|
Censorius
Censorius (died 448) was a count (''comes'') of the Western Roman Empire from 432 until his death. He is mentioned in the ''Chronicle'' of Hydatius under the years 432 and 440. In 432, 437, and 440 he was sent into Hispania as an ambassador to the Suevi. On his second expedition he was accompanied by the legate Fretimund. While returning from his third expedition he was captured by Rechila, the Suevic king, near Mértola (''Myrtilis''). He spent the next eight years in captivity before being executed by Agiulf at Seville (''Hispalis''). His execution may have some connection with the subsequent belligerent attitude of Rechila's successor, Rechiar, towards the Romans. Sources *Thompson, E. A. "The Conversion of the Spanish Suevi to Catholicism." ''Visigothic Spain: New Approaches''. ed. Edward James Edward Frank Willis James (16 August 1907 – 2 December 1984) was a British poet known for his patronage of the surrealist art movement. Early life and marriage James was born o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agiulf
Aioulf or Ag(r)iwulf (died June 457) was an obscure king of Galicia from 456. In 448, after eight years in captivity, the Roman ambassador Censorius was executed by one Agiulf at Seville (''Hispalis''). This Agiulf has sometimes been identified with Aioulf.Thompson, "The Suevic Kingdom of Galicia," 298 n40. According to the local and contemporary chronicler Hydatius, after the sack of Braga and the execution of Rechiar, the previous Suevic king, by the Visigoths, the Gothic king, Theodoric II, led his army south into Lusitania while one of his commanders, Aioulf, deserted him and remained behind in Galicia hoping to make himself king of the Sueves there.Thompson, "The Suevic Kingdom of Galicia," 168. However, the later, Pannonian historian Jordanes records that Aioulf was a Warnic ''cliens'' (retainer) of Theodoric appointed by the king to administer the Suevi and who, being provoked by the Suevi themselves, sought to make himself king but was defeated by Theodoric's army in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
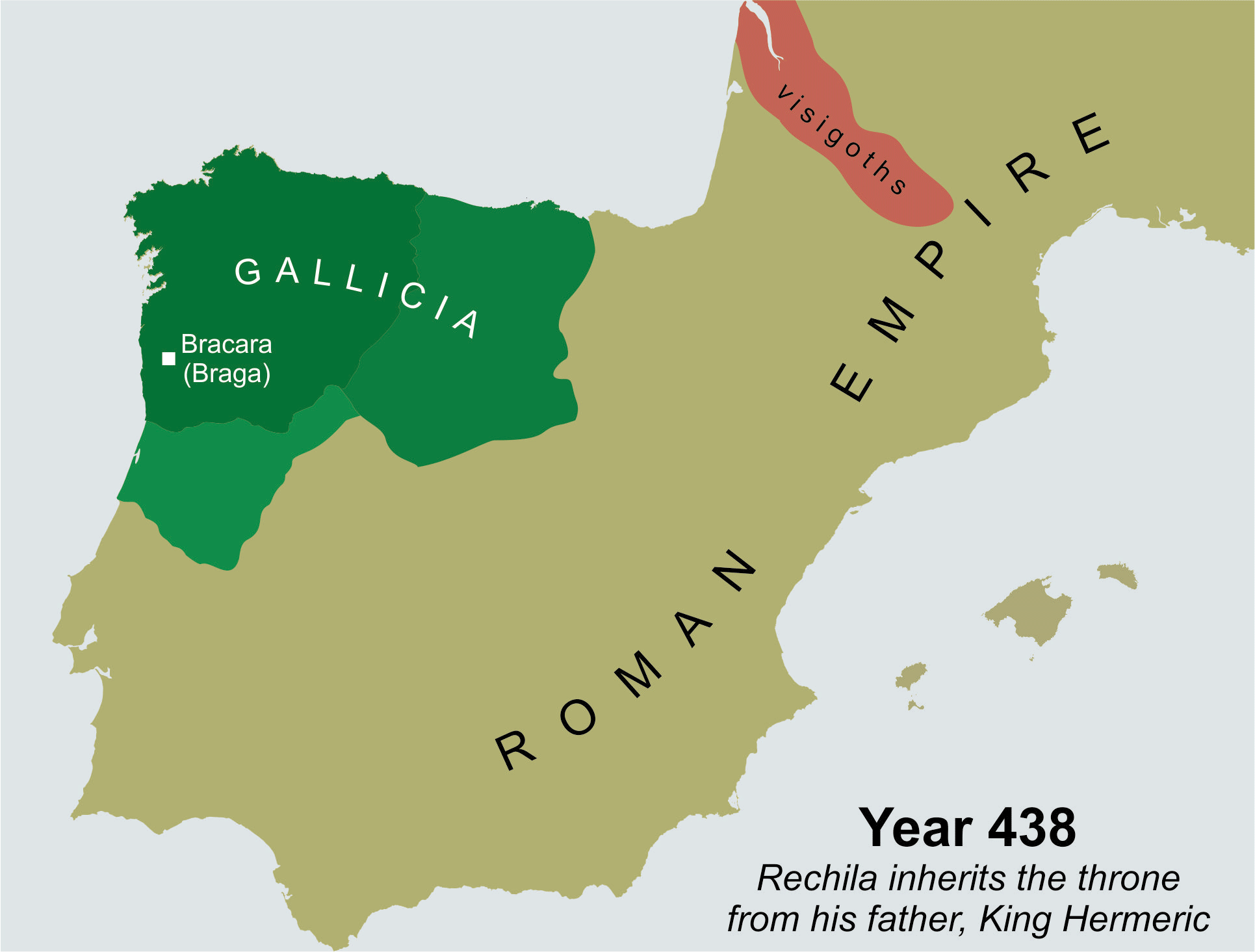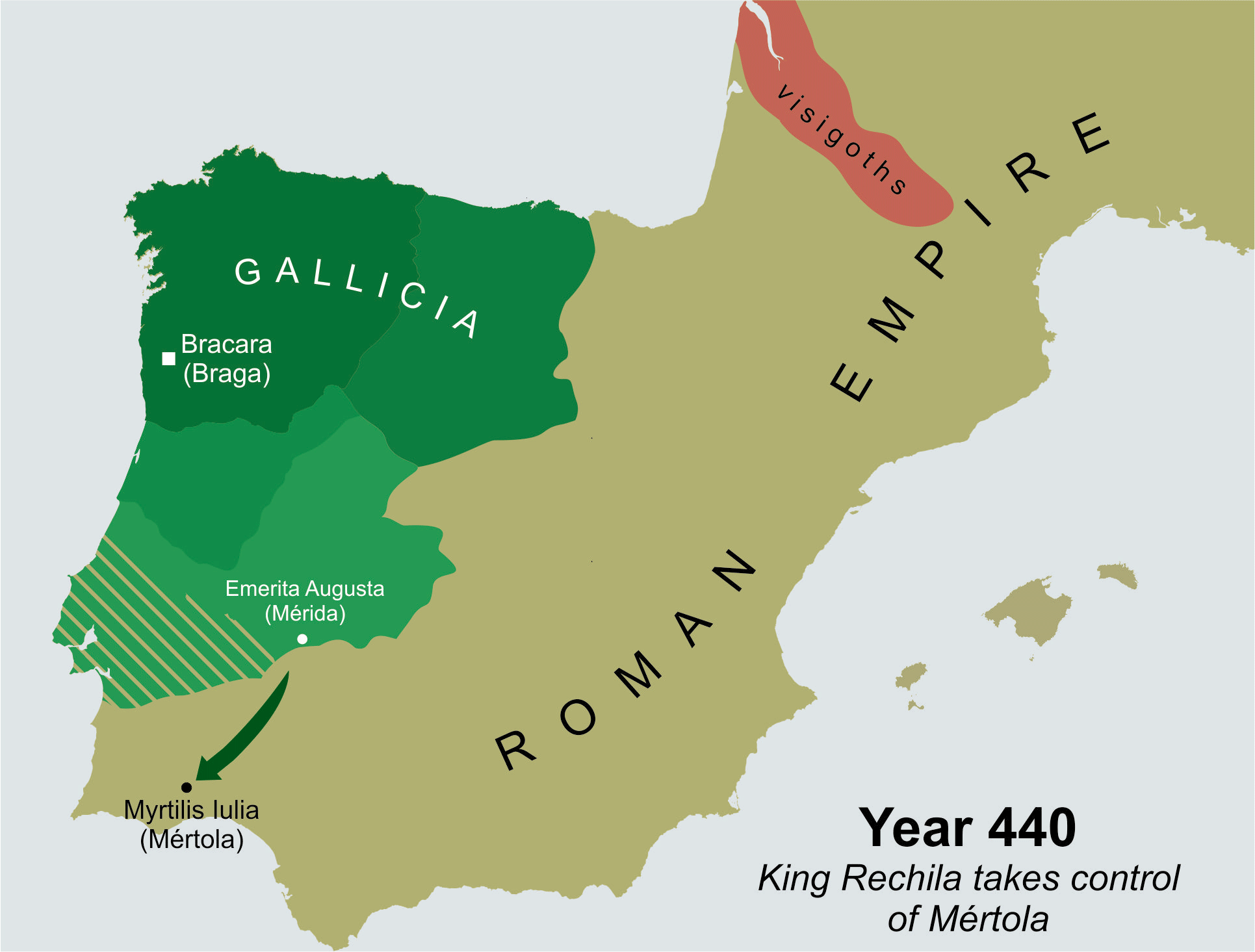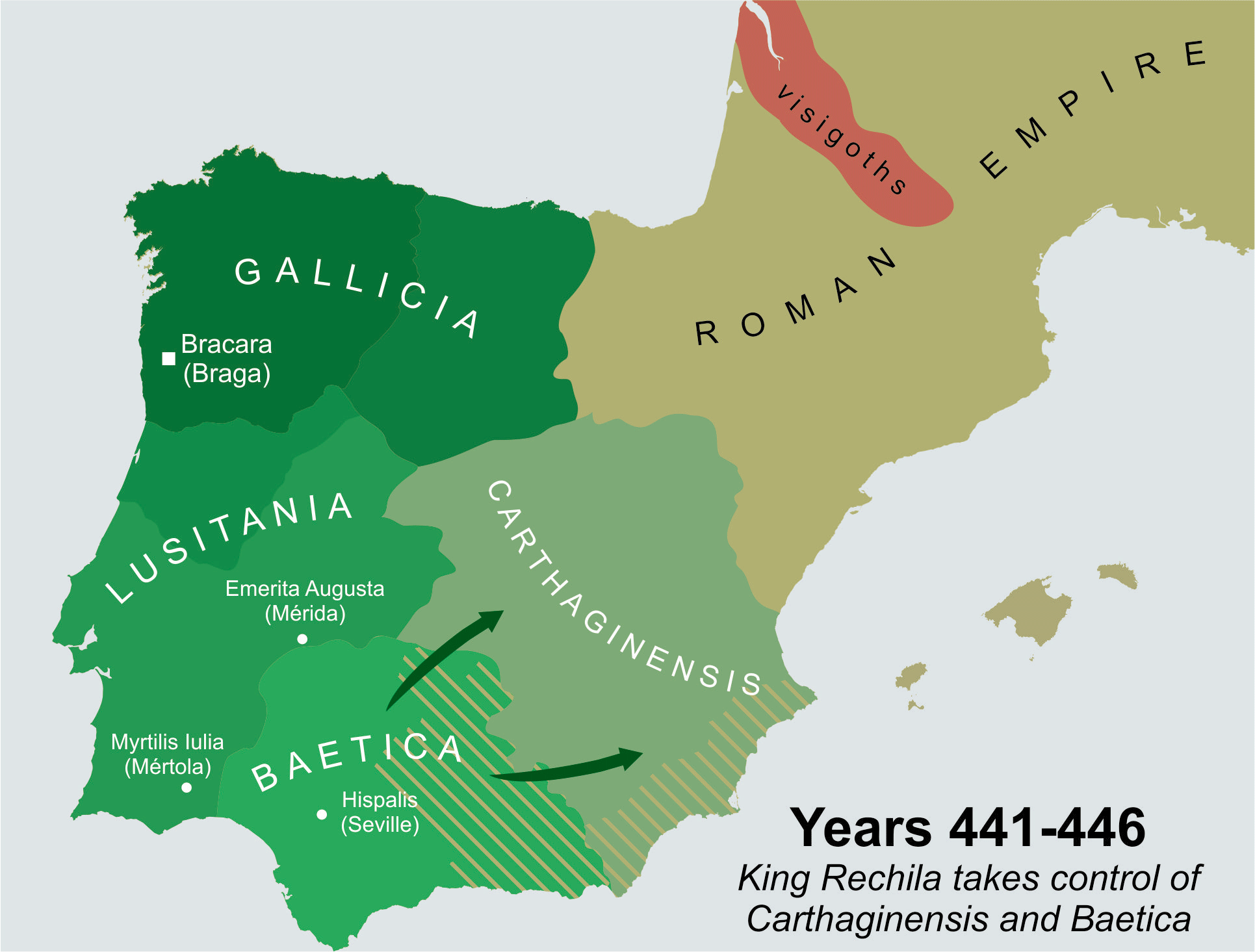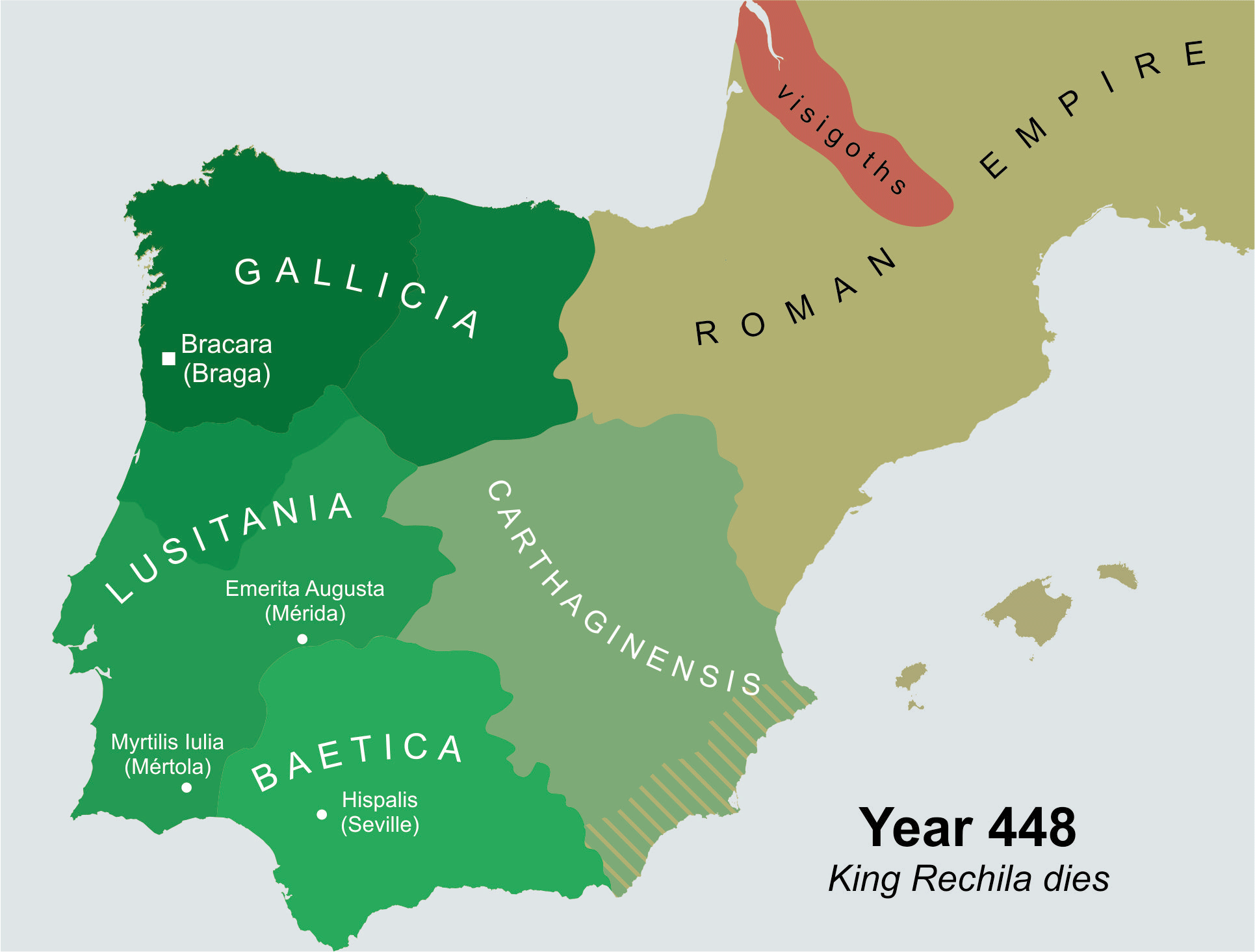
Rechila
Rechila (died 448) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non- Arian) chronicler in Galicia. When his father, Hermeric, turned ill in 438, he retired from active political life (dying in 441) and handed the reins of government and the royal title over to his son. He endeavoured to expand the Suevic kingdom to fill the vacuum left by the retiring Vandals and Alans. In 438 he defeated Andevotus, the '' comes Hispaniarum'', on the river Genil (Singillio). The Roman position in Iberia became so tenuous that three ''magistri utriusque militiae'' (masters of both services) were sent to the peninsula between 441 and 446. Invading southern Iberia, Rechila took the provincial capitals of Mérida in 439 and Seville in 441. These conquests were extremely significant, but nothing of the sequence of events leading to them is known. The provinces of Lusitania, Baetica, and Carthaginiens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rechiar
Rechiar or Flavius Rechiarius (after 415 – December 456) was the third Suevic king of Gallaecia, from 448 until his death, and also the first one to be born in Gallaecia. He was one of the most innovative and belligerent of the Suevi monarchs. Hydatius, the contemporary bishop and chronicler from Galicia who is the sole contemporary source for biographical details of Rechiar, established his reputation as that of a barbarian with little sense of Roman law, culture, or custom; accusations already discredited, but very common at that time. Religion Rechiar was almost certainly not raised Christian, though some scholars have raised the contention that his father raised him that way in order to foster good relations with the Church and the Romanized population who were, for the most part, Catholics as well.Thompson, "The Conversion of the Spanish Suevi", 79. What is certain is the Rechiar had been converted (''catholicus factus'' according to Isidore's '' Historia Suevorum'') be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comes
''Comes'' ( ), plural ''comites'' ( ), was a Roman title or office, and the origin Latin form of the medieval and modern title "count". Before becoming a word for various types of title or office, the word originally meant "companion", either individually or as a member of a collective denominated a "''Comitatus (classical meaning), comitatus''", especially the suite of a magnate, being in some instances sufficiently large and/or formal to justify specific denomination, e.g. a "''cohors amicorum''". "''Comes''" derives from "''com-''" ("with") and "''ire''" ("go"). Ancient Roman religion ''Comes'' was a common epithet or title that was added to the name of a hero or god in order to denote relation with another god. The coinage of Constantine I (emperor), Roman Emperor Constantine I declared him "''comes''" to Sol Invictus ("Unconquered Sun") ''qua'' god. Imperial Roman curial titles and offices styled ''Comites'' Historically more significant, "''comes''" became a secular ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period from 395 to 476, where there were separate coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western and the Eastern provinces, with a distinct imperial succession in the separate courts. The terms Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire were coined in modern times to describe political entities that were ''de facto'' independent; contemporary Romans did not consider the Empire to have been split into two empires but viewed it as a single polity governed by two imperial courts as an administrative expediency. The Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476, and the Western imperial court in Ravenna was formally dissolved by Justinian in 554. The Eastern imperial court survived until 1453. Though the Empire had seen periods with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydatius
Hydatius, also spelled Idacius (c. 400 – c. 469) was a late Western Roman writer and clergyman. The bishop of Aquae Flaviae in the Roman province of Gallaecia (almost certainly the modern Chaves, Portugal, in the modern district of Vila Real), he was the author of a chronicle of his own times that provides us with our best evidence for the history of Hispania in the 5th century. Biography Hydatius was born around the year 400 in the environs of Civitas Lemica, a Roman town near modern Xinzo de Limia in the Spanish Galician province of Ourense. As a young boy, he travelled as a pilgrim to the Holy Land with his mother, where he met Jerome in his hermitage at Bethlehem.Brown, Peter. ''The Rise of Western Christendom''. (Malden, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishing, 2003) p. 99 About the year 417 he joined the clergy, and in 427 was consecrated bishop probably of Chaves (the Roman ''Aquae Flaviae'') in Gallaecia. As bishop he had to come to terms with the presence of non-Roman power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divided into two new provinces, Baetica and Lusitania, while Hispania Citerior was renamed Hispania Tarraconensis. Subsequently, the western part of Tarraconensis was split off, first as Hispania Nova, later renamed "Callaecia" (or Gallaecia, whence modern Galicia). From Diocletian's Tetrarchy (AD 284) onwards, the south of the remainder of Tarraconensis was again split off as Carthaginensis, and all of the mainland Hispanic provinces, along with the Balearic Islands and the North African province of Mauretania Tingitana, were later grouped into a civil diocese headed by a ''vicarius''. The name Hispania was also used in the period of Visigothic rule. The mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suevi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later, such as the Alamanni and Bavarians, and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian. Although Tacitus specified that the Suebian group was not an old tribal group itself, the Suebian peoples are associated by Pliny the Elder with the Irminones, a grouping of Germanic peoples who claimed ancestral connections. Tacitus mentions Suebian languages, and a geographical "Suevia". The Suevians were first mentioned by Julius Caesar in connection with the invasion of Gaul by the Germanic king Ariovistus during the Gallic Wars. Unlike Tacitus he described them as a single people, distinct from the Marcomanni, within the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legatus
A ''legatus'' (; anglicised as legate) was a high-ranking Roman military officer in the Roman Army, equivalent to a modern high-ranking general officer. Initially used to delegate power, the term became formalised under Augustus as the officer in command of a legion. From the times of the Roman Republic, legates received large shares of the military's rewards at the end of a successful campaign. This made the position a lucrative one, so it could often attract even distinguished consuls or other high-ranking political figures within Roman politics (e.g., the consul Lucius Julius Caesar volunteered late in the Gallic Wars as a legate under his first cousin, Gaius Julius Caesar). History Roman Republic The rank of legatus existed as early as the Samnite Wars, but it was not until 190 BC that it started to be standardized, meant to better manage the higher numbers of soldiers the Second Punic War had forced to recruit. The legatus of a Roman Republican army was essentially a sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mértola
Mértola () is a municipality in southeastern Portuguese Alentejo near the Spanish border. In 2011, the population was 7,274, in an area of approximately : it is the sixth-largest municipality in Portugal. Meanwhile, it is the second-lowest population centre by density with approximately 5.62 persons/ (second to the adjacent Alcoutim). The seat of the municipality is the town of Mértola, which has around 2800 inhabitants (2011), located on a hill over the Guadiana River. Its strategic location made it an important fluvial commercial port in Classical Antiquity, through the period of Umayyad conquest of Hispania: Mértola's main church (the Church of Nossa Senhora da Anunciação) was the only medieval mosque to have survived the period in Portugal. In 2017 Mértola started the process to become a UNESCO World Heritage Site. History Romans Mértola was inhabited at least since the Iron Age at least by Conni and Cynetes settlements, was influenced by the Phoenicians and finally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 685,000 , and a metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia, the fourth-largest city in Spain and the 26th most populous municipality in the European Union. Its old town, with an area of , contains three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Alcázar palace complex, the Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded as the Roman city of . Known as ''Ishbiliyah'' after the Islamic conquest in 711, Seville became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward James (historian)
Edward Frederick James (born 14 May 1947) is a British scholar of medieval history and science fiction. He is Emeritus Professor of Medieval History at University College, Dublin. James received the Hugo Award for his non-fiction book ''The Cambridge Companion to Science Fiction'' (co-edited with Farah Mendlesohn), and the Pilgrim Award for lifetime contribution to SF and fantasy scholarship. Biography James was born in Solihull, Warwickshire. He attended the Solihull School and read Modern History at St John's College, Oxford (1965-1968). He completed postgraduate work at the Institute of Archaeology, Oxford, 1968-1970, supervised by Professor Christopher Hawkes. James was awarded D.Phil in 1975, for a thesis entitled ‘South-West Gaul from the fifth to the eighth century: the contribution of archaeology’. He began teaching in 1970 at University College, Dublin. He was a lecturer at the Department of Medieval History in University College Dublin from 1970 to 1978. He was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_Royal_Palace_of_Madrid%2C_Spain_-_20080109-ret.jpg)

_02.jpg)


