|
Chʼolan Languages
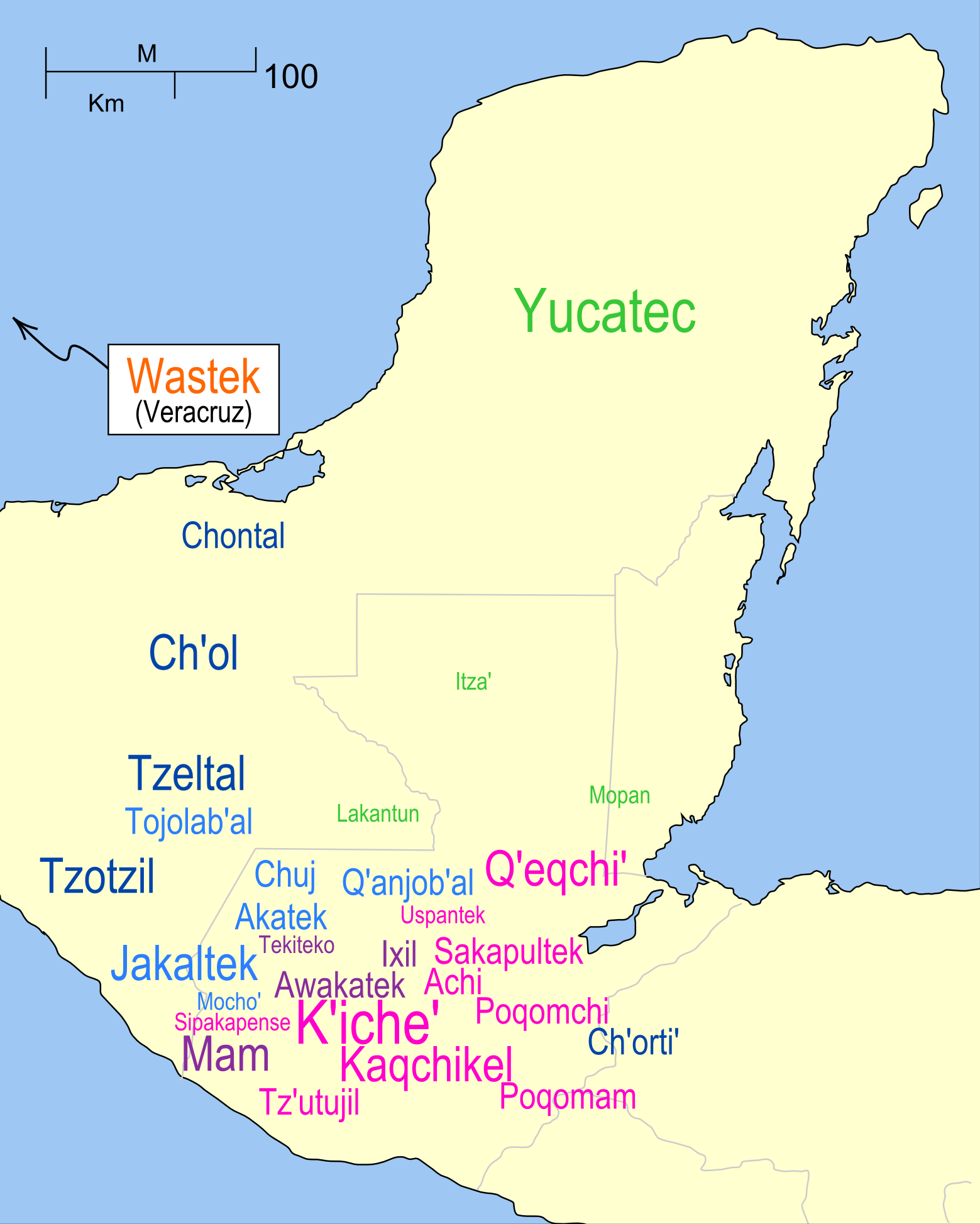
The Chʼolan ( Cholan–Tzeltalan languages) are a branch of the Mayan family of Mexico. These languages break into six sections being Cholan and Tzeltalan. Cholan has then two subsections being Western Cholan and Chʼoltiʼan; these composing the two larger sections of slight linguistic differences portrayed by Kuryłowicz's Fourth Law of Analogy. The language Tzeltalan also breaks up into sections; Tzendal (colonial Tzeltal), Tzotzil, and Wastekan. These subsections differ by similar linguistic differences. Languages *Cholan (proper): Chʼol– Chontal, Chʼortiʼ– Chʼoltiʼ (likely also Classic Maya) *Tzeltalan: Tzeltal, Tzotzil See Mayan languages#Western branch for details. See also *Acala Chʼol *Lakandon Chʼol *Manche Chʼol The Manche Chʼol were a former Chʼol-speaking Maya people inhabiting the extreme south of what is now the Petén Department of modern Guatemala, the area around Lake Izabal (also known as the ''Golfo Dulce''), and southern Belize. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Within this region pre-Columbian societies flourished for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoamerica was the site of two of the most profound historical transformations in world history: primary urban generation, and the formation of New World cultures out of the long encounters among indigenous, European, African and Asian cultures. In the 16th century, Eurasian diseases such as smallpox and measles, which were endemic among the colonists but new to North America, caused the deaths of upwards of 90% of the indigenous people, resulting in great losses to their societies and cultures. Mesoamerica is one of the five areas in the world where ancient civilization arose independently (see cradle of civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayan Languages
The Mayan languagesIn linguistics, it is conventional to use ''Mayan'' when referring to the languages, or an aspect of a language. In other academic fields, ''Maya'' is the preferred usage, serving as both a singular and plural noun, and as the adjectival form. form a language family spoken in Mesoamerica, both in the south of Mexico and northern Central America. Mayan languages are spoken by at least 6 million Maya people, primarily in Guatemala, Mexico, Belize, El Salvador and Honduras. In 1996, Guatemala formally recognized 21 Mayan languages by name,Achiʼ is counted as a variant of Kʼicheʼ by the Guatemalan government. and Mexico recognizes eight within its territory. The Mayan language family is one of the best-documented and most studied in the Americas. Modern Mayan languages descend from the Proto-Mayan language, thought to have been spoken at least 5,000 years ago; it has been partially reconstructed using the comparative method. The proto-Mayan language diver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chʼol Language
The Chʼol (Chol) language is a member of the western branch of the Mayan language family used by the Chʼol people in the Mexican state of Chiapas. There are two main dialects: *Chʼol of Tila spoken by 43,870 people of whom 10,000 are monolinguals in the villages of Tila, Vicente Guerrero, Chivalito and Limar in Chiapas. * Chʼol of Tumbalá spoken by 90,000 people of whom 30,000 are monolinguals in the villages of Tumbalá, Sabanilla, Misijá, Limar, Chivalita and Vicente Guerrero. The Cholan branch of the Mayan languages is considered to be particularly conservative and Chʼol along with its two closest relatives the Chʼortiʼ language of Guatemala and Honduras, and the Chontal Maya language of Tabasco are believed to be the modern languages that best reflect their relationship with the Classic Maya language.Houston, S., O. Chinchilla, Stuart D. "The Decipherment of Ancient Maya Writing", U. of Oklahoma Press, 2001. Chʼol-language programming is carried by the CDI's rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chontal Maya Language
''Yokotʼan'' (self-denomination), also known as Chontal Maya, is a Maya language of the Cholan family spoken in 2020 by around 60 thousand Chontal Maya people of the Mexican state of Tabasco. According to the National Catalog of Indigenous Languages of Mexico- INALIYokotʼanhas at least four dialects: Nacajuca (Central), Centla (Northern), Macuspana (Southern) and Tamulte (Eastern). Distribution The Chontal Maya are concentrated in 159 settlements in 5 municipalities of Tabasco (Brown 2005:122). *Centla *Centro *Jonuta *Macuspana *Nacajuca Nacajuca is a city in Nacajuca Municipality in the state of Tabasco, Mexico. It is part of the Chontalapa region in the north center of the state and a major center of Tabasco's Chontal Maya population. Although the local economy is still based on ... (comprising more than 50% of the Chontal Maya population) Some Chontal settlements near the town of Nacajuca include (Brown 2005:116): *El Tigre *Saloya *Guatacaloa *Olcuatitan *Tucta *Maz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chʼortiʼ Language
The Chʼortiʼ language (sometimes also ''Chorti'') is a Mayan language, spoken by the indigenous Maya people who are also known as the Chʼortiʼ or Chʼortiʼ Maya. Chʼortiʼ is a direct descendant of the Classic Maya language in which many of the pre-Columbian inscriptions using the Maya script were written. Chʼortiʼ is the modern version of the ancient Mayan language Chʼolan (which was actively used and most popular between the years of A.D 250 and 850).Houston, S, J Robertson, and D Stuart. "The language of Classic Maya inscriptions." Current Anthropology 41.3 (2000): 321–356. Print. Relationship to other Mayan languages Chʼortiʼ can be called a living " Rosetta Stone" of Mayan languages. The Chʼortiʼ language is an important factor to comprehend the contents of Maya glyphic writings, some of which are not yet fully understood. Over several years, many linguists and anthropologists expected to realize the Chʼortiʼ culture and language by studying its word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chʼoltiʼ Language
The Chʼoltiʼ language is an extinct Mayan language which was spoken by the Manche Chʼol people of eastern Guatemala and southern Belize. The post-colonial stage of the language is only known from a single manuscript written between 1685 and 1695 which was first studied by Daniel Garrison Brinton. Chʼoltiʼ belongs to the Choʼlan branch of the Mayan languages and is closely related to Chontal and especially Chʼortiʼ. The Chʼoltiʼ language has become of particular interest for the study of Mayan Hieroglyphs since it seems that most of the glyphic texts are written in an ancient variety of Chʼoltiʼ called Classic Chʼoltiʼan or Classic Maya A classic is an outstanding example of a particular style; something of lasting worth or with a timeless quality; of the first or highest quality, class, or rank – something that exemplifies its class. The word can be an adjective (a ''c ... by epigraphers and which is thought to have been spoken as a prestige dialect thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Maya Language
A classic is an outstanding example of a particular style; something of lasting worth or with a timeless quality; of the first or highest quality, class, or rank – something that exemplifies its class. The word can be an adjective (a ''classic'' car) or a noun (a ''classic'' of English literature). It denotes a particular quality in art, architecture, literature, design, technology, or other cultural artifacts. In commerce, products are named 'classic' to denote a long-standing popular version or model, to distinguish it from a newer variety. ''Classic'' is used to describe many major, long-standing sporting events. Colloquially, an everyday occurrence (e.g. a joke or mishap) may be described in some dialects of English as 'an absolute classic'. "Classic" should not be confused with ''classical'', which refers specifically to certain cultural styles, especially in music and architecture: styles generally taking inspiration from the Classical tradition, hence classicism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzeltal Language
Tzeltal or Tseltal () is a Mayan language spoken in the Mexican state of Chiapas, mostly in the municipalities of Ocosingo, Altamirano, Huixtán, Tenejapa, Yajalón, Chanal, Sitalá, Amatenango del Valle, Socoltenango, Las Rosas, Chilón, San Juan Cancuc, San Cristóbal de las Casas and Oxchuc. Tzeltal is one of many Mayan languages spoken near this eastern region of Chiapas, including Tzotzil, Chʼol, and Tojolabʼal, among others. There is also a small Tzeltal diaspora in other parts of Mexico and the United States, primarily as a result of unfavorable economic conditions in Chiapas. The area in which Tzeltal is spoken can be divided in half by an imaginary north-south line; to the west, near Oxchuc, is the ancestral home of the Tzeltal people, predating Spanish colonials, while the eastern portion was settled primarily in the second half of the twentieth century. Partially as a result of these migrations, during which the Tzeltal people and other cultural groups foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzotzil Language
Tzotzil (; ''Batsʼi kʼop'' ) is a Maya language spoken by the indigenous Tzotzil Maya people in the Mexican state of Chiapas. Most speakers are bilingual in Spanish as a second language. In Central Chiapas, some primary schools and a secondary school are taught in Tzotzil. Tzeltal is the most closely related language to Tzotzil and together they form a Tzeltalan sub-branch of the Mayan language family. Tzeltal, Tzotzil and Chʼol are the most widely spoken languages in Chiapas besides Spanish. There are six dialects of Tzotzil with varying degrees of mutual intelligibility, named after the different regions of Chiapas where they are spoken: Chamula, Zinacantán, San Andrés Larráinzar, Huixtán, Chenalhó, and Venustiano Carranza. ''Centro de Lengua, Arte y Literatura Indígena'' (CELALI) suggested in 2002 that the name of the language (and the ethnicity) should be spelled Tsotsil, rather than Tzotzil. Native speakers and writers of the language are picking up the habit o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acala Chʼol
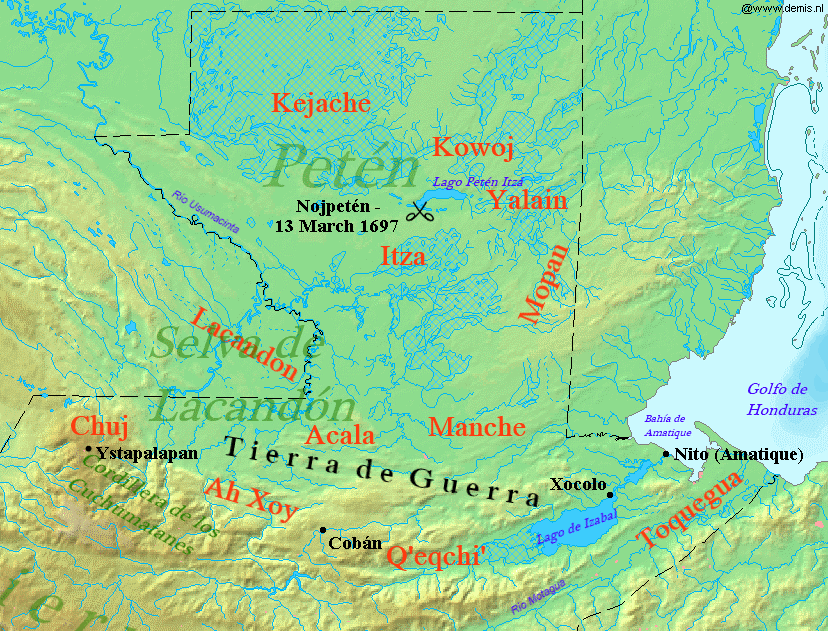
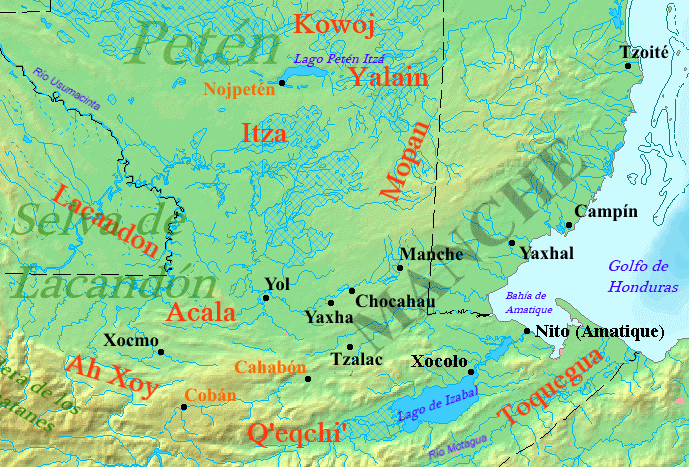
The Acala Chʼol were a former Chʼol-speaking Maya people who occupied a territory to the west of the Manche Chʼol and east of the Chixoy River in what is now the Alta Verapaz Department of Guatemala. The Acala should not be confused with the people of the former Maya territory of Acalan, near the Laguna de Terminos in Mexico. By the 17th century the Acala had two principal towns; Cagbalam had 300 multiple-family houses and Culhuacan had over 140. The towns were divided into four sections, each governed by their own ruler. The combined population of these two towns has been estimated at 7,000. The Acala were allies of the Lakandon Chʼol, their immediate neighbours to the west, and the two peoples sometimes cooperated militarily. The Acala are known to have cultivated cacao and achiote. In 1555 the Spanish carried out a military expedition against the Acala in retaliation for their killing of Dominican friar Domingo de Vico and his companion Andrés López. The Spanish and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakandon Chʼol
The Lakandon Chʼol were a former Chʼol-speaking Maya people inhabiting the Lacandon Jungle in what is now Chiapas in Mexico and the bordering regions of northwestern Guatemala, along the tributaries of the upper Usumacinta River and the foothills of the Sierra de los Cuchumatanes. The Lakandon Chʼol at contact with the Spanish The Lakandon Chʼol of the time of the Spanish conquest should not be confused with the modern Yucatec-speaking Lacandon people occupying the same region. At the time of Spanish contact in the 16th century, the Lacandon Jungle was inhabited by Chʼol people referred to as ''Lakam Tun''. This name was hispanicised, first to ''El Acantun'', then to ''Lacantun'' and finally to ''Lacandon''. The main Lakandon village was situated on an island in Lake Miramar, also referred to as Lakam Tun by the inhabitants. The Lakandons, together with their equally unconquered Itza enemies to the northeast, had an especially warlike reputation among the Spanish. Later histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manche Chʼol
The Manche Chʼol were a former Chʼol-speaking Maya people inhabiting the extreme south of what is now the Petén Department of modern Guatemala, the area around Lake Izabal (also known as the ''Golfo Dulce''), and southern Belize. The Manche Chʼol took the name ''Manche'' from the name of their main settlement. They were the last group of eastern Cholan-speakers to remain independent and ethnically distinct. It is likely that they were descended from the inhabitants of Classic period (c. 250-900 AD) Maya cities in the southeastern Maya region, such as Nim Li Punit, Copán and Quiriguá. The first Spanish contact with the Manche Chʼol was in 1525, when an expedition led by Hernán Cortés crossed their territory. From the early 17th century onwards, Dominican friars attempted to concentrate the Manche into mission towns and convert them to Christianity. These attempts alarmed their warlike Itza neighbours to the northwest, who attacked the mission towns and fomented rebell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |