|
Chakavian
Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , sh-Latn, čakavski proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic regiolect or language spoken primarily by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian Littoral and parts of coastal and southern Central Croatia (now collectively referred to as Adriatic Croatia). Chakavian, like Kajkavian, is not spoken in Serbo-Croatian-speaking regions beyond Croatia. Chakavian was the basis for early literary standards in Croatia. Today, it is spoken almost entirely within Croatia's borders, apart from the Burgenland Croatian in Austria and Hungary and a few villages in southern Slovenia. History Chakavian is one of the oldest written South Slavic varieties that had made a visible appearance in legal documents—as early as 1275 ( Istrian land survey) and 1288 (Vinodol codex), the predominantly vernacular Chakavian is recorded, mixed with elements of Church Slavic. Many of these a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern Istrian
Southwestern Istrian ( hr, Jugozapadni istarski dijalekt), also known as ''Chakavian-Shtokavian'', ''Shtokavian-Chakavian'', or ''Shtakavian-Chakavian ikavian'' ( hr, čakavsko-štokavski/štokavsko-čakavski/štakavsko-čakavski ikavski dijalekt), is one of the dialects of the Chakavian language in Istria, Croatia.Josip Lisac, ''Hrvatska dijalektologija 2: Čakavsko narječje'', 2009, Golden marketing / Tehnička knjiga, str. 51-72. Through the history there were different hypothesis which classified it, besides in Chakavian, instead in Shtokavian, because it is a transitional dialect.Sanja Holjevac, Govor Barbanštine (prilog za opis jugozapadnoga istarskoga ili štokavsko-čakavskoga dijalekta), Lina Pliško, Govor Barbanštine', 2001, časopis Fluminensia, god. 13 br. 1-2, str. 149-154Josip Lisac, Nastanak i razvoj jugozapadnoga istarskog dijalekta', 2003, časopis ''Nova Istra'', br. 8Josip Lisac, Tri dijalekta triju narječja kao najizrazitiji primjeri migracija u hrvatskome j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavic Languages
The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches (West and East) by a belt of German, Hungarian and Romanian speakers. History The first South Slavic language to be written (also the first attested Slavic language) was the variety of the Eastern South Slavic spoken in Thessaloniki, now called Old Church Slavonic, in the ninth century. It is retained as a liturgical language in Slavic Orthodox churches in the form of various local Church Slavonic traditions. Classification The South Slavic languages constitute a dialect continuum. Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin constitute a single dialect within this continuum. *Eastern ** Bulgarian – (ISO 639-1 code: bg; ISO 639-2 code: bul; SIL code: bul; Linguasphere: 53-AAA-hb) ** Macedonian – (ISO 639-1 code: mk; ISO 639-2(B) code: mac; IS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western South Slavic
The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches (West and East) by a belt of German, Hungarian and Romanian speakers. History The first South Slavic language to be written (also the first attested Slavic language) was the variety of the Eastern South Slavic spoken in Thessaloniki, now called Old Church Slavonic, in the ninth century. It is retained as a liturgical language in Slavic Orthodox churches in the form of various local Church Slavonic traditions. Classification The South Slavic languages constitute a dialect continuum. Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin constitute a single dialect within this continuum. *Eastern ** Bulgarian – (ISO 639-1 code: bg; ISO 639-2 code: bul; SIL code: bul; Linguasphere: 53-AAA-hb) ** Macedonian – (ISO 639-1 code: mk; ISO 639-2(B) code: mac; ISO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin. South Slavic languages historically formed a continuum. The turbulent history of the area, particularly due to expansion of the Ottoman Empire, resulted in a patchwork of dialectal and religious differences. Due to population migrations, Shtokavian became the most widespread dialect in the western Balkans, intruding westwards into the area previously occupied by Chakavian and Kajkavian (which further blend into Slovenian in the northwest). Bosniaks, Croats and Serbs differ in religion and were historically often part of different cultural circles, although a large part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kajkavian
Kajkavian (Kajkavian noun: ''kajkavščina''; Shtokavian adjective: ''kajkavski'' , noun: ''kajkavica'' or ''kajkavština'' ) is a South Slavic regiolect or language spoken primarily by Croats in much of Central Croatia, Gorski Kotar and northern Istria.The Kajkavian speech of northern Istria is conventionally called Kajkavian but the features that differentiate it from neighboring Chakavian are not strictly or distinctly Kajkavian nor are those speech forms located in continuum with any other Kajkavian speech in Croatia. Conversely, the same applies to the northeastern Slovene dialects under classification as Slovene that transition into or bundle with Kajkavian Croatian and dialects of both Slovenia and Croatia further south. They have features common to both Slovene across the border as well as Kajkavian elsewhere. There are differing opinions over whether Kajkavian is best considered a dialect of Serbo-Croatian or a fully-fledged language of its own, as it is only partiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgenland Croatian
Burgenland Croatian (; german: Burgenländisch-Kroatisch, Burgenlandkroatisch, burgenlandkroatische Sprache, burgenländisch-kroatischen Sprache, hu, gradiscsei horvát nyelv) is a regional variety of the Chakavian dialect of Croatian spoken in Austria, Hungary, the Czech Republic, Poland and Slovakia. Burgenland Croatian is recognized as a minority language in the Austrian state of Burgenland, where it is spoken by 19,412 people according to official reports (2001). Many of the Burgenland Croatian speakers in Austria also live in Vienna and Graz, due to the process of urbanization, which is mostly driven by the poor economic situation of large parts of Burgenland. Smaller Croatian minorities in western Hungary, southwestern Slovakia, southern Poland and southern Czech Republic are often also called Burgenland Croats. They use the Burgenland Croatian written language and are historically and culturally closely connected to the Austrian Croats. The representatives of the Burgen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Chakavian
Central Chakavian (also translated as Middle Chakavian; hr, srednječakavski dijalekt) is a dialect of the Chakavian variety of Croatian. It is spoken on the islands Dugi, Kornati, Lošinj, Krk, Rab, Ugljan (except the southernmost Southern Chakavian village of Kukljica, exhibiting many shared features with Ugljan's otherwise Central Chakavian dialects) Pag, on the land the cities of Vinodol, Ogulin, Brinje, Otočac, the area around Duga Resa, and part of Central and Northeastern Istria, i.e. between Northern Chakavian and Southern Chakavian This dialect is peculiar for its mixed Ikavian–Ekavian reflex of Common Slavic yat Yat or jat (Ѣ ѣ; italics: ) is the thirty-second letter of the old Cyrillic alphabet and the Rusyn alphabet. There is also another version of yat, the iotified yat (majuscule: , minuscule: ), which is a Cyrillic character combining a ... vowel, which was governed by Meyer–Jakubinskij's law. References * {{Chakavian dialects Diale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
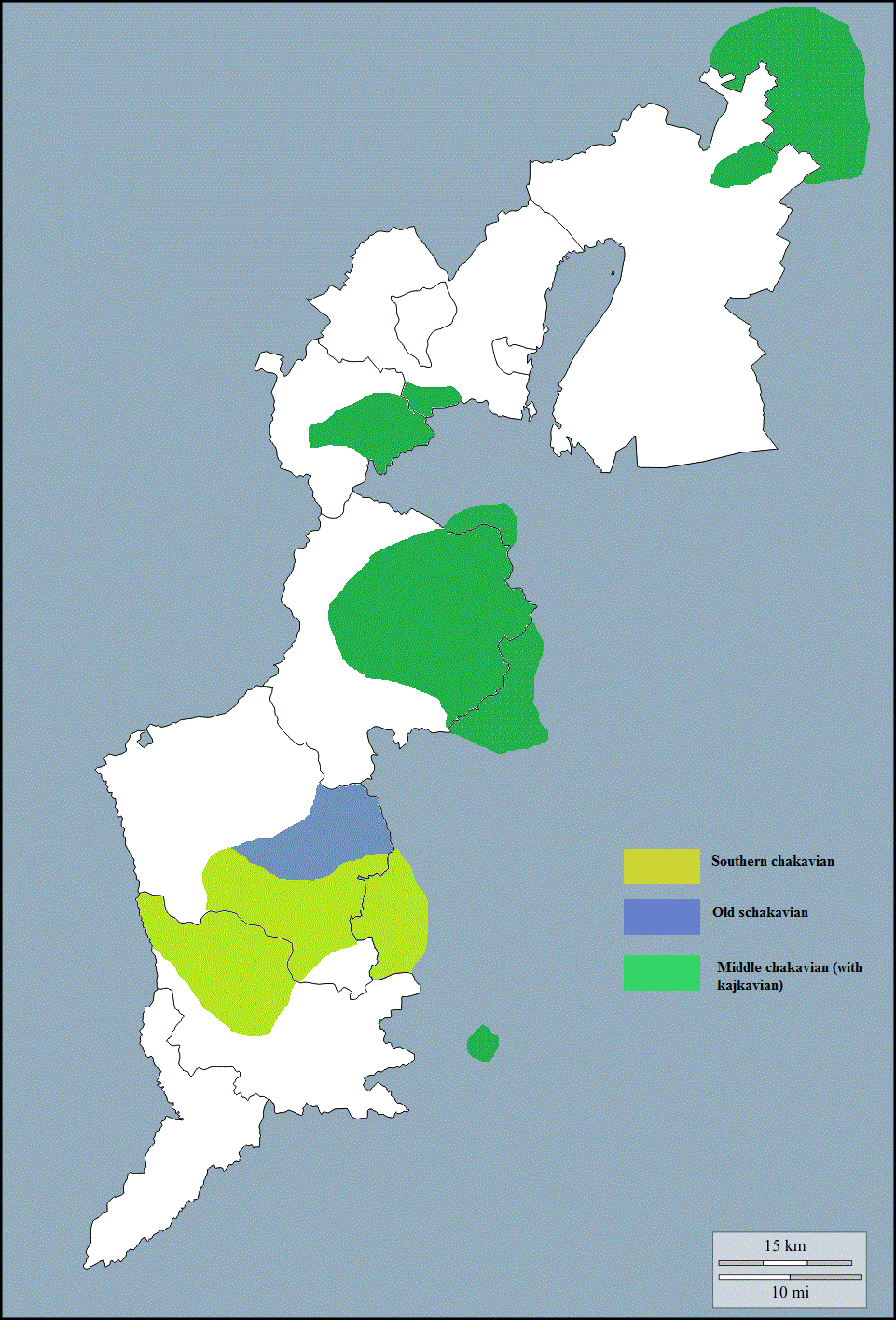
Southern Chakavian
Southern Chakavian ( sh, južnočakavski dijalekt) or Ikavian Chakavian is a dialect of the Chakavian variety of Croatian. It is spoken in the area south of the Central Chakavian area, in a narrow strip of Dalmatian littoral and the neighbouring islands: outskirts of Split and Zadar; Korčula, Pelješac, Brač, Hvar, Vis and Šolta. It is also present in the Northwestern part of Istria. The speech of Split originally belonged to this dialect, but under the influence of Shtokavian immigrants and standard Croatian promoted by the state media, a local variant that has lost many of characteristic Chakavian traits developed, even though a part of older population retains Chakavian in their speech. Much speech in this dialect mixes Chakavian and Shtokavian features. It is assumed that in the past this dialect covered larger territory in the hinterland, being gradually suppressed by constant migrations who carried Shtokavian speech at its cost. Common Slavic yat phoneme had a reflex of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buzet Dialect
The Buzet dialect ( hr, buzetski dijalekt) is a dialect of the Chakavian regiolect or language within Croatia. It is spoken in northern Istria around Buzet. The Buzet dialect is transitional between the Slovenian language and Kajkavian language. Some consider it part of the Kajkavian language area, and in the past it was classified (e.g. by Fran Ramovš) as a Slovenian dialect. The primary features that separate Buzet dialect from the rest of the Chakavian dialects are in the development of the Common Slavic Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium B.C. through the 6th ... vocalism: * */ ě/ > /ẹ/ (closed ''e'') * */e/, */ę/ > opened ''e'' (just like in most Kajkavian speeches) * */u/ > /ü/ * syllabic */l/ > /u/ * */ǫ/ > /a/ Prosodical system diverges from that of other Chakavian speeches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Chakavian
Northern Chakavian ( sh, sjevernočakavski dijalekt) is a dialect of the Chakavian variety of Croatian. It is spoken in eastern Istria, outskirts of Žminj and Pazin, Croatian Littoral up to Bakar, on the islands of Cres and northern Lošinj, north of Central Chakavian. The speech of the major Croatian city Rijeka used to belong to this dialect, but under the influence of Shtokavian immigrants a local idiom developed that lost most of the characteristical Chakavian features. In this dialect Common Slavic yat Yat or jat (Ѣ ѣ; italics: ) is the thirty-second letter of the old Cyrillic alphabet and the Rusyn alphabet. There is also another version of yat, the iotified yat (majuscule: , minuscule: ), which is a Cyrillic character combining a ... phoneme yielded /e/, and only exceptionally /i/ (e.g. 'maiden, girl' < Common Slavic ). References * {{Chakavian dialects[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Slovenia. Due to political, social and economic reasons, many Croats migrated to North and South America as well as New Zealand and later Australia, establishing a diaspora in the aftermath of World War II, with grassroots assistance from earlier communities and the Roman Catholic Church. In Croatia (the nation state), 3.9 million people identify themselves as Croats, and constitute about 90.4% of the population. Another 553,000 live in Bosnia and Herzegovina, where they are one of the three constituent ethnic groups, predominantly living in Western Herzegovina, Central Bosnia and Bosnian Posavina. The minority in Serbia number about 70,000, mostly in Vojvodina. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeastern Chakavian
Southeastern Chakavian ( sh, južnoistočni čakavski dijalekt) or Ijekavian accent is a dialect of the Chakavian variety of Croatian. It is spoken by the peoples of the diaspora of Lastovo, and on the islands of Janjina on Pelješac, Bigova on the south of Montenegro ) , image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Podgorica , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = M .... The Ijekavian accent (Lastovo island, Janjina in Pelješac): */ě/ > /je/ or /ije/ Dialects of Serbo-Croatian {{slavic-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)