|
Commelinids
In plant taxonomy, commelinids (originally commelinoids) (plural, not capitalised) is a clade of flowering plants within the monocots, distinguished by having cell walls containing ferulic acid. The commelinids are the only clade that the APG IV system has informally named within the monocots. The remaining monocots are a paraphyletic unit. Also known as the commelinid monocots it forms one of three groupings within the monocots, and the final branch; the other two groups are the alismatid monocots and the lilioid monocots. Description Members of the commelinid clade have cell walls containing UV-fluorescent ferulic acid. Taxonomy The commelinids were first recognized as a formal group in 1967 by Armen Takhtajan, who named them the Commelinidae and assigned them to a subclass of Liliopsida (monocots). The name was also used in the 1981 Cronquist system. However, by the release of his 1980 system of classification, Takhtajan had merged this subclass into a larger one, and no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lilioid Monocots
Lilioid monocots (lilioids, liliid monocots, petaloid monocots, petaloid lilioid monocots) is an informal name used for a grade (grouping of taxa with common characteristics) of five monocot orders (Petrosaviales, Dioscoreales, Pandanales, Liliales and Asparagales) in which the majority of species have flowers with relatively large, coloured tepals. This characteristic is similar to that found in lilies ("lily-like"). Petaloid monocots refers to the flowers having tepals which all resemble petals (petaloid). The taxonomic terms Lilianae or Liliiflorae have also been applied to this assemblage at various times. From the early nineteenth century many of the species in this group of plants were put into a very broadly defined family, Liliaceae ''sensu lato'' or ''s.l.'' (lily family). These classification systems are still found in many books and other sources. Within the monocots the Liliaceae ''s.l.'' were distinguished from the Glumaceae. The development of molecular phyloge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannales
The Zingiberales are flowering plants forming one of four orders in the commelinids clade of monocots, together with its sister order, Commelinales. The order includes 68 genera and 2,600 species. Zingiberales are a unique though morphologically diverse order that has been widely recognised as such over a long period of time. They are usually large herbaceous plants with rhizomatous root systems and lacking an aerial stem except when flowering. Flowers are usually large and showy, and the stamens are often modified (staminodes) to also form colourful petal-like structures that attract pollinators. Zingiberales contain eight families that are informally considered as two groups, differing in the number of fertile stamens. A " banana group" of four families appeared first and were named on the basis of large banana-like leaves. Later, a more genetically coherent (monophyletic) "ginger group" appeared, consisting of the remaining four families. The order, which has a fossil record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zingiberales
The Zingiberales are flowering plants forming one of four orders in the commelinids clade of monocots, together with its sister order, Commelinales. The order includes 68 genera and 2,600 species. Zingiberales are a unique though morphologically diverse order that has been widely recognised as such over a long period of time. They are usually large herbaceous plants with rhizomatous root systems and lacking an aerial stem except when flowering. Flowers are usually large and showy, and the stamens are often modified ( staminodes) to also form colourful petal-like structures that attract pollinators. Zingiberales contain eight families that are informally considered as two groups, differing in the number of fertile stamens. A " banana group" of four families appeared first and were named on the basis of large banana-like leaves. Later, a more genetically coherent (monophyletic) " ginger group" appeared, consisting of the remaining four families. The order, which has a fossil re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zingiberanae
The Zingiberales are flowering plants forming one of four orders in the commelinids clade of monocots, together with its sister order, Commelinales. The order includes 68 genera and 2,600 species. Zingiberales are a unique though morphologically diverse order that has been widely recognised as such over a long period of time. They are usually large herbaceous plants with rhizomatous root systems and lacking an aerial stem except when flowering. Flowers are usually large and showy, and the stamens are often modified ( staminodes) to also form colourful petal-like structures that attract pollinators. Zingiberales contain eight families that are informally considered as two groups, differing in the number of fertile stamens. A " banana group" of four families appeared first and were named on the basis of large banana-like leaves. Later, a more genetically coherent ( monophyletic) " ginger group" appeared, consisting of the remaining four families. The order, which has a fos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poales
The Poales are a large order of flowering plants in the monocotyledons, and includes families of plants such as the grasses, bromeliads, and sedges. Sixteen plant families are currently recognized by botanists to be part of Poales. Description The flowers are typically small, enclosed by bracts, and arranged in inflorescences (except in three species of the genus ''Mayaca'', which possess very reduced, one-flowered inflorescences). The flowers of many species are wind pollinated; the seeds usually contain starch. Taxonomy The APG III system (2009) accepts the order within a monocot clade called commelinids, and accepts the following 16 families: The earlier APG system (1998) adopted the same placement of the order, although it used the spelling "commelinoids". It did not include the Bromeliaceae and Mayaceae, but had the additional families Prioniaceae (now included in Thurniaceae), Sparganiaceae (now in Typhaceae), and Hydatellaceae (now transferred out of the monocots; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arecales
Arecales is an order of flowering plants. The order has been widely recognised only for the past few decades; until then, the accepted name for the order including these plants was Principes. Taxonomy The APG IV system of 2016 places Dasypogonaceae in this order, after studies showing Dasypogonaceae as sister to Arecaceae. However, this decision has been called into question. Historical taxonomical systems The Cronquist system of 1981 assigned the order to the subclass Arecidae in the class Liliopsida (= monocotyledons). The Thorne system (1992) and the Dahlgren system assigned the order to the superorder Areciflorae, also called Arecanae in the subclass Liliidae (= monocotyledons), with the single family Arecaceae. The APG II system of 2003 recognised the order and placed it in the clade commelinids in the monocots and uses this circumscription: * order Arecales *: family Arecaceae, alternative name Palmae This was unchanged from the APG system The APG system (Angiosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APG IV System
The APG IV system of flowering plant classification is the fourth version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy for flowering plants (angiosperms) being developed by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG). It was published in 2016, seven years after its predecessor the APG III system was published in 2009, and 18 years after the first APG system was published in 1998. In 2009, a linear arrangement of the system was published separately; the APG IV paper includes such an arrangement, cross-referenced to the 2009 one. Compared to the APG III system, the APG IV system recognizes five new orders (Boraginales, Dilleniales, Icacinales, Metteniusales and Vahliales), along with some new families, making a total of 64 angiosperm orders and 416 families. In general, the authors describe their philosophy as "conservative", based on making changes from APG III only where "a well-supported need" has been demonstrated. This has sometimes resulted in placements that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocots
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided; the rest of the flowering plants have two cotyledons and are classified as dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocotyledons have almost always been recognized as a group, but with various taxonomic ranks and under several different names. The APG III system of 2009 recognises a clade called "monocots" but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank. The monocotyledons include about 60,000 species, about a quarter of all angiosperms. The largest family in this group (and in the flowering plants as a whole) by number of species are the orchids (family Orchidaceae), with more than 20,000 species. About half as many species belong to the true grasses (Poaceae), which are ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided; the rest of the flowering plants have two cotyledons and are classified as dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocotyledons have almost always been recognized as a group, but with various taxonomic ranks and under several different names. The APG III system of 2009 recognises a clade called "monocots" but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank. The monocotyledons include about 60,000 species, about a quarter of all angiosperms. The largest family in this group (and in the flowering plants as a whole) by number of species are the orchids (family Orchidaceae), with more than 20,000 species. About half as many species belong to the true grasses ( Poaceae), which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
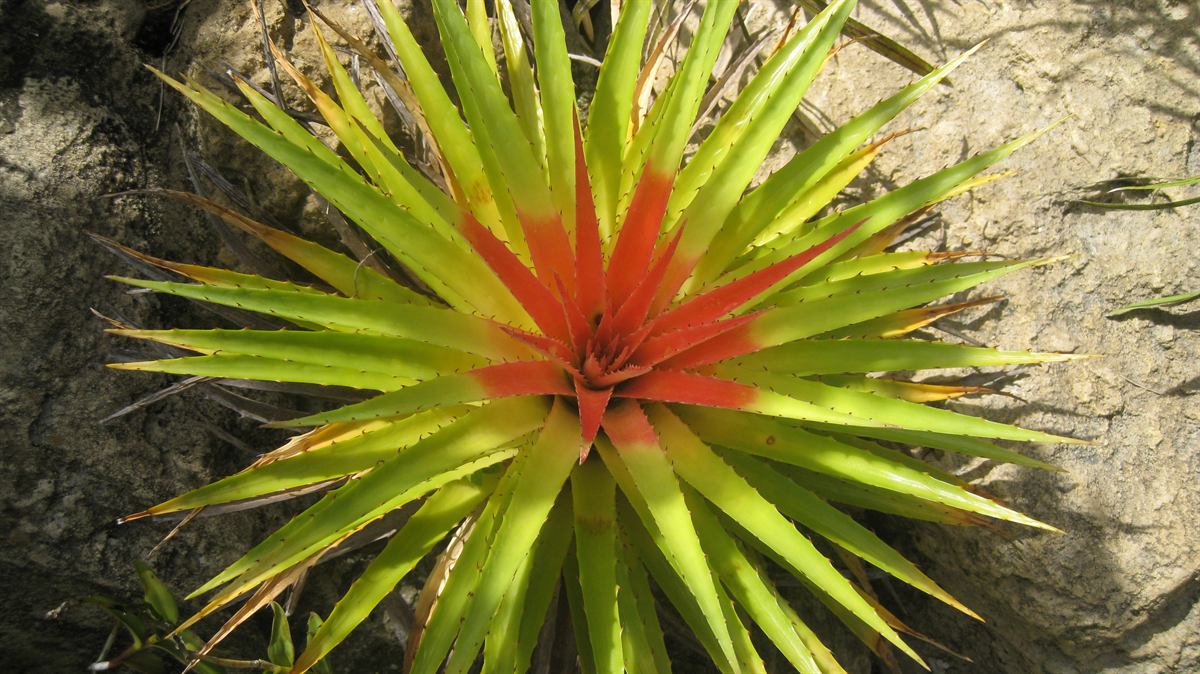
Bromeliales
Bromeliales is an order of flowering plants. Such an order has been recognized by a few systems of plant taxonomy, with a various placement. It appears that it always has had the same circumscription: consisting only of the family Bromeliaceae, the bromeliad or pineapple family. The order is not recognized in the APG II system, of 2003, which places the plants involved in the order Poales. Some examples are: * The Cronquist system of 1981 placed this order in subclass Zingiberidae, of class Liliopsida monocotyledons * The Thorne system (1992) placed the order in superorder Commelinanae in subclass Liliidae monocotyledons * The Dahlgren system placed the order in superorder Bromeliiflorae (also known as Bromelianae) in subclass Liliidae monocotyledonstogether with five other orders. * The Engler system, in its update of 1964, placed the order in class Monocotyledoneae Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |