|
Coloroid
The Coloroid Color System is a color space developed between 1962 and 1980 by Prof. Antal Nemcsics at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics for use by "architects and visual constructors". Since August 2000, the Coloroid has been registered as Hungarian Standard MSZ 7300. Like the OSA-UCS and Munsell systems, the Coloroid attempts to model a perceptually uniform color space or UCS. However, the UCS standard applied in the Coloroid system is equal appearing increments in color when the entire range of colors is presented to the viewer, in contrast to the standard of equal "just noticeable" or small color differences between pairs of similar colors presented in isolation. Colors in the Coloroid color space are fundamentally specified according to the perceptual attributes of "luminosity" (luminance factor, V), "saturation" (excitation purity, T) and hue (the matching or dominant spectral wavelength, A). The VAT components are used to define a cylindrical color geomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloroid
The Coloroid Color System is a color space developed between 1962 and 1980 by Prof. Antal Nemcsics at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics for use by "architects and visual constructors". Since August 2000, the Coloroid has been registered as Hungarian Standard MSZ 7300. Like the OSA-UCS and Munsell systems, the Coloroid attempts to model a perceptually uniform color space or UCS. However, the UCS standard applied in the Coloroid system is equal appearing increments in color when the entire range of colors is presented to the viewer, in contrast to the standard of equal "just noticeable" or small color differences between pairs of similar colors presented in isolation. Colors in the Coloroid color space are fundamentally specified according to the perceptual attributes of "luminosity" (luminance factor, V), "saturation" (excitation purity, T) and hue (the matching or dominant spectral wavelength, A). The VAT components are used to define a cylindrical color geomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names (including discrete numbers infor examplethe Pantone collection), or structured with mathematical rigor (as with the NCS System, Adobe RGB and sRGB). A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised. A "color model" is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers (e.g. tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antal Nemcsics
{{Disambiguation ...
Antal may refer to: * Andal, 8th-century poet saint of South India * Antal (given name) * Antal (surname) * 6717 Antal, a minor planet See also * Andal (other) Andal was a poet-saint of South India. Andal may also refer to: * Andal, Paschim Bardhaman, a census town in West Bengal, India ** Andal (community development block), an administrative division * Andal (crater), a crater on Mercury * Andals, a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest University Of Technology And Economics
The Budapest University of Technology and Economics ( hu, Budapesti Műszaki és Gazdaságtudományi Egyetem or in short ), official abbreviation BME, is the most significant university of technology in Hungary and is considered the world's oldest institute of technology which has university rank and structure. It was the first institute in Europe to train engineers at university level. It was founded in 1782. More than 110 departments and institutes operate within the structure of eight faculties. About 1100 lecturers, 400 researchers and other degree holders and numerous invited lecturers and practising expert specialists participate in education and research at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics. Approximately 1381 of the university's 21,171 students are foreigners, coming from 50 countries. The Budapest University of Technology and Economics issues about 70% of Hungary's engineering degrees. 34 professors/researchers of the university are members of the Hungar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OSA-UCS
In colorimetry the OSA-UCS (Optical Society of America Uniform Color Space) is a color space first published in 1947 and developed by the Optical Society of America’s Committee on Uniform Color Scales. Previously created color order systems, such as the Munsell color system, failed to represent perceptual uniformity in all directions. The committee decided that, in order to accurately represent uniform color differences in each direction, a new shape of three dimensional Cartesian geometry would need to be used. History and development The development of the OSA-UCS took place during many years, from 1947-1977. Not long after the first mathematical color model was developed by the CIE, David MacAdam showed that when selecting a color on the CIE chromaticity diagram, it could not be guaranteed that colors of the same perceived color difference around this color were at the same color distance with respect to the reference color. More simply, the Euclidean distance between an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munsell Color System
In colorimetry, the Munsell color system is a color space that specifies colors based on three properties of color: hue (basic color), chroma (color intensity), and value ( lightness). It was created by Professor Albert H. Munsell in the first decade of the 20th century and adopted by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as the official color system for soil research in the 1930s. Several earlier color order systems had placed colors into a three-dimensional color solid of one form or another, but Munsell was the first to separate hue, value, and chroma into perceptually uniform and independent dimensions, and he was the first to illustrate the colors systematically in three-dimensional space. Munsell's system, particularly the later renotations, is based on rigorous measurements of human subjects' visual responses to color, putting it on a firm experimental scientific basis. Because of this basis in human visual perception, Munsell's system has outlasted its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Difference
