|
Contemporary Jewish Religious Music
For the purposes of this article, “contemporary” refers to the period from 1967 ( Israel's Six-Day War) to the present day, “Jewish” refers to the various streams and traits of Judaism practiced. Many Orthodox Jews use the term “religious” to refer to a strict adherence to Jewish law. For the purposes of this article, “religious” refers to the content and context of the music itself: liturgical or implicit references to the divine. Jewish ethnomusicologist Mark Kligman notes, “The scope of contemporary Jewish music encompasses a wide range of genres and styles, including music for the synagogue, folk and popular music on religious themes, Yiddish songs, klezmer music, Israeli music, and art music by serious composers. Every sector of the Jewish community – from the most right-wing Orthodox to the most secular – participates in the Jewish music endeavor, creating, performing, and listening to the particular music that meets its taste and needs.”Kligman. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
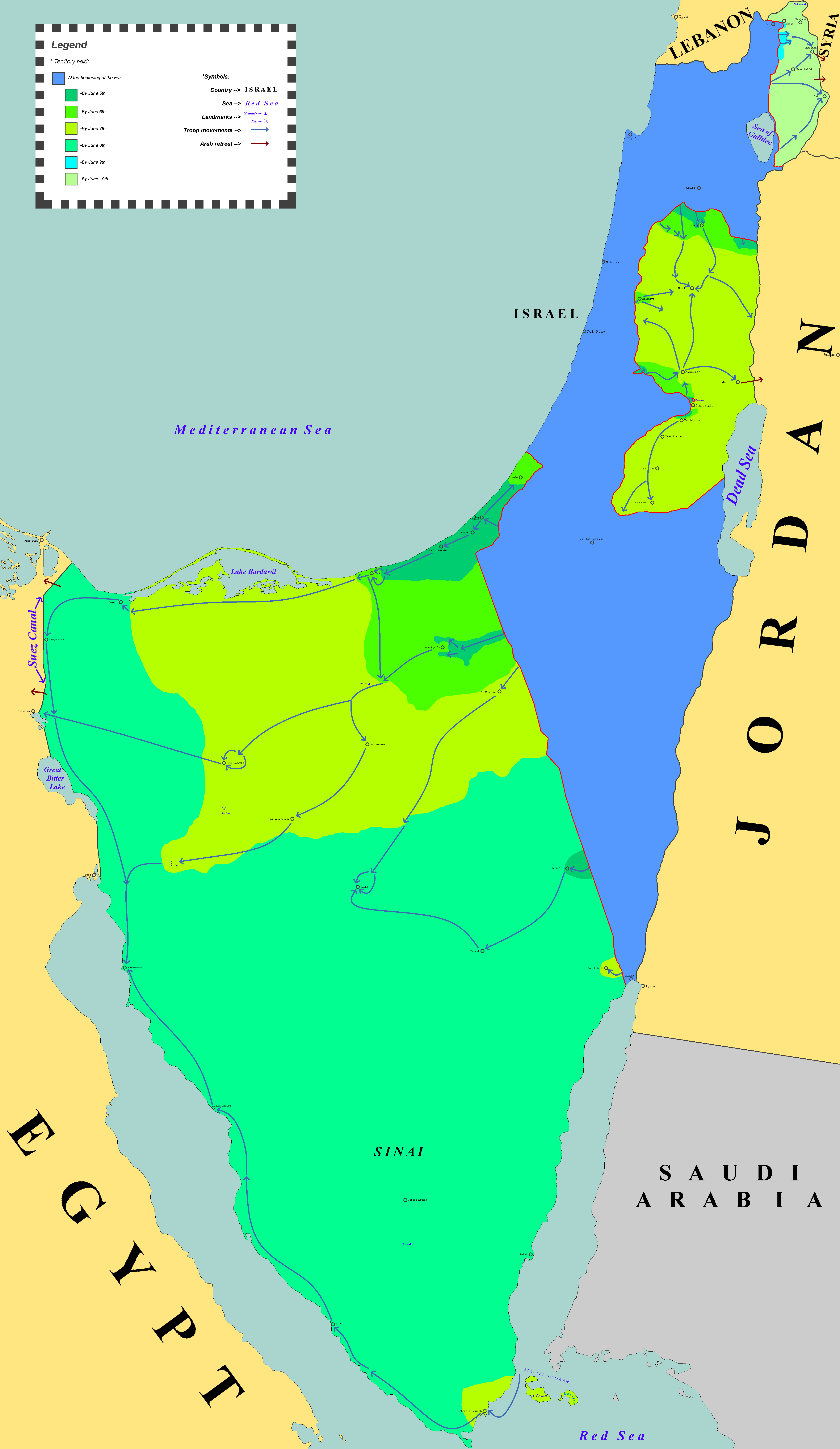
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sephardi Hebrew Pronunciation
Sephardi Hebrew (or Sepharadi Hebrew; he, עברית ספרדית, Ivrit S'faradít, lad, Hebreo Sefardíes) is the pronunciation system for Biblical Hebrew favored for liturgical use by Sephardi Jewish practice. Its phonology was influenced by contact languages such as Spanish, Judaeo-Spanish (Ladino), Arabic, Portuguese and Modern Greek. Phonology There is some variation between the various forms of Sephardi Hebrew, but the following generalisations may be made: *The stress tends to fall on the last syllable wherever that is the case in Biblical Hebrew. *The letter ע (`ayin) is realized as a sound, but the specific sound varies between communities. One pronunciation associated with the Hebrew of Western Sephardim (Spanish and Portuguese Jews of Northern Europe and their descendants) is a velar nasal () sound, as in English ''singing'', but other Sephardim of the Balkans, Anatolia, North Africa, and the Levant maintain the pharyngeal sound of Yemenite Hebrew or Arabic of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David's Tomb
, alternate_name= Makam Nabi Daoud; Cenacle , image = Jerusalem Tomb of David BW 1.JPG , alt= , caption= , map_type = Old Jerusalem , map_alt = , map_caption = Shown () within Jerusalem , map_size= , location = Jerusalem , region= , coordinates = , type= , part_of= , length= , width= , area= , height= , builder= , material= , built= , abandoned= , epochs = Late Roman, Byzantine, Crusader, Mamluk, Ottoman, Israel , cultures= , dependency_of= , occupants= , excavations= , archaeologists= Jacob Pinkerfeld , condition= , ownership= , public_access = yes , website= , notes= David's Tomb ( he, קבר דוד המלך ''Kever David Ha-Melekh'') is a site that, according to an early-medieval (9th-century) tradition, is associated with the burial of the biblical King David. Historians, archaeologists and Jewish religious authorities do not consider the site to be the actual resting place of King David. It occupies the ground floor of a former church, whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Forward
''The Forward'' ( yi, פֿאָרווערטס, Forverts), formerly known as ''The Jewish Daily Forward'', is an American news media organization for a Jewish American audience. Founded in 1897 as a Yiddish-language daily socialist newspaper, ''The New York Times'' reported that Seth Lipsky "started an English-language offshoot of the Yiddish-language newspaper" as a weekly newspaper in 1990. In the 21st century ''The Forward'' is a digital publication with online reporting. In 2016, the publication of the Yiddish version changed its print format from a biweekly newspaper to a monthly magazine; the English weekly paper followed suit in 2017. Those magazines were published until 2019. ''The Forward''s perspective on world and national news and its reporting on the Jewish perspective on modern United States have made it one of the most influential American Jewish publications. It is published by an independent nonprofit association. It has a politically progressive editorial fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lonely Planet
Lonely Planet is a travel guide book publisher. Founded in Australia in 1973, the company has printed over 150 million books. History Early years Lonely Planet was founded by married couple Maureen and Tony Wheeler. In 1972, they embarked on an overland trip through Europe and Asia to Australia, following the route of the Oxford and Cambridge Far Eastern Expedition. The company name originates from the misheard "lovely planet" in a song written by Matthew Moore. Lonely Planet's first book, ''Across Asia on the Cheap'', had 94 pages; it was written by the couple in their home. The original 1973 print run consisted of stapled booklets with pale blue cardboard covers. Tony returned to Asia to write ''Across Asia on the Cheap: A Complete Guide to Making the Overland Trip'', published in 1975. Expansion The Lonely Planet guide book series initially expanded to cover other countries in Asia, with the India guide book in 1981, and expanded to rest of the world later on. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluegrass Music
Bluegrass music is a genre of American roots music The term American folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as ''traditional music'', ''traditional folk music'', ''contemporary folk music'', ''vernacular music,'' or ''roots music''. Many traditional songs have been sung ... that developed in the 1940s in the Appalachian region of the United States. The genre derives its name from the band Bill Monroe, Bill Monroe and the Blue Grass Boys. Like Country music, mainstream country music, it largely developed out of Old-time music, old-time string music, though in contrast, bluegrass is traditionally played exclusively on Acoustic music, acoustic instruments and also has roots in traditional English, Scottish, and Irish Ballads, Irish ballads and dance tunes as well as in blues and jazz. Bluegrass was further developed by musicians who played with Monroe, including 5-string banjo player Earl Scruggs and guitarist Lester Flatt. Monroe characterized the genr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Music
Rock music is a broad genre of popular music that originated as " rock and roll" in the United States in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of different styles in the mid-1960s and later, particularly in the United States and United Kingdom.W. E. Studwell and D. F. Lonergan, ''The Classic Rock and Roll Reader: Rock Music from its Beginnings to the mid-1970s'' (Abingdon: Routledge, 1999), p.xi It has its roots in 1940s and 1950s rock and roll, a style that drew directly from the blues and rhythm and blues genres of African-American music and from country music. Rock also drew strongly from a number of other genres such as electric blues and folk, and incorporated influences from jazz, classical, and other musical styles. For instrumentation, rock has centered on the electric guitar, usually as part of a rock group with electric bass guitar, drums, and one or more singers. Usually, rock is song-based music with a time signature using a verse–chorus form, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Wexler
Adam Wexler is an American-Israeli musician, best known as the bassist for influential Jewish rock groups Diaspora Yeshiva Band and Reva L'Sheva. Biography Wexler grew up in Minneapolis, Minnesota and started playing at age five. He is a cousin of singer-songwriter Peter Himmelman. In 1975, Wexler became one of the founding members of the Diaspora Yeshiva Band, along with Avraham Rosenblum, Ben Zion Solomon, Simcha Abramson, Ruby Harris, and Gedalia Goldstein. The group, which played rock and bluegrass with Jewish lyrics, was highly influential in Jewish music and released six albums before disbanding in 1983. Wexler was an associate of Rabbi Shlomo Carlebach, performing on several albums in the 1980s and early 1990s. Shortly after Carlebach's death in 1994, Wexler and fellow Carlebach devotee Yehuda Katz co-formed the band Reva L'Sheva. Combining a Carlebach influence with a jam band rock sound, the band was a forebearer of the post-Carlebach Jewish rock scene, preceding band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Zion Solomon
Ben Zion Solomon is an American-born Israeli musician, best known as a founding member of the seminal Jewish rock group Diaspora Yeshiva Band, for whom he played fiddle and banjo from 1975 to 1983. A disciple of Shlomo Carlebach, Solomon and his family were among the first residents of Carlebach's moshav, Mevo Modi'im. His sons later founded the bands Moshav, Soulfarm, and Hamakor. Background Solomon graduated from Berklee College of Music, where he studied music history. While living in San Francisco's Haight-Ashbury neighborhood in the early 1970s, Solomon attended gatherings at The House of Love and Prayer. There, he met the shul's founder, Rabbbi Shlomo Carlebach, who convinced him to move to Israel. Career Diaspora Yeshiva Band Solomon attended the Diaspora Yeshiva and co-founded the Diaspora Yeshiva Band in 1975 with fellow students Avraham Rosenblum, Simcha Abramson, Ruby Harris, Adam Wexler, and Gedalia Goldstein. Playing a mix of rock and bluegrass with Jewish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishpacha
''Mishpacha'' ( he, משפחה, : Family) - Jewish Family Weekly is a Haredi weekly magazine package produced by The Mishpacha Group in both English and Hebrew. History The Mishpacha Publishing Group was founded in 1984 with the publication of the Hebrew Mishpacha magazine. Publisher and CEO Eli Paley teamed with Rabbi Moshe Grylak towards the goal of producing a magazine that would serve as a conduit for the exchange of ideas and values between the varying streams within Jewish orthodoxy, among them the Hasidic, Yeshivish, Sephardic, and Modern Orthodox communities. With no other weekly or monthly magazines geared towards Orthodox Jewish readership at that time, Mishpacha quickly gained popularity, in effect launching the Jewish Orthodox magazine industry. The first editor for the Hebrew edition was Asher Zuckerman (now the editor of the Hebrew newspaper ''Sha'ah Tova''). First beginning as a monthly, it became a weekly in the beginning of 1991. After a while the newspaper spli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaspora Yeshiva
The Diaspora Yeshiva Band ( he, להקת ישיבת התפוצות) was an Israeli Orthodox Jewish rock band founded at the Diaspora Yeshiva on Mount Zion, Jerusalem, by ''baal teshuva'' students from the United States. In existence from 1975 to 1983, the band infused Rock music, rock and bluegrass music with Jewish lyrics, creating a style of music it called "Hasidic rock" or "Country and Eastern". The band was very popular on college campuses in the early to mid-1980s, and was well known in Jerusalem for its Saturday-night concerts at David's Tomb. It had a considerable influence on contemporary Jewish religious music, inspiring later bands such as Blue Fringe, 8th Day, Reva L'Sheva, Soulfarm, the Moshav Band, and Shlock Rock. Fifteen years after it disbanded, band leader Avraham Rosenblum revived the band under the name Avraham Rosenblum & Diaspora and produced several more albums. Background The Diaspora Yeshiva (ישיבת התפוצות) was founded in 1967 by Rabbi Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaspora Yeshiva Band
The Diaspora Yeshiva Band ( he, להקת ישיבת התפוצות) was an Israeli Orthodox Jewish rock band founded at the Diaspora Yeshiva on Mount Zion, Jerusalem, by ''baal teshuva'' students from the United States. In existence from 1975 to 1983, the band infused Rock music, rock and bluegrass music with Jewish lyrics, creating a style of music it called "Hasidic rock" or "Country and Eastern". The band was very popular on college campuses in the early to mid-1980s, and was well known in Jerusalem for its Saturday-night concerts at David's Tomb. It had a considerable influence on contemporary Jewish religious music, inspiring later bands such as Blue Fringe, 8th Day, Reva L'Sheva, Soulfarm, the Moshav Band, and Shlock Rock. Fifteen years after it disbanded, band leader Avraham Rosenblum revived the band under the name Avraham Rosenblum & Diaspora and produced several more albums. Background The Diaspora Yeshiva (ישיבת התפוצות) was founded in 1967 by Rabbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |