|
Charles Feake
Charles Feake (c.1716–1762) was an English physician and Fellow of the Royal Society. Life He was the son of Samuel Feake (died 1757) of Durrington Hall in Essex from 1720. He was born in Cossimbazar, West Bengal, where his father was governor of Fort William (1718 to 1723). He was educated at Stoke Newington (Mr Stuckey), at Newcome's School for three years, and Caius College, Cambridge where he matriculated in 1732, later graduating later M.B. in 1738 and M.D. in 1743. Feake was physician to Guy's Hospital, from 1745, when for the first time the hospital took on a third physician. He became a Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians in 1745 and a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1748; and gave the Harveian Oration The Harveian Oration is a yearly lecture held at the Royal College of Physicians of London. It was instituted in 1656 by William Harvey, discoverer of the systemic circulation. Harvey made financial provision for the college to hold an annual feas ... in 1749. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellow, Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Wilks
Sir Samuel Wilks, 1st Baronet, (2 June 1824 – 8 November 1911) was a British physician and biographer. Early life Samuel Wilks was born on 2 June 1824 in Camberwell, London, the second son of Joseph Barber Wilks, a cashier at the East India House. After attending Aldenham School and University College School he was apprenticed to Richard Prior, a doctor in Newington. Career In 1842 he entered Guy's Hospital to study medicine. After graduating MB in 1848 he was hired as a physician to the Surrey Infirmary (1853). In 1856 he returned to Guy's Hospital, first as assistant physician and curator of its museum (a post he held for nine years), then as physician and lecturer on medicine (1857). From 1866 to 1870 he was examiner in the practice of medicine at the University of London and from 1868 to 1875 examiner in medicine at the Royal College of Surgeons. Achievements Among his major discoveries, Wilks recognised ulcerative colitis in 1859, differentiating it from bacterial dyse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki Ramakrishnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century English Medical Doctors
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1762 Deaths
Year 176 ( CLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Proculus and Aper (or, less frequently, year 929 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 176 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * November 27 – Emperor Marcus Aurelius grants his son Commodus the rank of ''Imperator'', and makes him Supreme Commander of the Roman legions. * December 23 – Marcus Aurelius and Commodus enter Rome after a campaign north of the Alps, and receive a triumph for their victories over the Germanic tribes. * The Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius is made. It is now kept at Museo Capitolini in Rome (approximate date). Births * Fa Zheng, Chinese nobleman and adviser (d. 220) * Liu Bian, Chinese emperor of the Han Dynasty ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harveian Oration
The Harveian Oration is a yearly lecture held at the Royal College of Physicians of London. It was instituted in 1656 by William Harvey, discoverer of the systemic circulation. Harvey made financial provision for the college to hold an annual feast on St. Luke's Day (18 October) at which an oration would be delivered in Latin to praise the college's benefactors and ''to exhort the Fellows and Members of this college to search and study out the secrets of nature by way of experiment''. Until 1865, the Oration was given in Latin, as Harvey had specified, and known as the ''Oratio anniversaria''; but it was thereafter spoken in English. Many of the lectures were published in book form. Lecturers (incomplete list) 1656–1700 *1656 Edward Emily *1657 Edmund Wilson *1659 Daniel Whistler *1660 Thomas Coxe *1661 Edward Greaves *1662 Charles Scarburgh *1663 Christopher Terne *1664 Nathan Paget *1665 Samuel Collins *1666-1678 No Orations due to rebuilding following Great Fire of Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal College Of Physicians
The Royal College of Physicians (RCP) is a British professional membership body dedicated to improving the practice of medicine, chiefly through the accreditation of physicians by examination. Founded by royal charter from King Henry VIII in 1518, the RCP is the oldest medical college in England. It set the first international standard in the classification of diseases, and its library contains medical texts of great historical interest. The college is sometimes referred to as the Royal College of Physicians of London to differentiate it from other similarly named bodies. The RCP drives improvements in health and healthcare through advocacy, education and research. Its 40,000 members work in hospitals and communities across over 30 medical specialties with around a fifth based in over 80 countries worldwide. The college hosts six training faculties: the Faculty of Forensic and Legal Medicine, the Faculty for Pharmaceutical Medicine, the Faculty of Occupational Medicine the Fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Thomas Bettany
George Thomas Bettany (30 March 1850 – 2 December 1891) was an English biologist, anthropologist, and author of scientific and popular works. Born in Penzance, Cornwall, the son of George Bettany, a schoolmaster and journalist. Bettany was educated privately and then from 1868 to 1870 at Guy's Hospital. On 1 October 1870 he matriculated at Caius College, Cambridge, where he graduated B.A. 1874 and M.A. 1877. He lectured for some years on biology at Girton and Newnham Colleges, Cambridge, and was lecturer on botany at Guy's Hospital from 1877 to 1886. He edited Ward, Lock, and Co.'s "Science Primers for the People," and the "Popular Library for Literary Treasures," and "The Minerva Library of Famous Books," and occupied the position of English editor of ''Lippincott's Monthly Magazine''. He wrote several books and contributed articles to the ''Dictionary of National Biography'', ''The Times'', '' The Athenaeum'', and other journals. He became a Fellow of the Linnean Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy's Hospital
Guy's Hospital is an NHS hospital in the borough of Southwark in central London. It is part of Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and one of the institutions that comprise the King's Health Partners, an academic health science centre. It is a large teaching hospital and is, with St Thomas' Hospital and King's College Hospital, the location of King's College London GKT School of Medical Education. The hospital's Tower Wing (originally known as Guy's Tower) was, when built in 1974, the tallest hospital building in the world, standing at with 34 floors. The tower was overtaken as the world's tallest healthcare-related building by The Belaire in New York City in 1988. As of June 2019, the Tower Wing, which remains one of the tallest buildings in London, is the world's fifth-tallest hospital building. History The hospital dates from 1721, when it was founded by philanthropist Thomas Guy, who had made a fortune as a printer of Bibles and greatly increased it by speculat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Feake
Samuel Feake (died 16 Jun 1757) was an administrator of the English East India Company. He served as President in the Bay, and Governor and Commander-in-Chief for Fort William. His son Charles Feake was an English physician and Fellow of the Royal Society. Feake was appointed on 12 January 1718 as the Governor of Bengal for the United East India Company after Robert Hedges Robert Hedges may refer to: *Robert Hedges (colonial administrator), President of Bengal, 1713–1718 *Robert Hedges (baseball) Robert Hedges (born 1869 in Jackson County, Missouri – died April 1932 in St. Louis, Missouri) was the owner of the .... He left office on 17 January 1723 and later returned to England due to illness. Death Feake died on 16 June 1757 in London at the aged 75 years. References Presidents of Bengal English businesspeople British East India Company people 18th-century British civil servants 1757 deaths {{UK-gov-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
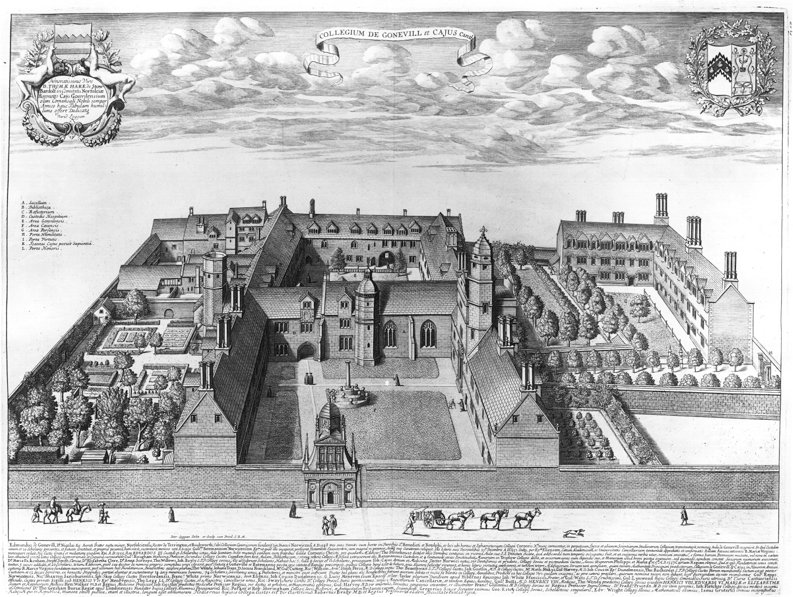
Caius College, Cambridge
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of the wealthiest. The college has been attended by many students who have gone on to significant accomplishment, including fifteen Nobel Prize winners, the second-highest of any Oxbridge college after Trinity College, Cambridge. The college has long historical associations with the teaching of medicine, especially due to its prominent alumni in the medical profession. It also has globally-recognized and prestigious academic programmes in law, economics, English literature, and history. Famous Gonville and Caius alumni include physicians John Caius (who gave the college the caduceus in its insignia) and William Harvey. Other alumni in the sciences include Francis Crick (joint discoverer of the structure of DNA with James Watson), James Chad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcome's School
Newcome's School was a fashionable boys' school in Hackney, then to the east of London, founded in the early 18th century. A number of prominent Whig families sent their sons there. The school closed in 1815, and the buildings were gutted in 1820. In 1825 the London Orphan Asylum opened on the site. Today the Clapton Girls' Academy is located here. History Newcome's school was established in the early 18th century. During the 18th century and early 19th century, Hackney was home to schools of all kinds, including a number of significant dissenting academies. It was considered a healthy area, close to London and with easy access in all weathers via the Old North Road. Many prominent Whig families sent their sons to the school, resulting in a large number of Members of Parliament having received their education there. Dr. Henry Newcome, who gave the school its name, was noted for Whig political principles, and the school stayed in the family for three generations, to 1803. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

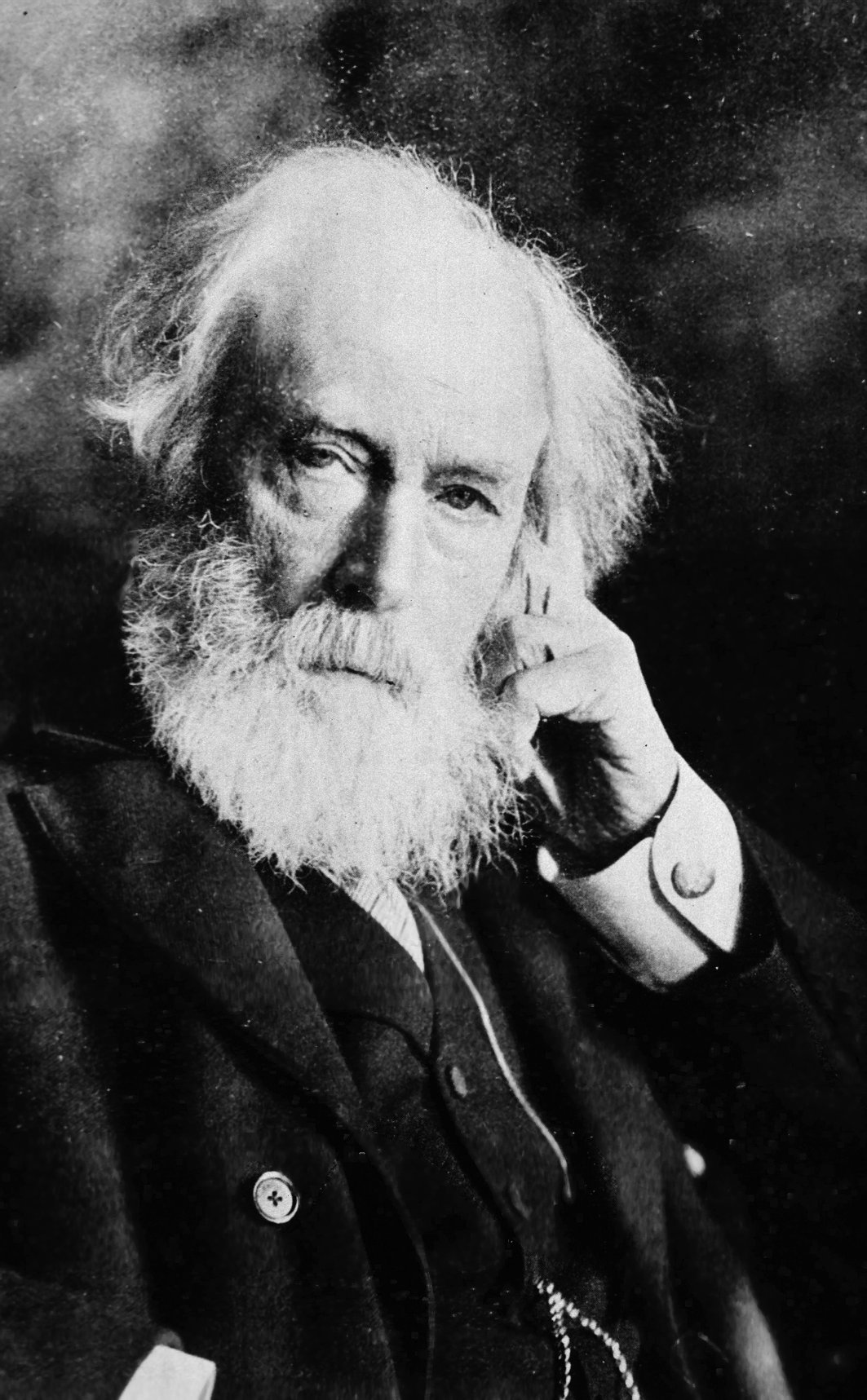
.jpg)