In color science, color difference or color distance is the separation between two colors. This metric allows quantified examination of a notion that formerly could only be described with adjectives. Quantification of these properties is of great importance to those whose work is color-critical. Common definitions make use of the Euclidean distance in a device-independent color space. Euclidean sRGB As most definitions of color difference are distances within a color space, the standard means of determining distances is the Euclidean distance. If one presently has an RGB (red, green, blue) tuple and wishes to find the color difference, computationally one of the easiest is to consider ''R'', ''G'', ''B'' linear dimensions defining the color space. \text = \sqrt. When the result should be computationally simple as well, it is often acceptable to remove the square root and simply use \text^2 = (R_2 - R_1)^2 + (G_2 - G_1)^2 + (B_2 - B_1)^2. This will work in cases when a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. Brightness is the term for the ''subjective'' impression of the ''objective'' luminance measurement standard (see for the importance of this contrast). The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre (cd/m2). A non-SI term for the same unit is the nit. The unit in the Centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS) (which predated the SI system) is the stilb, which is equal to one candela per square centimetre or 10 kcd/m2. Description Luminance is often used to characterize emission or reflection from flat, diffuse surfaces. Luminance levels indicate how much luminous power could be detected by the human eye looking at a particular surface from a particular angle of view. Luminance is thus an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorfulness
Colorfulness, chroma and saturation are attributes of perceived color relating to chromatic intensity. As defined formally by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) they respectively describe three different aspects of chromatic intensity, but the terms are often used loosely and interchangeably in contexts where these aspects are not clearly distinguished. The precise meanings of the terms vary by what other functions they are dependent on. * Colorfulness is the "attribute of a visual perception according to which the perceived color of an area appears to be more or less chromatic"., page 87. The colorfulness evoked by an object depends not only on its spectral reflectance but also on the strength of the illumination, and increases with the latter unless the brightness is very high ( Hunt effect). * Chroma is the "colorfulness of an area judged as a proportion of the brightness of a similarly illuminated area that appears white or highly transmitting". As a resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIE 1931 Color Space
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that define these color spaces are essential tools for color management, important when dealing with color inks, illuminated displays, and recording devices such as digital cameras. The system was designed in 1931 by the ''"Commission Internationale de l'éclairage"'', known in English as the International Commission on Illumination. The CIE 1931 RGB color space and CIE 1931 XYZ color space were created by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1931. They resulted from a series of experiments done in the late 1920s by William David Wright using ten observers and John Guild using seven observers. The experimental results were combined into the specification of the CIE RGB color space, from which the CIE XYZ color space was derived. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
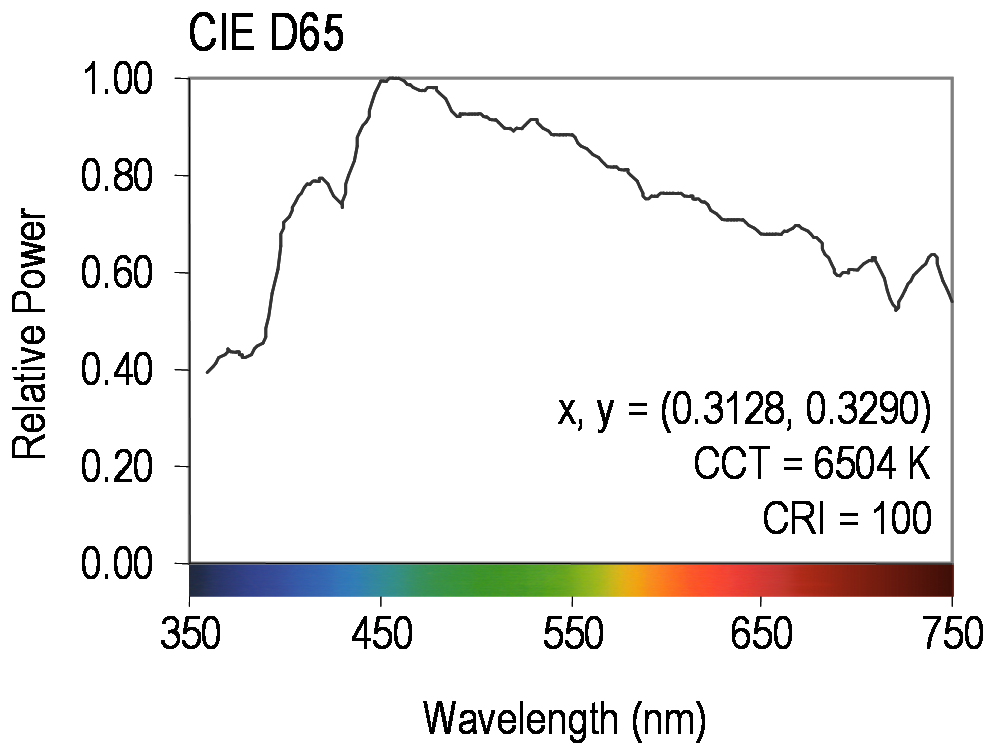
Illuminant D65
CIE standard illuminant D65 (sometimes written D65) is a commonly used standard illuminant defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). It is part of the D series of illuminants that try to portray standard illumination conditions at open-air in different parts of the world. D65 corresponds roughly to the average midday light in Western Europe / Northern Europe (comprising both direct sunlight and the light diffused by a clear sky), hence it is also called a daylight illuminant. As any standard illuminant is represented as a table of averaged spectrophotometric data, any light source which statistically has the same relative spectral power distribution (SPD) can be considered a D65 light source. There are no actual D65 light sources, only simulators. The quality of a simulator can be assessed with the CIE metamerism index. The CIE positions D65 as the standard daylight illuminant: History The CIE introduced three standard illuminants in 1931: * A: Inca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names (including discrete numbers infor examplethe Pantone collection), or structured with mathematical rigor (as with the NCS System, Adobe RGB and sRGB). A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised. A "color model" is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers (e.g. tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |