|
Carrick On Suir
Carrick-on-Suir () is a town in County Tipperary, Ireland. It lies on both banks of the River Suir. The part on the north bank of the Suir lies in the civil parish of "Carrick", in the historical barony of Iffa and Offa East. The part on the south bank lies in the civil parish of Kilmolerin in the barony of Upperthird, County Waterford. Location Carrick-on-Suir is situated in the south-eastern corner of South Tipperary, 21 kilometres (13 miles) east of Clonmel and 27 kilometres (17 miles) northwest of Waterford. Most of the town lies north of the river in the townland of ''Carrig Mór'' (''Big Rock''), with the remainder of the town on the opposite bank in the townland of ''Carrig Beg'' (Small Rock). The town is connected to Limerick and Waterford by the N24 road and a rail link. Carrick-on-Suir railway station opened on 15 April 1853. Two trains a day operate to Waterford and two trains a day operate to Limerick Junction via Clonmel, Cahir and Tipperary. There is no train se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine (Ireland)
The Great Famine ( ga, an Gorta Mór ), also known within Ireland as the Great Hunger or simply the Famine and outside Ireland as the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of starvation and disease in Ireland from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis which subsequently had a major impact on Irish society and history as a whole. With the most severely affected areas in the west and south of Ireland, where the Irish language was dominant, the period was contemporaneously known in Irish as , literally translated as "the bad life" (and loosely translated as "the hard times"). The worst year of the period was 1847, which became known as "Black '47".Éamon Ó Cuív – the impact and legacy of the Great Irish Famine During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million Irish diaspora, fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% (in some towns falling as much as 67%) between 1841 and 1871.Carolan, MichaelÉireann's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
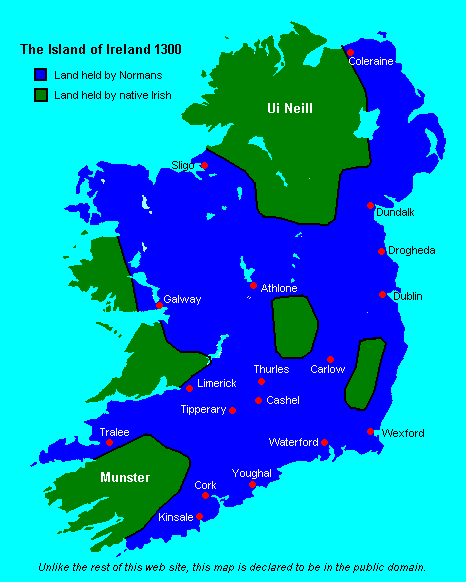
Hiberno-Norman
From the 12th century onwards, a group of Normans invaded and settled in Gaelic Ireland. These settlers later became known as Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans. They originated mainly among Cambro-Norman families in Wales and Anglo-Normans from England, who were loyal to the Kingdom of England, and the English state supported their claims to territory in the various realms then comprising Ireland. During the High Middle Ages and Late Middle Ages the Hiberno-Normans constituted a feudal aristocracy and merchant oligarchy, known as the Lordship of Ireland. In Ireland, the Normans were also closely associated with the Gregorian Reform of the Catholic Church in Ireland. Over time the descendants of the 12th-century Norman settlers spread throughout Ireland and around the world, as part of the Irish diaspora; they ceased, in most cases, to identify as Norman, Cambro-Norman or Anglo-Norman. The dominance of the Norman Irish declined during the 16th century, after a new English Protest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambro-Norman
Cambro-Normans ( la, Cambria; "Wales", cy, Normaniaid Cymreig; nrf, Nouormands Galles) were Normans who settled in South Wales, southern Wales, and the Welsh Marches, after the Norman invasion of Wales, allied with their counterpart families who settled England following its conquest. Usage in Ireland Some Irish historians prefer to use this term instead of Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman because many of the knights who invaded Ireland in 1170, such as the FitzGerald dynasty, FitzGeralds, originated and settled in modern-day Wales, following the Norman conquest. South Wales was under Franco-Norman, House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet control at this point in history and the Cambro-Normans living in south Wales owed their allegiance to the Le Mans born Henry II of England, Henry II, not a native Welsh prince, therefore are often confused with Anglo-Normans, due to their allegiance. Contemporary Irish accounts of this period erroneously called the incomers ''Saxain'', which means " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1247 In Ireland
Events from the year 1247 in Ireland. Incumbent *Lord: Henry III Events *The earliest known records of a settlement at Carrick-on-Suir are dated to 1247, when a charter of three fairs per year was awarded to Matthew Fitzgriffin, Anglo-Norman Lord of the Manor of Carrick. *Battle between Anglo-Normans and Irish led to the Sack of Dun Gallimhe by Irish forces. Births Deaths References 1240s in Ireland Ireland Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ... Years of the 13th century in Ireland {{Ireland-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipperary (Dáil Constituency)
Tipperary is a parliamentary constituency that has been represented in Dáil Éireann, the lower house of the Irish parliament or Oireachtas, since the 2016 general election. The constituency elects 5 deputies ( Teachtaí Dála, commonly known as TDs) on the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV). A constituency of the same name existed between 1923 and 1948. History and boundaries The constituency was created under the Electoral Act 1923, and was first used at the 1923 general election, incorporating the separate counties of North Tipperary and South Tipperary. It was abolished in 1948. The Constituency Commission proposed in its 2012 report that at the next general election a new constituency called Tipperary be created, as part of changes that reduced the total number of TDs from 166 to 158. This occurred in 2016, shortly after the administrative amalgamation in 2014 of the separate counties to form County Tipperary. TDs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dáil Éireann
Dáil Éireann ( , ; ) is the lower house, and principal chamber, of the Oireachtas (Irish legislature), which also includes the President of Ireland and Seanad Éireann (the upper house).Article 15.1.2º of the Constitution of Ireland reads: "The Oireachtas shall consist of the President and two Houses, viz.: a House of Representatives to be called Dáil Éireann and a Senate to be called Seanad Éireann." It consists of 160 members, each known as a (plural , commonly abbreviated as TDs). TDs represent 39 constituencies and are directly elected for terms not exceeding five years, on the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV). Its powers are similar to those of lower houses under many other bicameral parliamentary systems and it is by far the dominant branch of the Oireachtas. Subject to the limits imposed by the Constitution of Ireland, it has power to pass any law it wishes, and to nominate and remove the Taoiseach (head of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahir
Cahir (; ) is a town in County Tipperary in Ireland. It is also a civil parish in the barony of Iffa and Offa West. Location and access For much of the twentieth century, Cahir stood at an intersection of two busy national roadways: the Dublin to Cork N8, and the Limerick to Waterford N24. The N8 was realigned in 1991 to run west of the town, while the old road through it was renumbered the R670. Traffic from the N24 still left the town badly congested, however, until October 2007 when this road was also realigned to bypass Cahir to the north and east. The same road improvement scheme saw major changes to the N8 corridor: a new motorway, the M8, was constructed west of the town between 2006 and 2008. Access to Cahir from this motorway is gained at Junctions 10 and 11. Cahir is on the Limerick–Waterford railway line. The town's railway station opened on 1 May 1852. There are two trains a day to Tipperary and Limerick Junction and two to Clonmel, Carrick on Suir and Waterf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick Junction
Limerick Junction ( ga, Gabhal Luimnigh) is the interchange railway station for trains originating in , , , , and stations. The station opened on 3 July 1848. The station was highly noted for its layout which prior to 1967 required every train making a stop at the station to make a reversal to do so. The latest changes in 2019, including the addition of a new island platform, mean only trains to and from the Waterford direction need to reverse before and after accessing the station. Location The station is located in the townland of Ballykisteen, County Tipperary, Ireland, in the county's historical barony of Clanwilliam. It is some from Limerick City, from , and from . Tipperary town is about away to the south-east, and the station was originally named "Tipperary Junction". The station lies just of the N24 road from Limerick to Waterford. Tipperary Racecourse lies just to the west of the station. Beyond a cluster of railway cottages there has been no development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
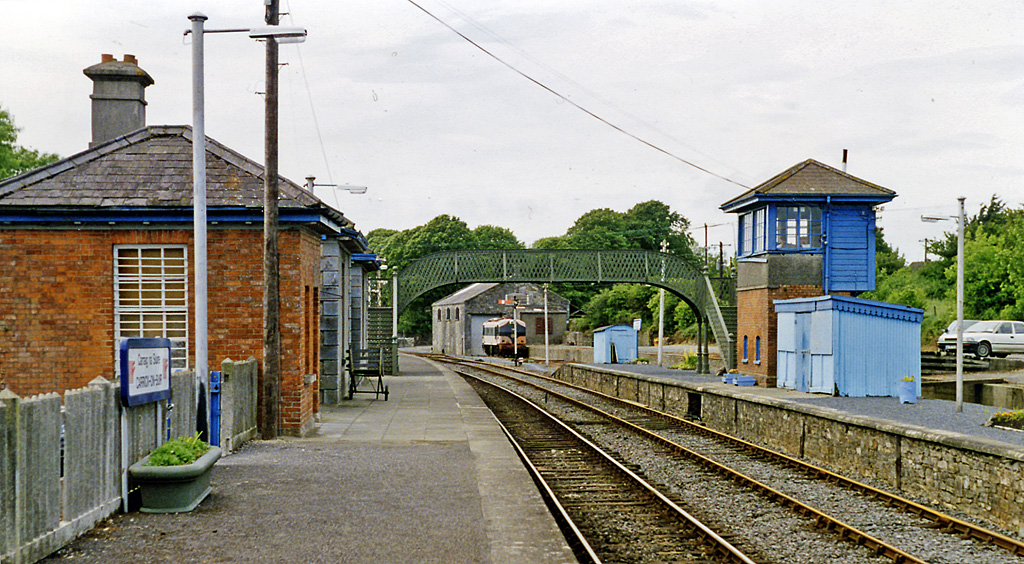
Carrick-on-Suir Railway Station
Carrick-on-Suir railway station serves the town of Carrick-on-Suir, County Tipperary in Ireland. It has a weekday passenger service of two trains to Waterford and two to Limerick Junction. There is no Sunday service. Until 19 January 2013 (inclusive) there were three trains each way. However the late-morning Waterford to Limerick Junction and early-afternoon Limerick Junction to Waterford trains are now discontinued. The station consists of two platforms, a waiting room, toilets and small car park at present free for rail passengers. The second platform, on which the signal cabin is located, was served by a passing loop until November 2013. There is also a siding, used by the Irish Traction Group to store preserved diesel locomotives. History The station opened on 15 April 1853. Statistics Passenger statistics are compiled by the National Transport Authority. The passenger decline is due to unreliable timetables. See also * List of railway stations in Ireland This art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Ireland
Rail transport in Ireland (InterCity, commuter and freight) is provided by Iarnród Éireann in the Republic of Ireland and by Northern Ireland Railways in Northern Ireland. Most routes in the Republic radiate from Dublin. Northern Ireland has suburban routes from Belfast and two main InterCity lines, to Derry and cross-border to Dublin. The accompanying map of the current railway network shows lines that are fully operational (in red), carrying freight only traffic (in black) and with dotted black lines those which have been "mothballed" (i.e. closed to traffic but potentially easy to re-open). Some airports are indicated but none are rail-connected, although Kerry Airport and Belfast City Airport are within walking distance of a railway station. Both the City of Derry Airport and Belfast International (Aldergrove) are near railway lines but not connected. Ports are marked, although few remain rail-connected. Dublin Port, Larne Harbour, Belview Port and Rosslare Europort ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N24 Road (Ireland)
The N24 road is a national primary road in Ireland forming a route from Limerick to Waterford, running through County Tipperary and passing Tipperary Town, Cahir, Carrick-on-Suir and Clonmel. The route begins at its junction with the Limerick Southern M7 ring road (Junction 29). Pallasgreen and Oola are two small villages through which the route passes before reaching Tipperary. Before the town the road passes by Limerick Junction, a major railway intersection for the region. Bansha lies further southeast along the route, and the road meets the M8 Cork – Dublin motorway just outside Cahir. The N24 passes north of Cahir, turning east towards Clonmel. A bypass brings the road around the north of Clonmel, and the road continues east to Carrick-on-Suir. From here the road undulates in an east/southeast/south direction to reach Waterford. The road ends at the start of the M9 to Dublin. History Due to its winding alignment between Clonmel and Cahir, the road now known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_The_Old_Bridge_-_geograph.org.uk_-_95512.jpg)