|
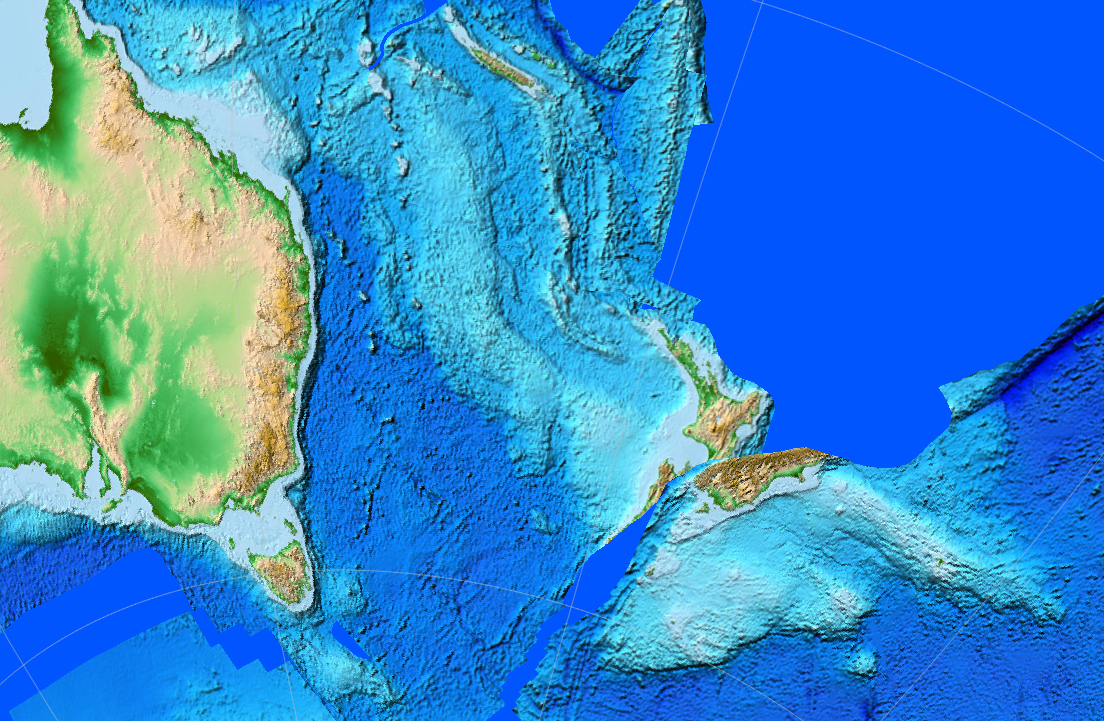
Clarence Fault
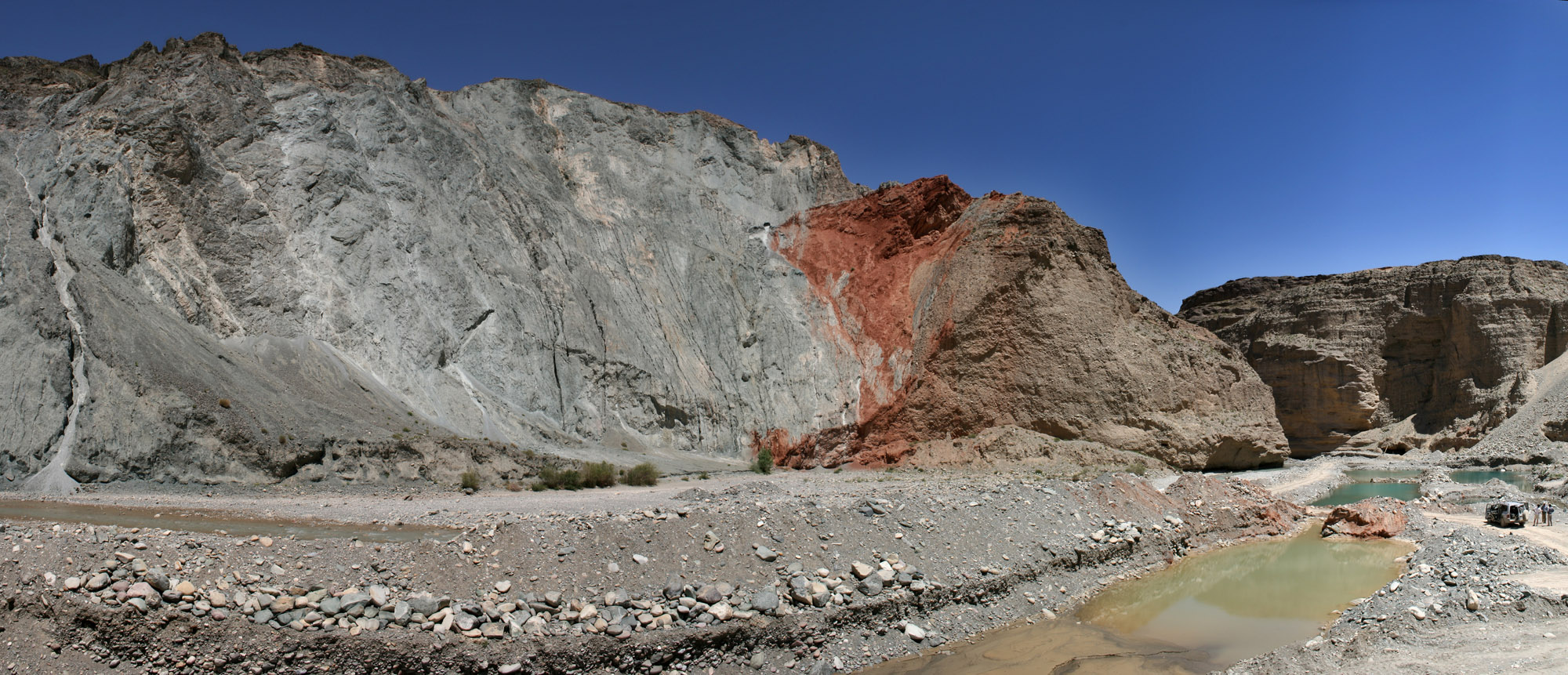
The Clarence Fault is an active fault, active dextral (right lateral) Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, strike-slip fault in the northeastern part of South Island, New Zealand. It forms part of the Marlborough Fault System, which accommodates the transfer of displacement along the oblique convergent boundary between the Indo-Australian Plate and Pacific Plate, from the Transform fault, transform Alpine Fault to the Hikurangi Trench Subduction, subduction zone. Extent The Clarence Fault extends from about 5 km south of Haupiri, close to the Alpine Fault to about 10 km west of Ward, New Zealand, Ward. This fault is the only member of the Marlborough Fault System to have neither a clear junction with the Alpine fault to the southwest nor a northeastward continuation to the coast. The southwestern part of the fault consists of many fault traces and has a Transpression, transpressive "pop-up" geometry. To the northeast the strands merge to form a single fault trace in the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hikurangi Trench
The Hikurangi Trench, also called the Hikurangi Trough, is an oceanic trench in the bed of the Pacific Ocean off the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand, lying between the southern end of the Cook Strait and the Chatham Rise. It is the southward continuation of the much deeper Kermadec Trench. It lies in the Hikurangi Margin subduction zone, which is the southern extension of the Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone. The Hikurangi Margin is the subduction zone where the thick oceanic Hikurangi Plateau is subducting beneath continental crust of the Indo-Australian Plate. By contrast, the Kermadec and Tonga trenches represent the parts of the subduction zone where oceanic crust of the Pacific Plate is subducting beneath oceanic crust of the Indo-Australian Plate. Although shallower than the trenches north of it, the Hikurangi Trench reaches depths of 3,000 metres as close as 80 kilometres from shore. Its maximum depth is about .Keith B. Lewis, Jean-Yves Collott and Serge E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular ''klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is referred to as a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaikōura Ranges
The Kaikōura Ranges are two parallel ranges of mountains located in the northeast of the South Island of New Zealand. The two ranges are visible from a great distance, including from the southern coast of the North Island. Description Formed along New Zealand's Marlborough Fault System, they can be seen as the northernmost extension of the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana in the South Island. Named the ''Looker-on mountains,'' by Captain James Cook, they take their name from the town of Kaikōura at the southern extreme of the more eastern range, the Seaward Kaikōuras. This range rises straight from (and dominates) the coast to the north of the town, and reaches its highest point with the Manakau (mountain), Mount Manakau. The long straight river valley of the Waiau Toa / Clarence River separate the Seaward Kaikōuras from the longer and loftier Inland Kaikōuras. This latter range contains the highest peak in the ranges, the Tapuae-o-Uenuku, the translation from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waiau Toa / Clarence River
The Clarence River (; officially Waiau Toa / Clarence River) is a major river which flows through the Kaikōura Ranges in the northeast of New Zealand's South Island. At roughly long, it is the longest river in Canterbury and the eighth longest in New Zealand. For its first , the river runs in a generally southeastern direction. It then turns northeast, running down a long straight valley between the Inland and Seaward Kaikōura Ranges. At the end of the Seaward Kaikōuras, the river meanders through undulating hill country before draining into the Pacific Ocean near the town of Clarence. A large part of the river is within the boundaries of Molesworth Station. The river and its tributaries cut through rock formed on the seafloor of the Pacific during the late Cretaceous through to the middle Eocene, during which period the majority of New Zealand was at points almost entirely submerged. This provides a useful record of this time period, and has contributed to our understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpression
In geology, transpression is a type of strike-slip deformation that deviates from simple shear because of a simultaneous component of shortening perpendicular to the fault plane. This movement ends up resulting in oblique shear. It is generally very unlikely that a deforming body will experience "pure" shortening or "pure" strike-slip. The relative amounts of shortening and strike-slip can be expressed in the convergence angle alpha which ranges from zero (ideal strike-slip) to 90 degrees (ideal convergence). During shortening, unless material is lost, transpression produces vertical thickening in the crust. Transpression that occurs on a regional scale along plate boundaries is characterized by oblique convergence. More locally, transpression occurs within restraining bends in strike-slip fault zones. Transpressional structures Transpressional shear zones are characterized by an association of structures that suggest zone-normal shortening and zone-parallel shearing. Commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ward, New Zealand
Ward is a small town in Marlborough, New Zealand. It is located on State Highway 1, north of Kaikoura. The Flaxbourne River flows past to the north and into the Pacific Ocean at Ward Beach to the south-east of Ward. A current initiative aims to have the town renamed as Flaxbourne. History Flaxbourne Station was established in the area around 1847. In 1905, most of the station was subdivided as part of the government's land reform, and Ward township was formed. The area was known by the name of the station. On the initiative of Richard Seddon, who was prime minister at the time, the township was named after his friend and political colleague Joseph Ward; a measure that was controversial at the time. The township of Seddon, named after Richard Seddon at the same time, is north of Ward. In 1961 the population was 218. As of 2017, there is a campaign to have the town renamed as Flaxbourne. The NZ Geographic Board, i.e. the organisation that has the final say on place names in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haupiri
Haupiri is a locality in the West Coast region of New Zealand's South Island. Greymouth lies to the west. The Ahaura and Haupiri Rivers run through the area. The population of the Haupiri statistical district, which covers a much larger area than the locality, was 531 in the 2013 census, an increase of 150 people from 2006. Lake Haupiri, located north of the settlement, is used for trout fishing. It has an amenity area protected under the Conservation Act 1987. The surrounding area includes native forest, dairy farming, scrub, tussock and wetlands. Gloriavale Christian Community Gloriavale Christian Community is a private commune often described as a cult based south of Lake Haupiri. Established in 1990 when its members relocated from Springbank Christian Community in North Canterbury Canterbury ( mi, Waitaha) is a region of New Zealand, located in the central-eastern South Island. The region covers an area of , making it the largest region in the country by area. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Fault
The Alpine Fault is a geological fault that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island (c. 480 km) and forms the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The Southern Alps have been uplifted on the fault over the last 12 million years in a series of earthquakes. However, most of the motion on the fault is strike-slip (side to side), with the Tasman district and West Coast moving North and Canterbury and Otago moving South. The average slip rates in the fault's central region are about 38 mm a year, very fast by global standards. The last major earthquake on the Alpine Fault was in c. 1717 AD, and the probability of another one occurring within the next 50 years is estimated at about 75 percent. Geographic extent and plate motion ThPacific Plate and Indo-Australian Plate boundaryforms the Macquarie Fault Zone in the Puysegur Trench off the southwestern corner of the South Island and comes onshore as the Alpine Fault just nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Fault
An active fault is a fault that is likely to become the source of another earthquake sometime in the future. Geologists commonly consider faults to be active if there has been movement observed or evidence of seismic activity during the last 10,000 years. * Active faulting is considered to be a geologic hazard - one related to earthquakes as a cause. Effects of movement on an active fault include strong ground motion, surface faulting, tectonic deformation, landslides and rockfalls, liquefaction, tsunamis, and seiches. Quaternary faults are those active faults that have been recognized at the surface and which have evidence of movement during the Quaternary Period. Related geological disciplines for ''active-fault'' studies include geomorphology, seismology, reflection seismology, plate tectonics, geodetics and remote sensing, risk analysis, and others. Location Active faults tend to occur in the vicinity of tectonic plate boundaries, and active fault research has foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a ''strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This is a result of oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addition or loss of lithosphere at the Earth's surface. Background Geophysicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |