|
Cryptocaryon Irritans
''Cryptocaryon irritans'' is a species of ciliates that parasitizes marine fish, causing marine white spot disease or marine ich (pronounced ''ick''). It is one of the most common causes of disease in marine aquaria. Taxonomy ''Cryptocaryon irritans'' was originally classified as ''Ichthyophthirius marinus'', but it is not closely related to the other species. It belongs to the class Prostomatea, but beyond that its placement is still uncertain. Clinical The symptoms and life-cycle are generally similar to those of '' Ichthyophthirius'' in freshwater fish, including white spots, on account of which ''Cryptocaryon'' is usually called marine ich. However, ''Cryptocaryon'' can spend a much longer time encysted. Fish that are infected with Cryptocaryon may have small white spots, nodules, or patches on their skin, fins, or gills. They may also have ragged fins, cloudy eyes, pale gills, increased mucus production, or changes in skin color, and they may appear thin. Behaviorally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebrasoma Flavescens
The yellow tang (''Zebrasoma flavescens'') is a saltwater fish species of the family Acanthuridae. It is one of the most popular marine aquarium fish. It is bright yellow in color, and it lives in reefs. The yellow tang spawn around a full moon. The yellow tang eats algae. The yellow tang has a white barb, located just before the tail fin, to protect itself. Taxonomy and etymology The yellow tang was first described by English naturalist Edward Turner Bennett as ''Acanthurus flavescens'' in 1828 from a collection in the Hawaiian Islands. ''Zebrasoma'' refers to the body and the zebra-like stripes or bars on the body of other fish in the genus. Its species name is the Latin adjective ''flavescens'' which refers to the tang's yellow color. Yellow tangs are in the surgeonfish family. Evolution and genetics Based on the gene Cytochrome C-oxidase 1 (CO1), a group of researchers was able to reconstruct the phylogenetic tree of the genus ''Zebrasoma'' with mitochondrial barcodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formalin
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below), hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin), which is also used to store animal specimens. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid. Formaldehyde is an important precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 1996, the installed capacity for the production of formaldehyde was estimated at 8.7 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that it adopts several diverse forms. These compounds can often be used interchangeably and can be interconverted. *Molecular formaldeh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
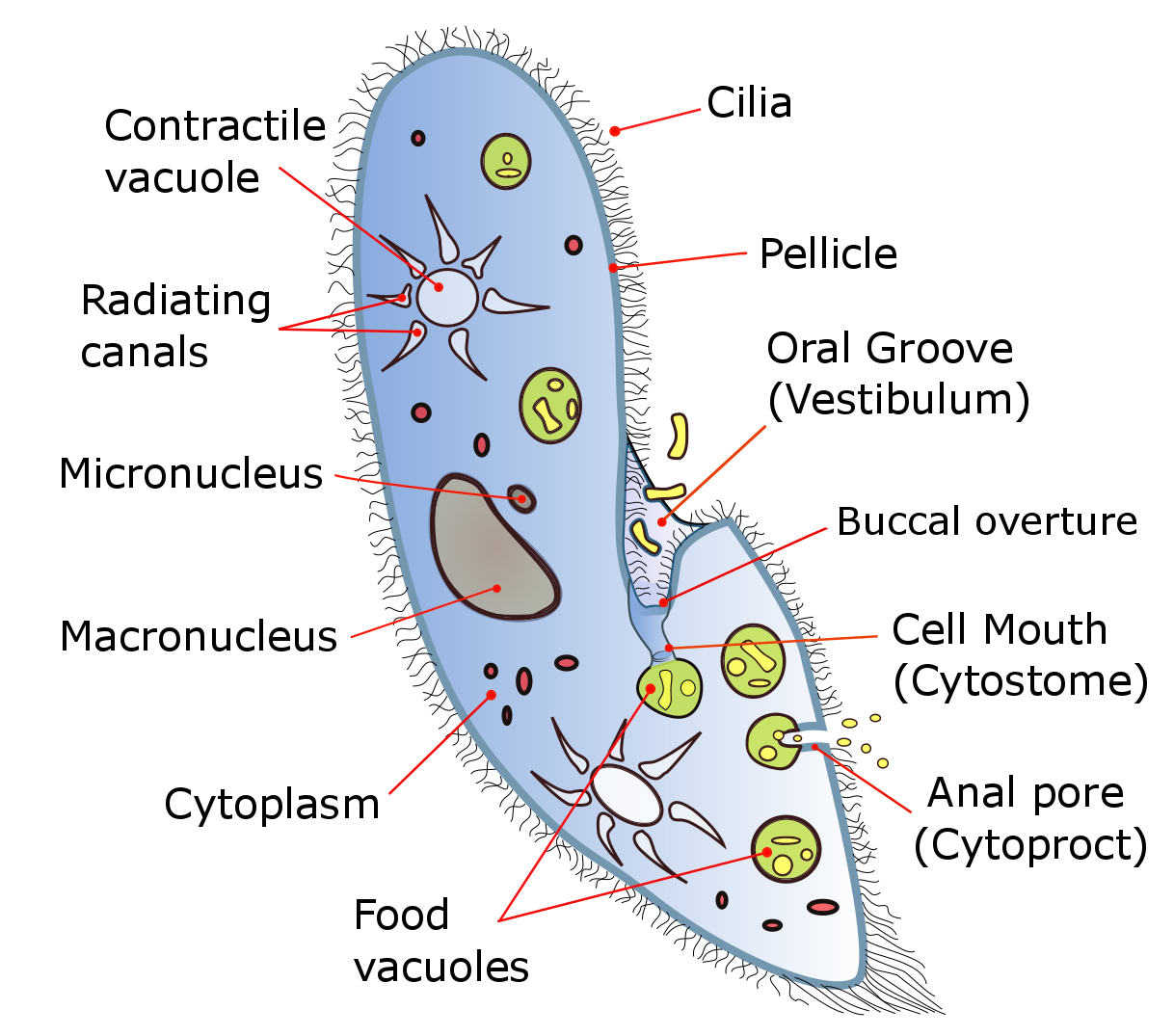
Ciliate Genera
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some obligate and opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species range in size from as little as 10 µm in some colpodeans to as much as 4 mm in length in some gel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramacronucleata
Intramacronucleata is a subphylum of ciliates. The group is characterized by the manner in which division of the macronucleus is accomplished during binary fission of the cell. In ciliates of this subphylum, division of the macronucleus is achieved by the action of microtubules which are assembled ''inside'' the macronucleus itself. This is in contrast to heterotrich The heterotrichs are a class of ciliates. They typically have a prominent adoral zone of membranelles circling the mouth, used in locomotion and feeding, and shorter cilia on the rest of the body. Many species are highly contractile, and are ... ciliates of the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora, in which division of the macronucleus relies on microtubules formed ''outside'' the macronuclear envelope. References * * External links * Ciliate taxonomy Bikont subphyla {{Ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Ich
''Ichthyophthirius multifiliis'', often termed "Ich", is a parasitic ciliate described by the French parasitologist Fouquet in 1876. Only one species is found in the genus which also gave name to the family. The name literally translates as "the fish louse with many children". The parasite can infect most freshwater fish species and, in contrast to many other parasites, shows very low host specificity. It penetrates gill epithelia, skin and fins of the fish host and resides as a feeding stage (the trophont) inside the epidermis. It is visible as a white spot on the surface of the fish but, due to its internal microhabitat, it is a true endoparasite and not an ectoparasite. It causes a disease commonly referred to as white spot disease due to the macroscopically visible trophonts (up to 1 mm in diameter) in the skin and fins. The trophont, continuously rotating, is surrounded by host cells (epidermal cells and leukocytes), producing a minute elevation of the skin. These ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cell (biology), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a Fabaceae, bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) Rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies nutrient, food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomont
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is typified by a ''cellular variety'' with a distinct morphology and biochemistry. Not all apicomplexa develop all the following cellular varieties and division methods. This presentation is intended as an outline of a hypothetical generalised apicomplexan organism. Methods of asexual replication Apicomplexans (sporozoans) replicate via ways of multiple fission (also known as schizogony). These ways include , and , although the latter is sometimes referred to as schizogony, despite its general meaning. Merogony is an asexually reproductive process of apicomplexa. After infecting a host cell, a trophozoite ( see glossary below) increases in size while repeatedly replicating its nucleus and other organelles. During this process, the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have been exposed to a communicable disease, yet do not have a confirmed medical diagnosis. It is distinct from medical isolation, in which those confirmed to be infected with a communicable disease are isolated from the healthy population. Quarantine considerations are often one aspect of border control. The concept of quarantine has been known since biblical times, and is known to have been practised through history in various places. Notable quarantines in modern history include the village of Eyam in 1665 during the bubonic plague outbreak in England; East Samoa during the 1918 flu pandemic; the Diphtheria outbreak during the 1925 serum run to Nome, the 1972 Yugoslav smallpox outbreak, the SARS pandemic, the Ebola pandemic and extensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroquine
Chloroquine is a medication primarily used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to its effects. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. Chloroquine is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus. While it has not been formally studied in pregnancy, it appears safe. It was studied to treat COVID-19 early in the pandemic, but these studies were largely halted in the summer of 2020, and is not recommended for this purpose. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash. Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures, and low blood cell levels. Chloroquine is a member of the drug class 4-aminoquinoline. As an antimalarial, it works against the asexual form of the malaria parasite in the stage of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
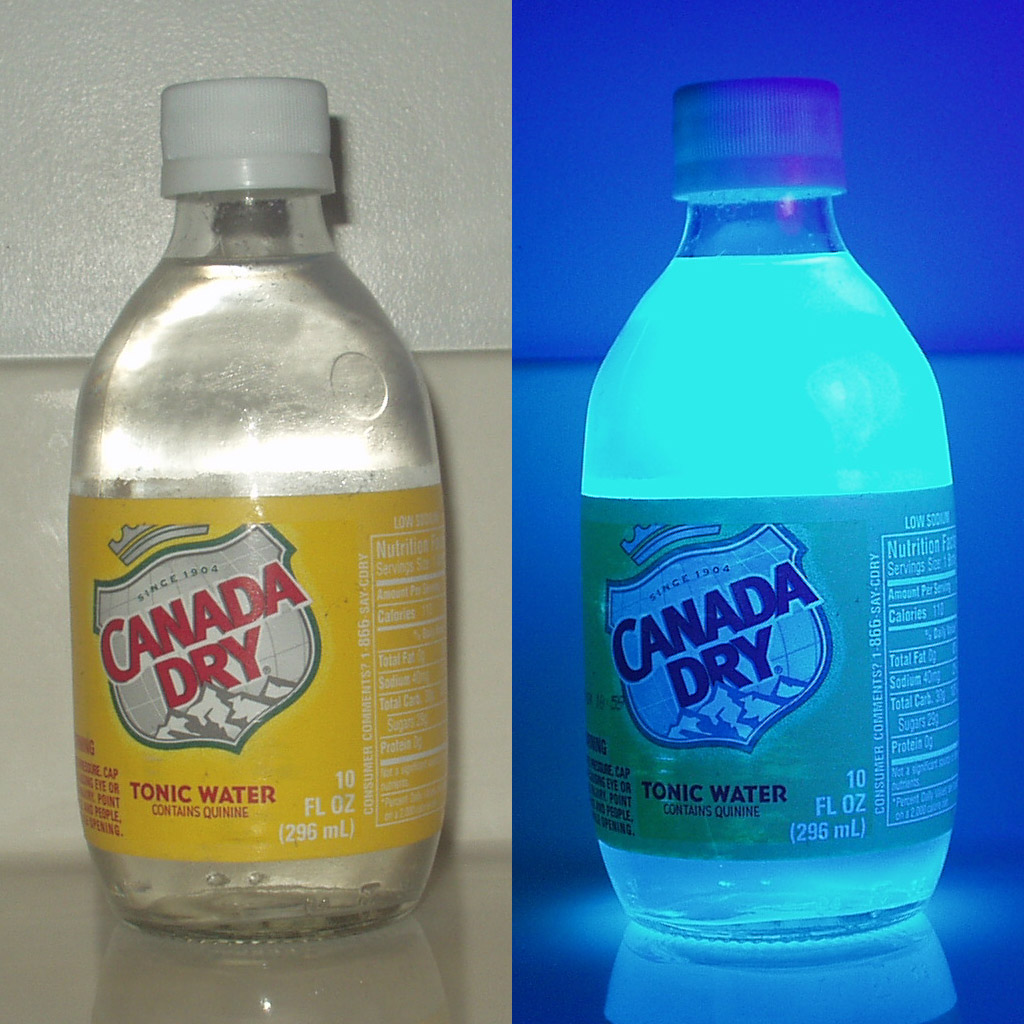
Quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cramps, quinine is not recommended for this purpose due to the risk of serious side effects. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Malaria resistance to quinine occurs in certain areas of the world. Quinine is also used as an ingredient in tonic water to impart a bitter taste. Common side effects include headache, ringing in the ears, vision issues, and sweating. More severe side effects include deafness, low blood platelets, and an irregular heartbeat. Use can make one more prone to sunburn. While it is unclear if use during pregnancy causes harm to the baby, treating malaria during pregnancy with quinine when appropriate is still recommended. Quinine is an alkaloid, a naturally occurring chemical compound. How it works as a medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



