|
Iratais Point
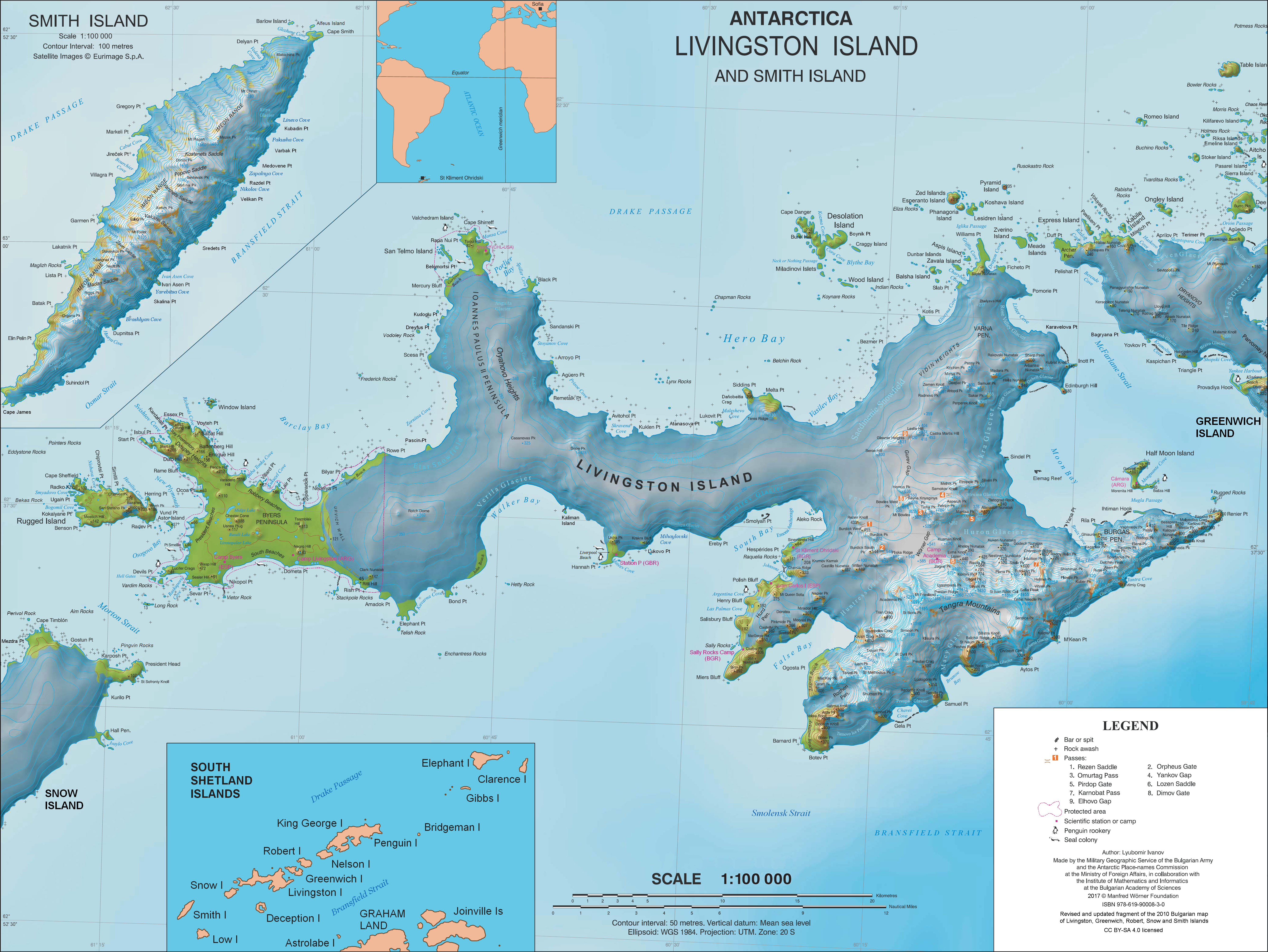
Iratais Point (Nos Iratais \'nos i-ra-'ta-is\) is a point forming both the south extremity and the vertex of the V-shaped Desolation Island situated in the entrance to Hero Bay, Livingston Island, Antarctica. Separated from Miladinovi Islets to the south by Neck or Nothing Passage. The feature is named after Kavhan (hereditary viceroy function) Iratais, governor of the southern Bulgarian Black Sea region under Khan Krum the Horrible (9th century AD). Location The point is located at which is 3.33 km south-southeast of Cape Danger, 10.55 km west-southwest of Williams Point, 9.75 km north-northeast of Siddins Point and 23.27 km east by south of Cape Shirreff (British mapping in 1968, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009). Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krum Of Bulgaria
Krum ( bg, Крум, el, Κροῦμος/Kroumos), often referred to as Krum the Fearsome ( bg, Крум Страшни) was the Khan of Bulgaria from sometime between 796 and 803 until his death in 814. During his reign the Bulgarian territory doubled in size, spreading from the middle Danube to the Dnieper and from Odrin to the Tatra Mountains. His able and energetic rule brought law and order to Bulgaria and developed the rudiments of state organization. Biography Origins Krum was a Bulgar chieftain from Pannonia. His family background and the surroundings of his accession are unknown. It has been speculated that Krum might have been a descendant of the old Bulgar royal house of Kubrat. The name Krum is of Turkic origin and means "governor prince" (from ''kurum'' "rule, leadership, administration"). Establishment of new borders Around 805, Krum defeated the Avar Khaganate to destroy the remainder of the Avars and to restore Bulgar authority in Ongal again, the traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headlands Of Livingston Island
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. . Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff. Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, and granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gazett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Gazetteer Of Antarctica
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Shirreff
Cape Shirreff is a prominent cape at the north end of the rocky peninsula which separates Hero Bay and Barclay Bay on the north coast of Livingston Island, in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. The cape was named by Edward Bransfield in 1820 after Captain William H. Shirreff, the British commanding officer in the Pacific at that time. The seasonal scientific field station Doctor Guillermo Mann Base has been operated by Chile since 1991 and the Shirreff Base by the USA since 1996. Description Situated on a small, ice-free peninsula forming the northern extremity of Ioannes Paulus II Peninsula, which is protected by the Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources Ecosystem Monitoring Programme and requires a permit to enter. It is 24 km north-east of Essex Point, 34 km west-south-west of Williams Point and 21 km north-west of Siddins Point. Lying also 809 km south-south-east of Cape Horn, Cape Shirreff is the locality in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddins Point
Siddins Point () is a point projecting into the middle of the head of Hero Bay on the north coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) an ... (UK-APC) in 1958 for Captain Richard Siddins, Master of the Australian sealer Lynx of Sydney, who visited the South Shetland Islands in 1820-21 and 1821–22. Until 2011 the name was incorrectly spelt 'Siddons Point'. UK Antarctic Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams Point
Williams Point is the point forming both the north extremity of Varna Peninsula and the northeast tip of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Separated from Zed Islands to the north by Iglika Passage. The discovery of the South Shetland Islands was first reported in 1819 by William Smith, Master of the brig ''Williams'' who had sighted the point on 19 February that year. An 1820 publication suggests that Smith gave the name ‘Williams’ to a point of land in this vicinity. In recent years the place name Williams Point has been established in international usage for the point described. Location The point is located at which is 9.47 km north of Miziya Peak in Vidin Heights, 8.8 km east of Desolation Island, 1.5 km south of Zed Islands and 5.5 km west of Duff Point on Greenwich Island. British mapping in 1822, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, Spanish in 1991, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009. Maps Chart of South Shetland inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Danger
Cape Danger is the rocky point forming the northwest extremity of the ice-free Desolation Island situated in the entrance to Hero Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The cape forms the west side of the entrance to Kozma Cove. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Blythe Bay. The feature was charted in 1935 by Discovery Investigations personnel and so named because of a group of sunken rocks extending from the cape. Location The cape is located at which is 12.13 km west of Williams Point, 3.33 km north-northwest of Iratais Point, 11.68 km north-northeast of Siddins Point and 21.6 km east of Cape Shirreff (British mapping in 1935, 1942, 1948 and 1968, Argentine in 1948, 1953 and 1954, Chilean in 1971, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009). Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea covers (not including the Sea of Azov), has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end of the Balkan Mountains; and the Dobruja Plateau considerably farth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |