|
Castlereagh Nature Reserve
The Castlereagh Nature Reserve is a protected nature reserve located in the western suburbs of Sydney in New South Wales, Australia. The reserve is situated west of the central business district, approximately north-east of and located near the townships of and . In 1960, was reclaimed for use as a Child Welfare Training School, and in 1971, was reclaimed for the establishment of a liquid waste disposal facility. The boundary of the reserve is marked by The Northern Road to the west, by Llandilo Road to the east, rural properties to the south and by the Castlereagh Waste Management Centre to the north. The nature reserve was formerly Castlereagh State Forest and was managed as a production forest from 1917 to 1988, then as a demonstration forest from 1988 to 1995. Features Geology The Castlereagh Nature Reserve contains a geographically restricted substrate of Tertiary alluvials producing clays, sand, gravel and shales at depth. Parts of the reserve support Cumbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castlereagh, New South Wales
Castlereagh is a suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Castlereagh is north-west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Penrith and is part of the Greater Western Sydney region. History The suburb is one of the most historic sites in Australia's colonial history, being one of the five Macquarie towns officially proclaimed on 6 December 1810. Governor Lachlan Macquarie recorded the following in his journal "the Township for the Evan or Nepean District I have named Castlereagh in honor (sic) of Lord Viscount Castlereagh", Secretary of State for War and the Colonies 1805–1806. He, in turn, was named after Castlereagh in Northern Ireland. The official Government and General Order issued from Government House, Sydney was dated 15 December 1810. The earliest known European development was the building of '' Hadley Park'', between what is now Castlereagh Road and the Nepean River. Charles Hadley was given a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mugga
''Eucalyptus sideroxylon'', commonly known as mugga ironbark, or red ironbark is a small to medium-sized tree that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has dark, deeply furrowed ironbark, lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds in groups of seven, white, red, pink or creamy yellow flowers and cup-shaped to shortened spherical fruit. Description ''Eucalyptus sideroxylon'' is a tree that typically grows to a height of and forms a lignotuber. The bark is dark grey to black, deeply furrowed ironbark on the trunk and larger branches, smooth white to grey on the thinnest branches. Young plants and coppice regrowth have lance-shaped to oblong or linear leaves that are long and wide. Adult leaves are lance-shaped, the same shade of green on both sides, long and wide tapering to a petiole long. The flower buds are arranged in leaf axils on an unbranched peduncle long, the individual buds on pedicels long. Mature buds are oval or diamond-shaped, long and wide with a conical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawkesbury River
The Hawkesbury River, or Hawkesbury-Nepean River, is a river located northwest of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The Hawkesbury River and its associated main tributary, the Nepean River, almost encircle the metropolitan region of Sydney. The Hawkesbury River has its origin at the confluence of the Nepean River and the Grose River, to the north of Penrith and travels for approximately in a north–easterly and then a south–easterly direction to its mouth at Broken Bay, about from the Tasman Sea. The Hawkesbury River is the main tributary of Broken Bay. Secondary tributaries include Brisbane Water and Pittwater, which, together with the Hawkesbury River, flow into Broken Bay and thence into the Tasman Sea north of Barrenjoey Head. The total catchment area of the river is approximately and the area is generally administered by the Hawkesbury–Nepean Catchment Management Authority. The land adjacent to the Hawkesbury River was occupied by Aboriginal peoples: th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Reserves In Sydney
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Of New South Wales
The Protected areas of New South Wales include both terrestrial and marine protected areas. there are 225 national parks in New South Wales. Based on the Collaborative Australian Protected Area Database (CAPAD) 2020 data there are 2136 separate terrestrial protected areas with a total land area of (9.61% of the state's area). CAPAD data also shows 18 marine protected areas with a total area of , covering 39.63% of NSW waters. History New South Wales established the first known protected area in Australia, Royal National Park in 1879. The formation of the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service in 1967 saw a bid in the conservation of the state's diversity of natural ecosystems and cultural heritage. Today New South Wales contains more than 16.4 million acres within 870 protected areas, as well as 225 different national parks, each with their own pristine beauty and tranquil scenery. New conservation areas In June 2020 the Government of New South Wales acquired , or of priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Composition
Species richness is the number of different species represented in an community (ecology), ecological community, landscape or region. Species richness is simply a count of species, and it does not take into account the Abundance (ecology), abundances of the species or their Relative species abundance, relative abundance distributions. Species richness is sometimes considered synonymous with species diversity, but the formal metric species diversity takes into account both species richness and species evenness. Sampling considerations Depending on the purposes of quantifying species richness, the individuals can be Forest inventory#Simple random sampling, selected in different ways. They can be, for example, trees found in an forest inventory, inventory plot, birds observed from a monitoring point, or beetles collected in a pitfall trap. Once the set of individuals has been defined, its species richness can be exactly quantified, provided the species-level Taxonomy (biology), taxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
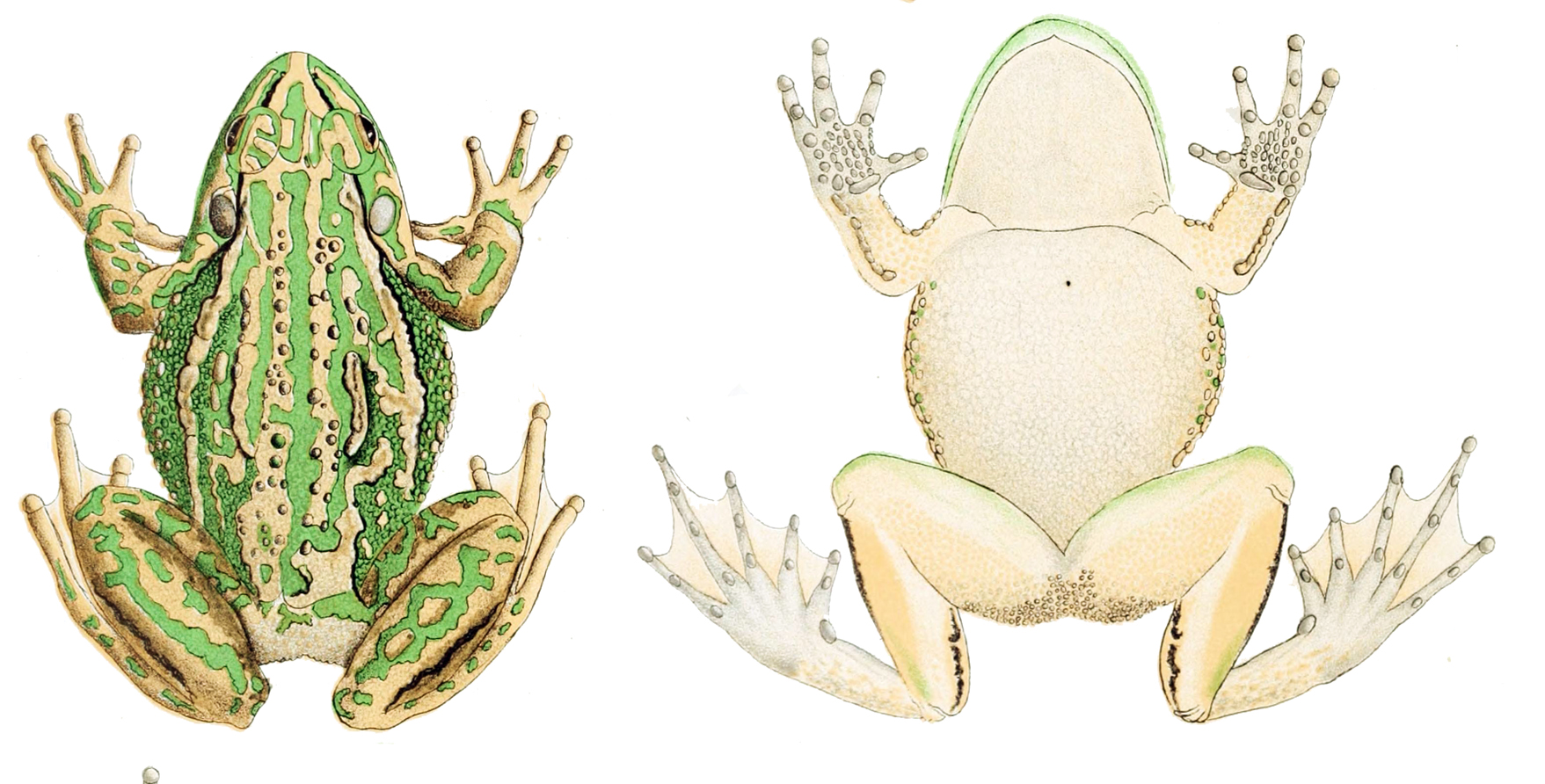
Litoria Aurea
The green and golden bell frog (''Ranoidea aurea''), also named the green bell frog, green and golden swamp frog and green frog, is a species of ground-dwelling tree frog native to eastern Australia. Despite its classification and climbing abilities, it does not live in trees and spends almost all of its time close to ground level. It can reach up to in length, making it one of Australia's largest frogs. Coloured gold and green, the frogs are voracious eaters of insects, but will also eat larger prey, such as worms and mice. They are mainly diurnal, although this is mostly to warm in the sun. They tend to be less active in winter except in warmer or wetter periods, and breed in the warmer months. Males reach maturity after around 9 months, while for the larger females, this does not occur until they are two years old. The frogs can engage in cannibalism, and males frequently attack and injure one another if they infringe on one another's space. Many populations, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudonaja Textilis
The eastern brown snake (''Pseudonaja textilis''), often referred to as the common brown snake, is a species of highly venomous snake in the family Elapidae. The species is native to eastern and central Australia and southern New Guinea. It was first described by André Marie Constant Duméril, Gabriel Bibron, and Auguste Duméril in 1854. The adult eastern brown snake has a slender build and can grow to in length. The colour of its surface ranges from pale brown to black, while its underside is pale cream-yellow, often with orange or grey splotches. The eastern brown snake is found in most habitats except dense forests, often in farmland and on the outskirts of urban areas, as such places are populated by its main prey, the house mouse. The species is oviparous. The International Union for Conservation of Nature classifies the snake as a least-concern species, though its status in New Guinea is unclear. Considered the world's second-most venomous land snake after the inland t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
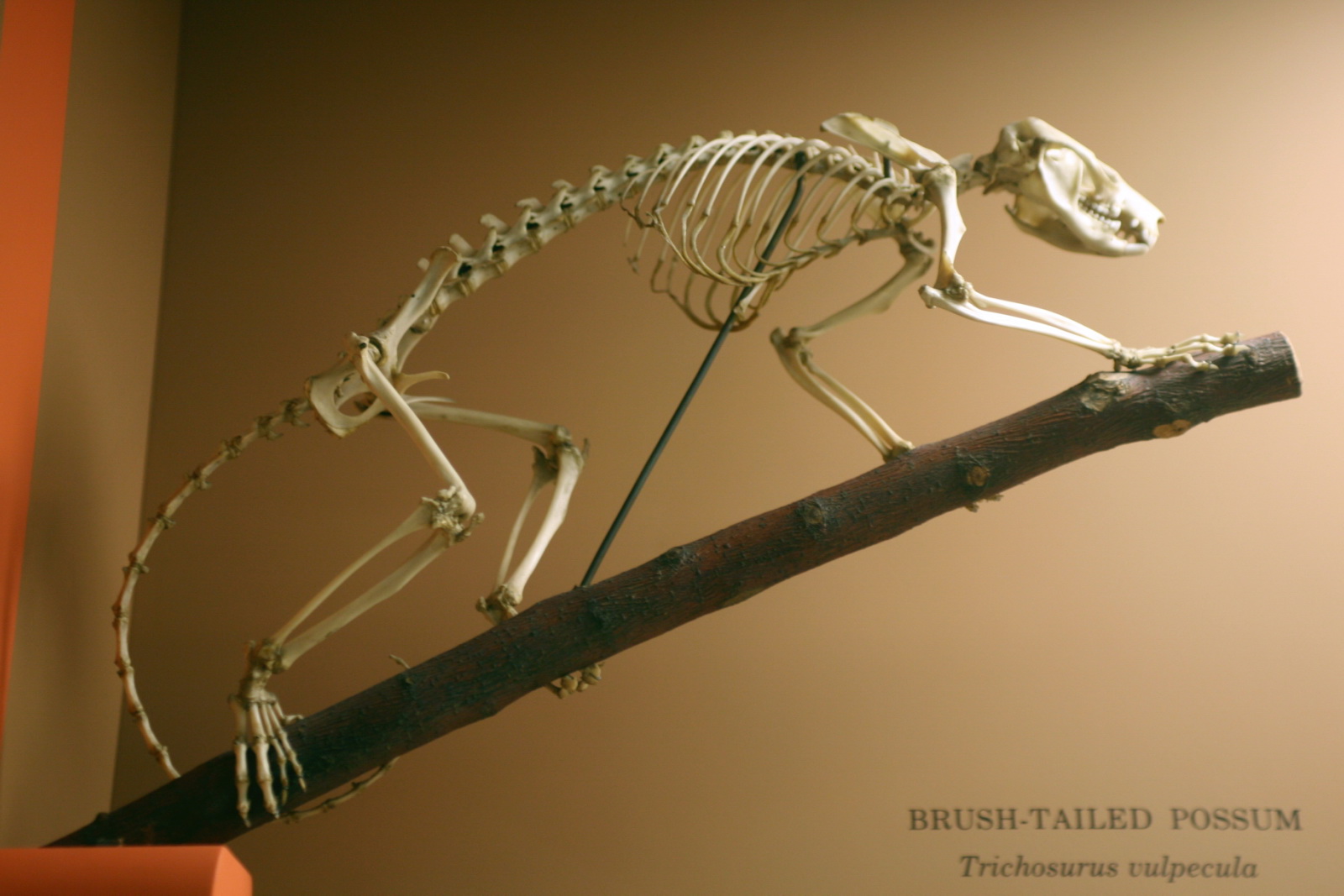
Trichosurus Vulpecula
The common brushtail possum (''Trichosurus vulpecula'', from the Greek for "furry tailed" and the Latin for "little fox", previously in the genus ''Phalangista'') is a nocturnal, semiarboreal marsupial of the family Phalangeridae, native to Australia and naturalised in New Zealand, and the second-largest of the possums. Like most possums, the common brushtail possum is nocturnal. It is mainly a folivore, but has been known to eat small mammals such as rats. In most Australian habitats, eucalyptus leaves are a significant part of the diet, but rarely the sole item eaten. Its tail is prehensile and naked on its lower underside. The four colour variations are silver-grey, brown, black, and gold. It is the Australian marsupial most often seen by city dwellers, as it is one of few that thrive in cities and a wide range of natural and human-modified environments. Around human habitations, common brushtails are inventive and determined foragers with a liking for fruit trees, vegetable g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sideroxylon
''Sideroxylon'' is a genus of trees in the family Sapotaceae described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753. They are collectively known as bully trees. The generic name is derived from the Greek words σιδηρος (''sideros''), meaning "iron", and ξύλον (''xylon''), meaning "wood." Distribution The genus is distributed mainly in North and South America, but also in Africa, Madagascar, southern Asia, and various oceanic islands. Some species, such as gum bully ('' S. lanuginosum''), '' S. tenax'', and buckthorn bully ('' S. lycioides''), are found in subtropical areas of North America. The only South African species, the white milkwood ('' S. inerme''), is associated with three historical sites, and these individuals were declared national monuments due to their unusual longevity. Ecology Several species have become rare due to logging and other forms of habitat destruction. The Tambalacoque ('' S. grandiflorum'', syn. ''Calvaria major'') of Mauritius was affected by the exti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironbark
Ironbark is a common name of a number of species in three taxonomic groups within the genus ''Eucalyptus'' that have dark, deeply furrowed bark. Instead of being shed annually as in many of the other species of ''Eucalyptus'', the dead bark accumulates on the trees, forming the fissures. It becomes rough after drying out and becomes impregnated with kino (red gum), a dark red tree sap exuded by the tree. The tree is so named for the apparent resemblance of its bark to iron slag. The bark is resistant to fire and heat and protects the living tissue within the trunk and branches from fire. In cases of extreme fire, where leaves and shoots are removed, the protective bark aids in protecting epicormic buds which allow the tree to reshoot. Being a very dense, hard wood, a length of ironbark is often used as a bug shoe on the bottom of a ship's skeg to protect it from shipworms. Ironbark was widely used in the piles of 19th and early 20th century bridges and wharves in New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)