|
Circinn
Circin was a Pictish territory recorded in contemporary sources between the 6th and 9th centuries, located north of the Firth of Tay and south of the Grampian mountains within modern-day Scotland. It is associated with the nominative plural form ''Cirig'', the name of one of the mythical founders of Pictish territories mentioned in the 9th century origin myth of the Picts ''Seven Children of Cruithne''. Circin is the second most commonly-attested Pictish territory in contemporary historical sources, after the dominant kingdom of Fortriu Fortriu ( la, Verturiones; sga, *Foirtrinn; ang, Wærteras; xpi, *Uerteru) was a Pictish kingdom that existed between the 4th and 10th centuries. It was traditionally believed to be located in and around Strathearn in central Scotland, but is ..., but is not itself described in any source as a kingdom. References Bibliography * * Scotland in the Early Middle Ages Pictish territories {{Scotland-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from early medieval texts and Pictish stones. Their Latin name, , appears in written records from the 3rd to the 10th century. Early medieval sources report the existence of a distinct Pictish language, which today is believed to have been an Insular Celtic language, closely related to the Common Brittonic, Brittonic spoken by the Celtic Britons, Britons who lived to the south. Picts are assumed to have been the descendants of the Caledonians, Caledonii and other British Iron Age, Iron Age tribes that were mentioned by Roman historians or on the Ptolemy's world map, world map of Ptolemy. The Pictish kingdom, often called Pictland in modern sources, achieved a large degree of political unity in the late 7th and early 8th centuries through the expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firth Of Tay
The Firth of Tay (; gd, Linne Tatha) is a firth on the east coast of Scotland, into which the River Tay (Scotland's largest river in terms of flow) empties. The firth is surrounded by four council areas: Fife, Perth and Kinross, City of Dundee, and Angus. Its maximum width (at Invergowrie) is . Two bridges span the firth: the Tay Road Bridge and the Tay Rail Bridge. The marshy Mugdrum Island is the only major island in the firth. The Firth of Tay in Antarctica was discovered in 1892–93 by Captain Thomas Robertson of the Dundee whaling expedition and named by him after the one in Scotland. He also named nearby Dundee Island in honour of the main city on the firth. Natural heritage The Firth of Tay and the Eden Estuary (which lies to the south of the firth) were designated as Special Protection Areas on 2 February 2000, as Ramsar wetlands a few months later (on 28 July 2000), and as Special Areas of Conservation five years later (on 17 March 2005). Several parts of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grampian Mountains
The Grampian Mountains (''Am Monadh'' in Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic) is one of the three major mountain ranges in Scotland, that together occupy about half of Scotland. The other two ranges are the Northwest Highlands and the Southern Uplands. The Grampian range extends southwest to northeast between the Highland Boundary Fault and the Great Glen. The range includes many of the highest mountains in the British Isles, including Ben Nevis (whose peak contains the highest point in the British Isles at above sea level) and Ben Macdhui (Scotland), Ben Macdui (whose peak contains second-highest at ). A number of rivers and streams rise in the Grampians, including the River Tay, Tay, River Spey, Spey, Cowie Water, Burn of Muchalls, Burn of Pheppie, Burn of Elsick, Cairnie Burn, River Don, Aberdeenshire, Don, River Dee, Aberdeenshire, Dee and River South Esk, Esk. The area is generally sparsely populated. There is some ambiguity about the extent of the range, and until the nineteenth c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Myth
An origin myth is a myth that describes the origin of some feature of the natural or social world. One type of origin myth is the creation or cosmogonic myth, a story that describes the creation of the world. However, many cultures have stories set in a time after a first origin - such stories aim to account for the beginnings of natural phenomena or of human institutions within a preexisting universe. In Graeco-Roman scholarship, the terms etiological myth and ''aition'' (from the Ancient Greek αἴτιον, "cause") are sometimes used for a myth that explains an origin, particularly how an object or custom came into existence. Nature of origin myths Every origin myth is a tale of creation: origin myths describe how some reality came into existence.Eliade, p. 21 In many cases, origin myths also justify the established order by explaining that it was established by sacred forces (see section on "Social function" below). The distinction between cosmogonic myths and origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Children Of Cruithne
''Seven Children of Cruithne'' ( sga, Mórseiser do Chruithne claind) is a quatrain written in Old Irish that forms the earliest known record of one of the origin myths of the Picts. In this myth, the Pictish kingdom's legendary founder Cruithne divides his territory into seven districts for each of his seven sons, each of which succeed him sequentially in ruling the entire kingdom. Background The verse is written in Old Irish and has four lines, each of seven syllables, grouped into two rhyming pairs. It exists as part of a detached section of the ''Lebor Bretnach'' called "Concerning Pictish Origins" ( sga, Do Bunad Cruithnech) that was added to the main text at the same time as the related list of Pictish Kings was extended forward to include Causantín son of Cinaed, and backward to include the mythical Cruithne and his seven sons described in the poem. It was therefore probably added to the text during Causantín's reign between 862 and 876, and probably dates as a verse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
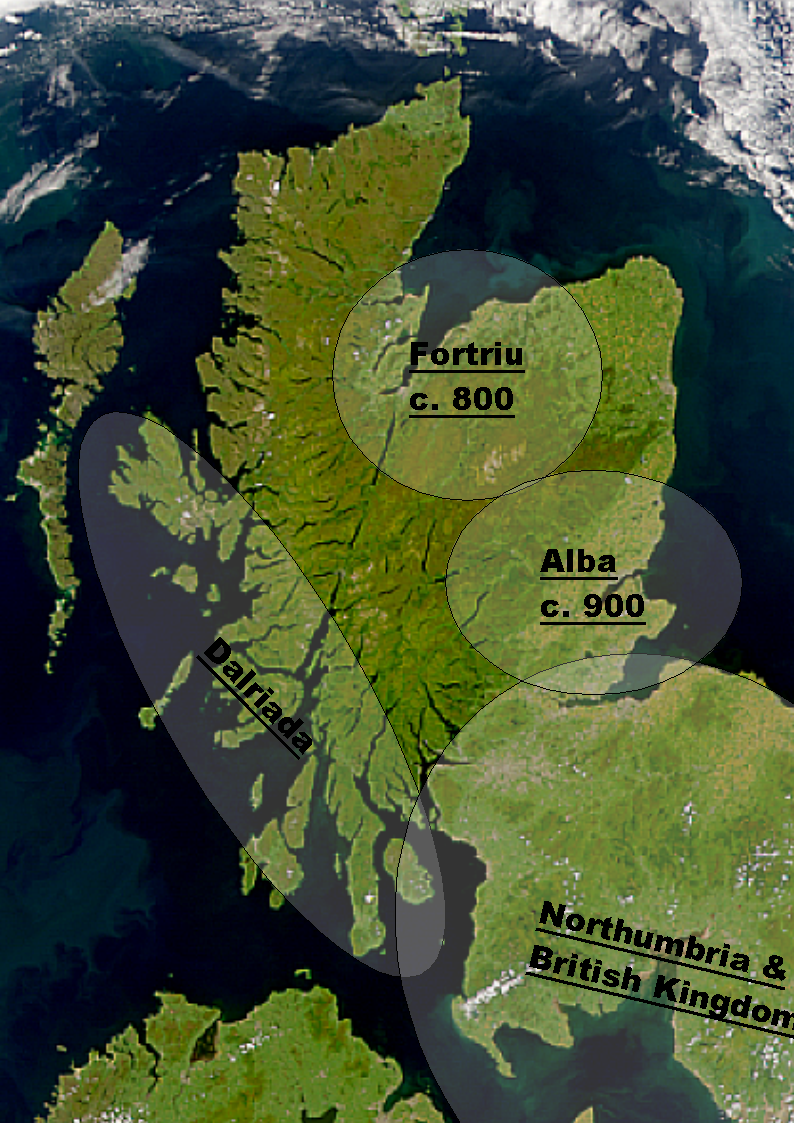
Fortriu
Fortriu ( la, Verturiones; sga, *Foirtrinn; ang, Wærteras; xpi, *Uerteru) was a Pictish kingdom that existed between the 4th and 10th centuries. It was traditionally believed to be located in and around Strathearn in central Scotland, but is more likely to have been based in the north, in the Moray and Easter Ross area. ''Fortriu'' is a term used by historians as it is not known what name its people used to refer to their polity. Historians also sometimes use the name synonymously with Pictland in general. Name The people of Fortriu left no surviving indigenous writings and the name they used to describe themselves is unrecorded. They were first documented in the late 4th century by the Roman historian Ammianus Marcellinus, who referred to them in Latin as the ''Verturiones (or Vecturiones)''. The Latin root ''verturio'' has been connected etymologically by John Rhys with the later Welsh word ''gwerthyr'', meaning "fortress", suggesting that both came from a Common Brittonic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland In The Early Middle Ages
Scotland was divided into a series of kingdoms in the early Middle Ages, i.e. between the end of Roman authority in southern and central Britain from around 400 CE and the rise of the kingdom of Alba in 900 CE. Of these, the four most important to emerge were the Picts, the Gaels of Dál Riata, the Britons of Alt Clut, and the Anglian kingdom of Bernicia. After the arrival of the Vikings in the late 8th century, Scandinavian rulers and colonies were established on the islands and along parts of the coasts. In the 9th century, the House of Alpin combined the lands of the Scots and Picts to form a single kingdom which constituted the basis of the Kingdom of Scotland. Scotland has an extensive coastline and vast areas of difficult terrain and poor agricultural land. In this period, more land became marginal due to climate change, resulting in relatively light human settlement, particularly in the interior and Highlands. Northern Britain lacked urban centres and settlements were bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Named_(HR).png)