|
Cinchona
''Cinchona'' (pronounced or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae containing at least 23 species of trees and shrubs. All are native to the Tropical Andes, tropical Andean forests of western South America. A few species are reportedly naturalization (biology), naturalized in Central America, Jamaica, French Polynesia, Sulawesi, Saint Helena in the South Atlantic, and São Tomé and Príncipe off the coast of tropical Africa, and others have been cultivated in India and Java, where they have formed hybrids. ''Cinchona'' has been historically sought after for its medicinal value, as the bark of several species yields quinine and other alkaloids. These were the only effective treatments against malaria during the height of European colonialism, which made them of great economic and political importance. Trees in the genus are also known as fever trees because of their anti-malarial properties. The artificial Quinine total synthesis, synthesis of quinine in 1944 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
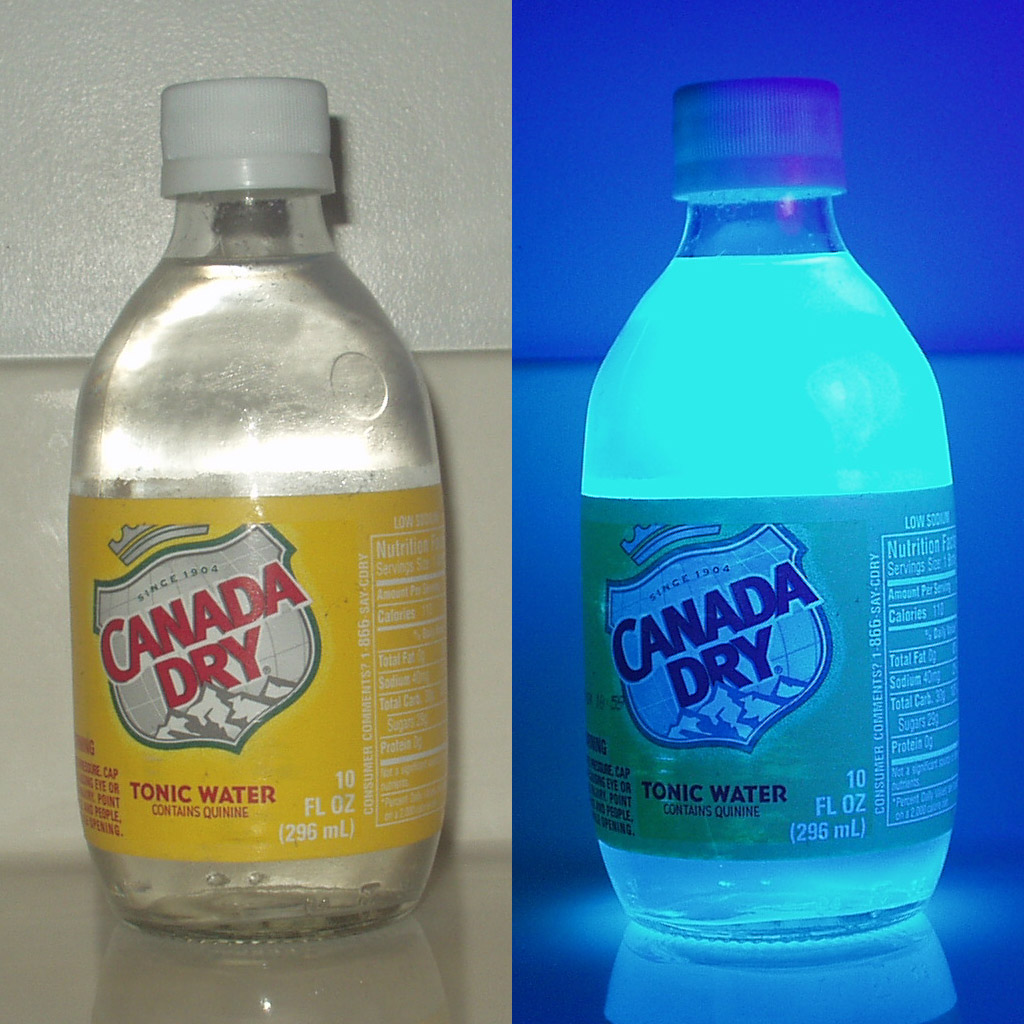
Quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cramps, quinine is not recommended for this purpose due to the risk of serious side effects. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Malaria resistance to quinine occurs in certain areas of the world. Quinine is also used as an ingredient in tonic water to impart a bitter taste. Common side effects include headache, ringing in the ears, vision issues, and sweating. More severe side effects include deafness, low blood platelets, and an irregular heartbeat. Use can make one more prone to sunburn. While it is unclear if use during pregnancy causes harm to the baby, treating malaria during pregnancy with quinine when appropriate is still recommended. Quinine is an alkaloid, a naturally occurring chemical compound. How it works as a medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit's Bark
Jesuit's bark, also known as cinchona bark, Peruvian bark or China bark, is a former remedy for malaria, as the bark contains quinine used to treat the disease. The bark of several species of the genus ''Cinchona'', family Rubiaceae indigenous to the western Andes of South America, was discovered as a folk medicine treatment for malaria by Jesuit missionaries in Peru during the 17th century. History The western history of cinchona bark dates back more than 350 years. Circa 1650, the physician Sebastiano Bado declared that this bark had proved more precious to mankind than all the gold and silver that the Spaniards had obtained from South America. In the 18th century, the Italian professor of medicine Bernardino Ramazzini said that the introduction of Peruvian bark would be of the same importance to medicine that the discovery of gunpowder was to the art of war, an opinion endorsed by contemporary writers on the history of medicine. The value of Jesuit's bark, and the controvers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clements Markham
Sir Clements Robert Markham (20 July 1830 – 30 January 1916) was an English geographer, explorer and writer. He was secretary of the Royal Geographical Society (RGS) between 1863 and 1888, and later served as the Society's president for a further 12 years. In the latter capacity he was mainly responsible for organising the British National Antarctic Expedition of 1901–1904, and for launching the polar career of Robert Falcon Scott. Markham began his career as a Royal Navy cadet and midshipman, during which time he went to the Arctic with in one of the many searches for Franklin's lost expedition. Later, Markham served as a geographer to the India Office, and was responsible for the collection of cinchona plants from their native Peruvian forests, and their transplantation in India. By this means, the Indian government acquired a home source from which quinine could be extracted. Markham also served as geographer to Sir Robert Napier, 1st Baron Napier of Magdala, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of National Trees ...
This is a list of national trees, most official, but some unofficial. National trees See also * National emblem * Floral emblem * List of U.S. State and territory trees References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of National Trees N Trees In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubiaceae
The Rubiaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the coffee, madder, or bedstraw family. It consists of terrestrial trees, shrubs, lianas, or herbs that are recognizable by simple, opposite leaves with interpetiolar stipules and sympetalous actinomorphic flowers. The family contains about 13,500 species in about 620 genera, which makes it the fourth-largest angiosperm family. Rubiaceae has a cosmopolitan distribution; however, the largest species diversity is concentrated in the tropics and subtropics. Economically important genera include ''Coffea'', the source of coffee, '' Cinchona'', the source of the antimalarial alkaloid quinine, ornamental cultivars (''e.g.'', '' Gardenia'', ''Ixora'', ''Pentas''), and historically some dye plants (''e.g.'', ''Rubia''). Description The Rubiaceae are morphologically easily recognizable as a coherent group by a combination of characters: opposite or whorled leaves that are simple and entire, interpetiolar stipules, tubu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are usable as lumber or plants above a specified height. In wider definitions, the taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos are also trees. Trees are not a taxonomic group but include a variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some reaching several thousand years old. Trees have been in existence for 370 million years. It is estimated that there are some three trillion mature trees in the world. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground by the trunk. This trunk typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis Jerónimo De Cabrera, 4th Count Of Chinchón
Luis Jerónimo Fernández de Cabrera Bobadilla Cerda y Mendoza, 4th Count of Chinchón, also known as Luis Xerónimo Fernandes de Cabrera Bobadilla y Mendoza, (1589 in Madrid – October 28, 1647 in Madrid) was a Spanish nobleman, Comendador of Criptana, Alcaide of the Alcázar de Segovia, Treasurer of Aragón, and captain general and Viceroy of Peru, from January 14, 1629, to December 18, 1639. His wife, Ana de Osorio (1599–1625), is credited as being one of the first Europeans to be treated with quinine, and as the person who introduced that medicine into Europe. Birth Fernández de Cabrera Bobadilla was born in Madrid in 1589 (or perhaps 1590), into a family close to the Spanish throne. His parents were Diego Fernández de Cabrera, third Count of Chinchón and Inés Pacheco, the daughter of the marquis of Villena and 3rd Duke of Escalona, Diego López Pacheco, and Luisa Bernarda de Cabrera Bobadilla, third marquesa of Moya. Don Luis's parents were first cousins. He was k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinine Total Synthesis
The total synthesis of quinine, a naturally-occurring antimalarial drug, was developed over a 150-year period. The development of synthetic quinine is considered a milestone in organic chemistry although it has never been produced industrially as a substitute for natural occurring quinine. The subject has also been attended with some controversy: Gilbert Stork published the first stereoselective total synthesis of quinine in 2001, meanwhile shedding doubt on the earlier claim by Robert Burns Woodward and William Doering in 1944, claiming that the final steps required to convert their last synthetic intermediate, quinotoxine, into quinine would not have worked had Woodward and Doering attempted to perform the experiment. A 2001 editorial published in ''Chemical & Engineering News'' sided with Stork, but the controversy was eventually laid to rest once and for all when Williams and coworkers successfully repeated Woodward's proposed conversion of quinotoxine to quinine in 2007. Chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
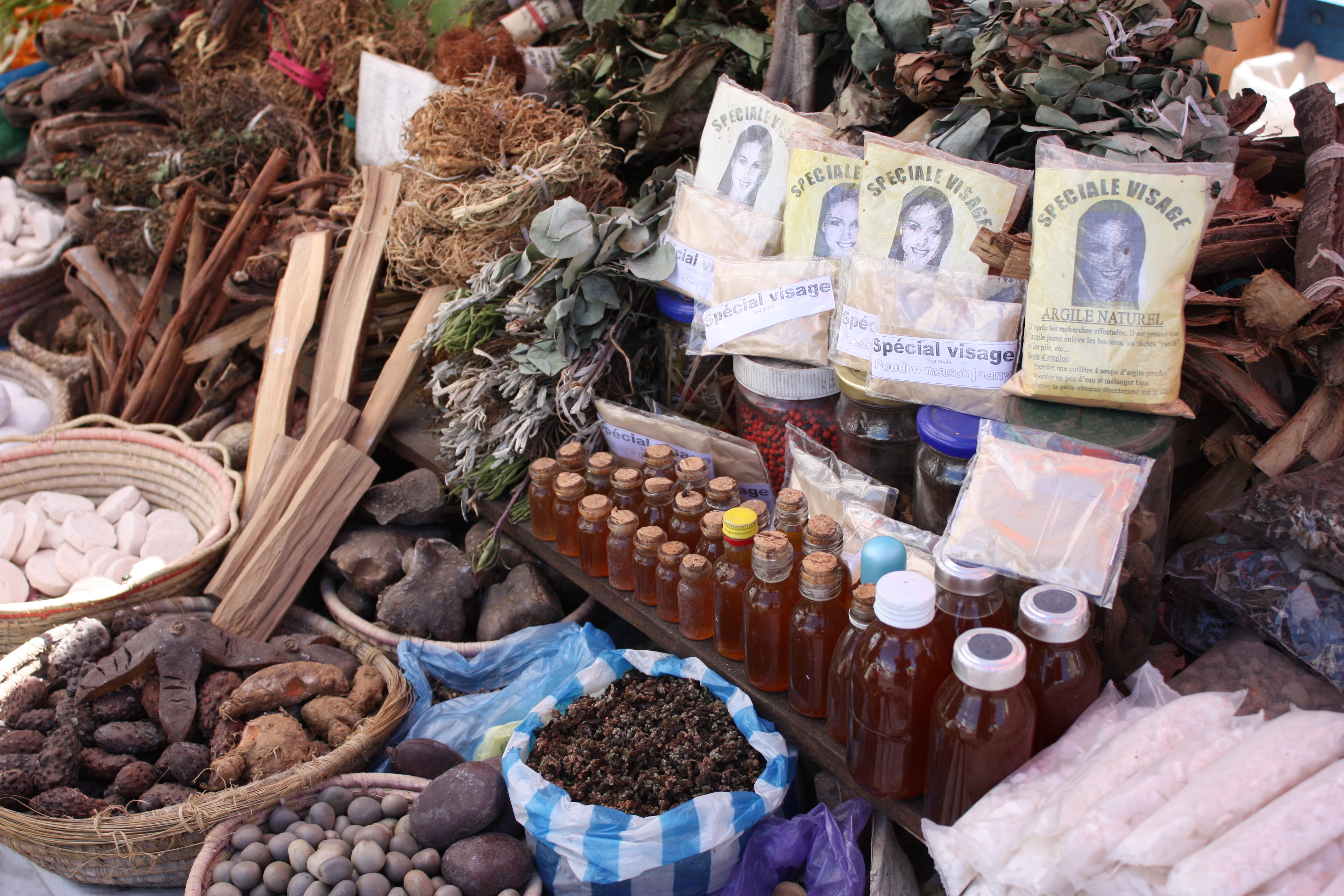
Traditional Medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the era of modern medicine. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines traditional medicine as "the sum total of the knowledge, skills, and practices based on the theories, beliefs, and experiences indigenous to different cultures, whether explicable or not, used in the maintenance of health as well as in the prevention, diagnosis, improvement or treatment of physical and mental illness". Traditional medicine is often contrasted with scientific medicine. In some Asian and African countries, up to 80% of the population relies on traditional medicine for their primary health care needs. When adopted outside its traditional culture, traditional medicine is often considered a form of alternative medicine. Practices known as traditional medicines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




