfred Bolton acquired a site on what is now College Road and in 1906 mining classes began there. In 1907, pottery classes followed, being transferred from Tunsta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. Among many uses, diodes are found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily used as an electronic switch, which, as it was developed, came to combine high efficiency and fast switching. It consists of four alternating layers (P–N–P–N) that are controlled by a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) Metal gate, gate structure. Although the structure of the IGBT is topologically the same as a thyristor with a "MOS" gate (MOS-controlled thyristor, MOS-gate thyristor), the thyristor action is completely suppressed, and only the transistor action is permitted in the entire device operation range. It is used in switching power supply, switching power supplies in high-power applications: variable-frequency drives (VFDs), electric cars, trains, variable-speed refrigerators, lamp ballasts, arc-welding machines, induction hobs, and air conditioners. Since it is designed to turn on and off rapidly, the IGBT can synthesize complex waveforms with pulse-width modulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or holes. In an electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in plasma, an ionized gas, they are ions and electrons. The SI unit of electric current is the ampere, or ''amp'', which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. The ampere (symbol: A) is an SI base unit. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter. Electric currents create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, generators, inductors, and transformers. In ordinary con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristors
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily used as an electronic switch, which, as it was developed, came to combine high efficiency and fast switching. It consists of four alternating layers (P–N–P–N) that are controlled by a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) Metal gate, gate structure. Although the structure of the IGBT is topologically the same as a thyristor with a "MOS" gate (MOS-controlled thyristor, MOS-gate thyristor), the thyristor action is completely suppressed, and only the transistor action is permitted in the entire device operation range. It is used in switching power supply, switching power supplies in high-power applications: variable-frequency drives (VFDs), electric cars, trains, variable-speed refrigerators, lamp ballasts, arc-welding machines, induction hobs, and air conditioners. Since it is designed to turn on and off rapidly, the IGBT can synthesize complex waveforms with pulse-width modulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
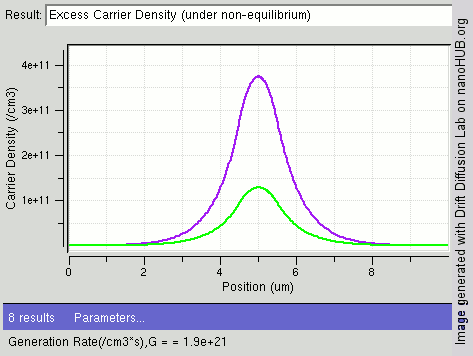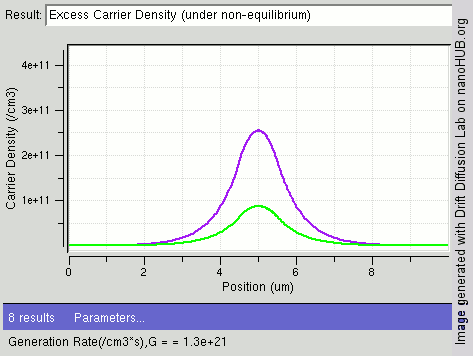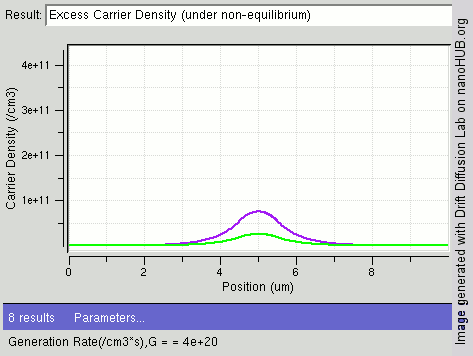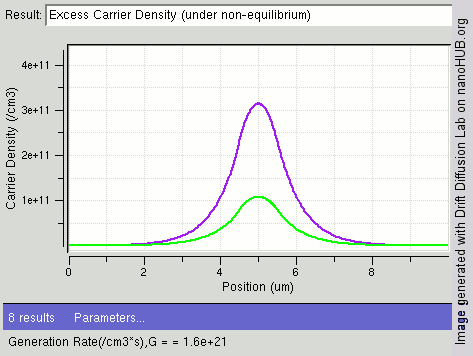
Carrier Generation And Recombination
In the solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as photodiodes, light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. They are also critical to a full analysis of p-n junction devices such as bipolar junction transistors and p-n junction diodes. The electron–hole pair is the fundamental unit of generation and recombination in inorganic semiconductors, corresponding to an electron transitioning between the valence band and the conduction band where generation of electron is a transition from the valence band to the conduction band and recombination leads to a reverse transition. Overview Like other solids, semiconductor materials have an electronic band structure determined by the crystal properties of the material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Device Under Test
A device under test (DUT), also known as equipment under test (EUT) and unit under test (UUT), is a manufactured product undergoing testing, either at first manufacture or later during its life cycle as part of ongoing functional testing and calibration checks. This can include a test after repair to establish that the product is performing in accordance with the original product specification. Electronics testing In the electronics industry a DUT is any electronic assembly under test. For example, cell phones coming off of an assembly line may be given a final test in the same way as the individual chips were earlier tested. Each cell phone under test is, briefly, the DUT. For circuit boards, the DUT is often connected to the test equipment using a bed of nails tester of pogo pins. Semiconductor testing In semiconductor testing, the device under test is a die on a wafer or the resulting packaged part. A connection system is used, connecting the part to automatic or manual test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |