|
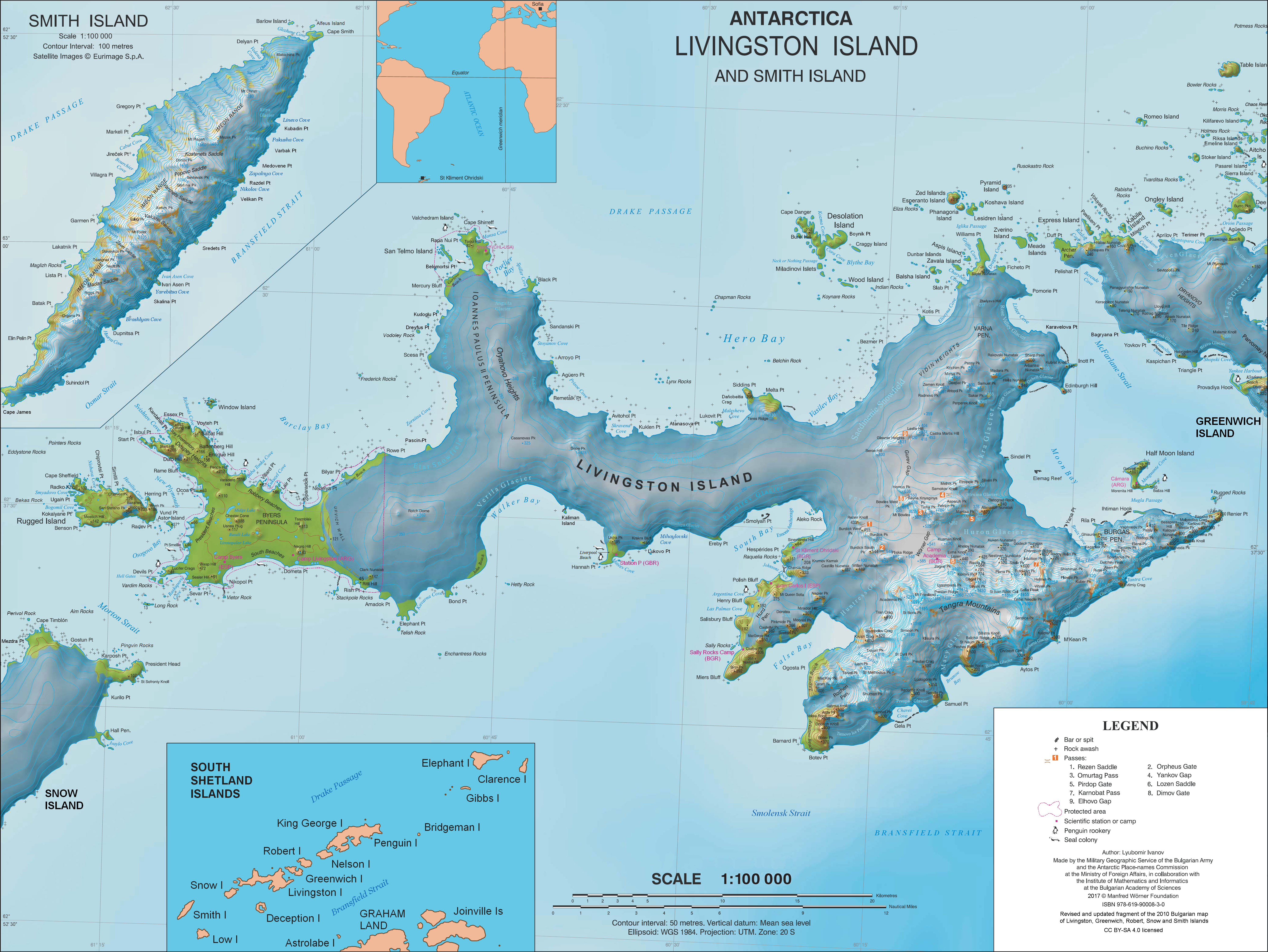
Chapman Rocks
Chapman Rocks is a group of rocks in central Hero Bay on the north side of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Blythe Bay. The feature is named after Thomas Chapman, English trunk-maker of Southwark who in 1795 discovered a method of processing fur seal skins for use in the hat trade, thus initiating the industry in London. Location The rocks are located at which is north-northwest of Siddins Point, northeast of Lynx Rocks, east of Black Point, west-southwest of Iratais Point, Desolation Island, west-southwest of Miladinovi Islets, west by south of Koynare Rocks and northwest of Belchin Rock (British mapping in 1968, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, and Bulgarian in 2009). See also * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Point (Antarctica)
Black Point is a rocky promontory of L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. projecting 800 m northwards from the northeast coast of Ioannes Paulus II Peninsula into Hero Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica to form the east side of the entrance to Porlier Bay. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers. The name of the point is a descriptive one. Fortín Rock is a sea stack lying off Black Point. Location The point is located at which is 4.8 km southeast of Cape Shirreff, 18.3 km west-southwest of Desolation Island, 15.88 km west-northwest of Siddins Point, 10 km north-northwest of Avitohol Point, 6.3 km north by west of Agüero Point and 3 km north by west of Sandanski Point. British mapping in 1968, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, Spanish in 1991, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territorial Claims In Antarctica
Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom – have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and study facilities within their respective claimed territories; however, a number of such facilities are located outside of the area claimed by their respective countries of operation, and countries without claims such as China, India, Italy, Pakistan, Russia, South Africa ( SANAE), Ukraine, and the United States have constructed research facilities within the areas claimed by other countries. There are overlaps among the territories claimed by Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom. History Spanish claims According to Argentina and Chile, the Spanish Crown had claims on Antarctica. The ''capitulación'' (governorship) granted to the conquistador Pedro Sánchez de la Hoz in 1539 by the King of Spain, Charles V, explicitly included al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Committee On Antarctic Research
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scientific work is administered through several discipline-themed ''science groups''. The organisation has observer status at, and provides independent advice to Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings, and also provides information to other international bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). History At the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU)’s Antarctic meeting held in Stockholm from 9–11 September 1957, it was agreed that a committee should be created to oversee scientific research in Antarctica. At the time there were 12 nations actively conducting Antarctic research and they were each invited to nominate one delegate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belchin Rock
Belchin Rock ( bg, text=скала Белчин, italic=no, ‘Skala Belchin’ ska-'la bel-'chin) is a rock off the north coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated in Hero Bay northeast of Siddins Point and north of Melta Point. The rock is named after the settlement of Belchin in western Bulgaria. Location Belchin Rock is located at . Bulgarian mapping in 2009 and 2010. See also * Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research * Territorial claims in Antarctica Map * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. Notes References Belchin Rock.SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer.Antarctic Place-names Commission The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koynare Rocks
Koynare Rocks ( bg, скали Койнаре, ‘Skali Koynare’ ska-'li koy-'na-re) are a small group of rocks in Hero Bay off the north coast Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated northeast of Siddins Point, northwest of Bezmer Point, and south of Miladinovi Islets. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers. The rocks are named after the town of Koynare in northwestern Bulgaria. Location Koynare Rocks are located at (Bulgarian mapping in 2009). See also * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR * Territorial claims in Antarctica Maps * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. Notes References Koynare Rocks.SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer.Antarctic Place-names Commission The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miladinovi Islets
Miladinovi Islets (Miladinovi Ostrovi \mi-la-'di-no-vi 'o-stro-vi\) is a group of two small rocky islands, (surface area L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. ), and respectively, situated south of Iratais Point on Desolation Island off the north coast of Livingston Island, Antarctica. The islands are separated from Desolation Island by Neck or Nothing Passage. The area was frequented by early nineteenth century English and American sealers operating from the adjacent Blythe Bay. Named after the Bulgarian poets and folklorists Dimitar Miladinov (1810–62) and Konstantin Miladinov (1830–62), popular as ‘ Miladinovi Brothers’. See also * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR * Territorial claims in Antarctica Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al., Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desolation Island (South Shetland Islands)
Desolation Island is one of the minor islands in the South Shetlands archipelago, Antarctica situated at the entrance to Hero Bay, Livingston Island. The island is V-shaped with its northern coast indented by Kozma Cove. Surface area .L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. (First edition 2009. ) The island was discovered on 15 October 1819 by Captain William Smith in the English merchant brig ''Williams'' during his second visit to the islands. The anchorage Blythe Bay at the southeast side of Desolation Island was frequented by the early Nineteenth century English and American sealers. Location The island's midpoint is located at , with the island lying northwest of Kotis Point, west of Williams Point and north-northeast of Siddins Point. British mapping in 1820 and 1968, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iratais Point
Iratais Point (Nos Iratais \'nos i-ra-'ta-is\) is a point forming both the south extremity and the vertex of the V-shaped Desolation Island situated in the entrance to Hero Bay, Livingston Island, Antarctica. Separated from Miladinovi Islets to the south by Neck or Nothing Passage. The feature is named after Kavhan (hereditary viceroy function) Iratais, governor of the southern Bulgarian Black Sea region under Khan Krum the Horrible (9th century AD). Location The point is located at which is 3.33 km south-southeast of Cape Danger, 10.55 km west-southwest of Williams Point, 9.75 km north-northeast of Siddins Point and 23.27 km east by south of Cape Shirreff (British mapping in 1968, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009). Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynx Rocks
Lynx Rocks is a group of rocks in southwestern Hero Bay on the north side of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Blythe Bay. The feature is named after the Australian sealing vessel ''Lynx'' under Captain Richard Siddins that visited the South Shetland in 1820-21 and 1821–22, wintering in the Falkland Islands in 1821. Location The rocks are centred at which is west of Siddins Point, north-northeast of Kuklen Point, east of Agüero Point, southeast of Black Point and southwest of Chapman Rocks (British mapping in 1968, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, and Bulgarian in 2009). See also * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |