|
Chesterfield Central Railway Station
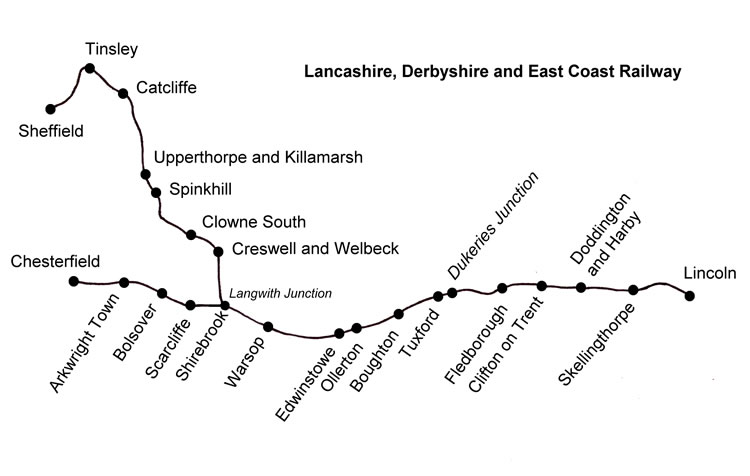
Chesterfield Central was a railway station serving the town of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, England. History The station was on the Great Central (GCR) Chesterfield Loop which ran between and Heath Junction (just north of Heath railway station) on the Great Central Main Line. The station opened in 1892 and was closed in 1963. Although the official closing date was 4 March 1963, the last passenger train to use the station did so on 15 June, when 'Flying Scotsman' stopped there during a Railway Preservation Society tour from to . It remained open for goods traffic until 11 September, and a private siding continued in use after that. Compared to nearby Chesterfield Midland, the station was little used. The number of passengers using the station during the week ending 19 August 1961 was 1,829, whereas Midland station was used by 22,285 passengers in the same week, over twelve times as many. The station was demolished by 1973 to make way for Chesterfield's inner-relief road, much of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesterfield, Derbyshire
Chesterfield is a market town and unparished area in the Borough of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, England, north of Derby and south of Sheffield at the confluence of the River Rother and River Hipper. In 2011 the built-up-area subdivision had a population of 88,483, making it the second-largest settlement in Derbyshire, after Derby. The wider borough had a population of 103,801 in 2011. In 2011, the town had a population of 76,753. It has been traced to a transitory Roman fort of the 1st century CE. The name of the later Anglo-Saxon village comes from the Old English ''ceaster'' (Roman fort) and ''feld'' (pasture). It has a sizeable street market three days a week. The town sits on an old coalfield, but little visual evidence of mining remains. The main landmark is the crooked spire of the Church of St Mary and All Saints. History Chesterfield was in the Hundred of Scarsdale. The town received its market charter in 1204 from King John, which constituted the town as a free boro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesterfield Railway Station
Chesterfield railway station serves the town of Chesterfield in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the Midland Main Line. Four tracks pass through the station which has three platforms. It is currently operated by East Midlands Railway. The station has the PlusBus scheme where train and bus tickets can be bought together at a saving. Chesterfield is a Penalty fare station for East Midlands Railway services. History The first line into Chesterfield was the North Midland Railway from Derby to Leeds in 1840. The original station was built in a Jacobean style similar to the one at Ambergate railway station, Ambergate but it was replaced in 1870 by a new one further south in the current location, when the Midland Railway built the ''"New Road"'' to Sheffield Midland station, Sheffield. This new station of 1870 was designed by the company architect John Holloway Sanders. In 1892 the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway, later to become the Great Central Railway, crossed under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Great Central Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Chesterfield, Derbyshire
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the :Human habitats, human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Demolished In 1973
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheepbridge And Brimington Railway Station
Sheepbridge and Brimington railway station was on the outskirts of the town of Chesterfield, Derbyshire. The station was on the Great Central Chesterfield Loop which ran between Staveley Central and Heath Junction (just north of Heath railway station Heath railway station was a railway station in the village of Holmewood, Derbyshire. The station name of Heath was named after the neighbouring village of Heath although the station was in Holmewood instead. The station was just before the Gr ...) on the Great Central Main Line. The station opened on 4 June 1892, was renamed to Brimington on 18 June 1951 and closed on 2 January 1956. References Disused railway stations in Derbyshire Former Great Central Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1892 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1956 Buildings and structures in Chesterfield, Derbyshire {{EastMidlands-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grassmoor Railway Station
Grassmoor railway station is a disused station serving the suburb of Hasland in Chesterfield and village of Grassmoor, Derbyshire, England. It operated from 1893 until 1940. The station was on the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway which was amalgamated into the Great Central Chesterfield Loop which ran between Staveley Central and Heath Junction (just north of Heath railway station Heath railway station was a railway station in the village of Holmewood, Derbyshire. The station name of Heath was named after the neighbouring village of Heath although the station was in Holmewood instead. The station was just before the Gr ...) on the Great Central Main Line. References Disused railway stations in Derbyshire Former Great Central Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1893 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1940 {{EastMidlands-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesterfield Market Place Railway Station
Chesterfield Market Place railway station was a former railway station in the centre of the town of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, England. Three stations Chesterfield Market Place station was the third and final station to be built in the town. Services from the first two: * Chesterfield Midland, which remains open as "Chesterfield", and * Chesterfield Central, which closed in 1963 - ran north–south, but those from Chesterfield Market Place ran to the east. History Opening The station was opened as "Chesterfield" by the LD&ECR on 8 March 1897 and was the headquarters of the line. It was renamed "Chesterfield Market Place" on 1 January 1907. The station was closed to passengers by BR on 3 December 1951 because of the prohibitive cost of maintaining and repairing Bolsover Tunnel, together with concerns over Doe Lea Viaduct and the limited amount of traffic. Goods services continued until 4 March 1957. Market Place station was situated on West Bars, adjacent to two old inns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A61 Road , in the Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings
{{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ...
A61 or A-61 may refer to: * A61 road (England), a road connecting Derby and Thirsk * A61 motorway (France), a road connecting Narbonne and Bordeaux * A61 motorway (Germany), a road connecting Venlo and Hockenheim * Benoni Defense The Benoni Defense is a chess opening characterized by an early reply of ...c5 against White's opening move 1.d4. Most commonly, it is reached by the sequence: :1. d4 Nf6 :2. c4 c5 :3. d5 Black can then sacrifice a pawn with 3...b5 (the Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the north-west, West Yorkshire to the north, South Yorkshire to the north-east, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south-east, Staffordshire to the west and south-west and Cheshire to the west. Kinder Scout, at , is the highest point and Trent Meadows, where the River Trent leaves Derbyshire, the lowest at . The north–south River Derwent is the longest river at . In 2003, the Ordnance Survey named Church Flatts Farm at Coton in the Elms, near Swadlincote, as Britain's furthest point from the sea. Derby is a unitary authority area, but remains part of the ceremonial county. The county was a lot larger than its present coverage, it once extended to the boundaries of the City of Sheffield district in South Yorkshire where it cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Central Main Line
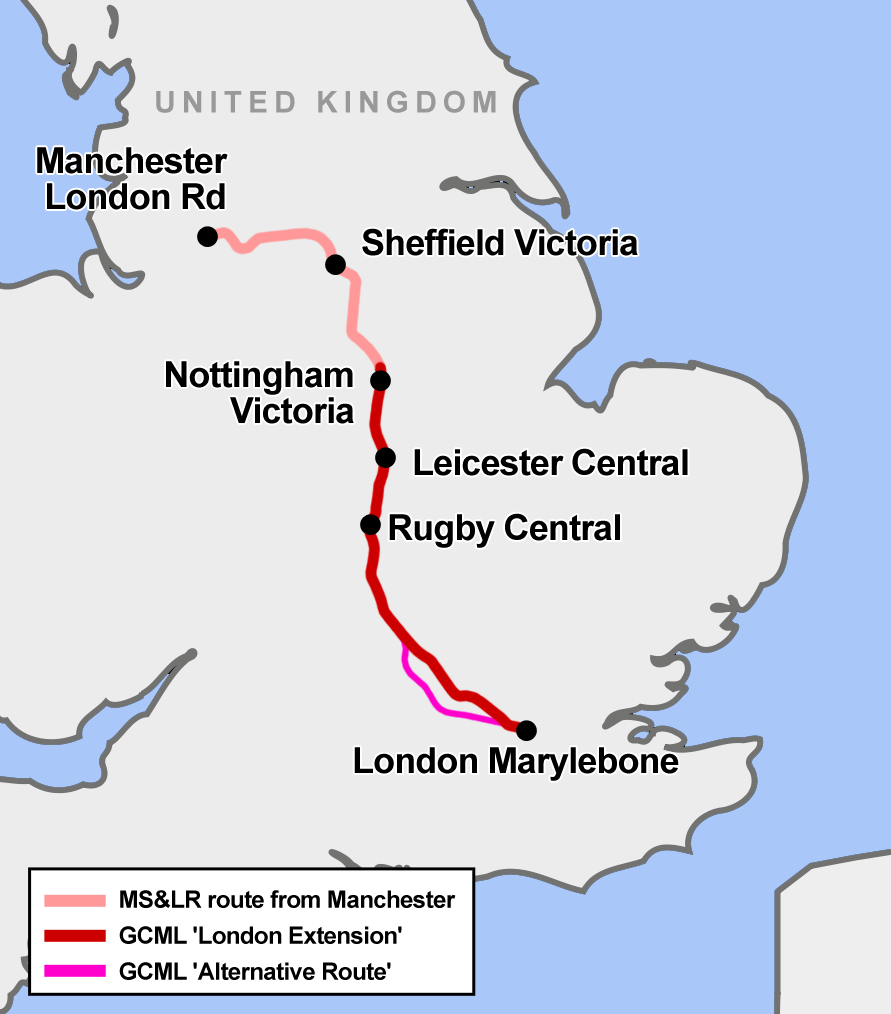
The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railway running from Sheffield in the North of England, southwards through Nottingham and Leicester to Marylebone in London. The GCML was the last main line railway to be built in Britain during the Victorian period. Built by the railway entrepreneur Edward Watkin with the aim to run as a fast trunk route from the North and the East Midlands to London and the south of England. Initially not a financial success, it recovered under the leadership of Sam Fay. Although initially planned for long-distance passenger services, in practice the line's most important function became to carry goods traffic, notably coal. In the 1960s, the line was considered by Dr Beeching as an unnecessary duplication of other lines that served the same places, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_4_Station_geograph-2152795.jpg)