|
Carnegie Pension
Andrew Carnegie (, ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century and became one of the richest Americans in history. He became a leading philanthropist in the United States, Great Britain, and the British Empire. During the last 18 years of his life, he gave away around $350 million (roughly $ billion in ), almost 90 percent of his fortune, to charities, foundations and universities. His 1889 article proclaiming "The Gospel of Wealth" called on the rich to use their wealth to improve society, expressed support for progressive taxation and an estate tax, and stimulated a wave of philanthropy. Carnegie was born in Dunfermline, Scotland, and emigrated to Pittsburgh with his parents in 1848 at age 12. Carnegie started work as a telegrapher, and by the 1860s had investments in railroads, railroad sleeping cars, bridges, and oil derricks. He accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunfermline
Dunfermline (; sco, Dunfaurlin, gd, Dùn Phàrlain) is a city, parish and former Royal Burgh, in Fife, Scotland, on high ground from the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. The city currently has an estimated population of 58,508. According to the National Records of Scotland, the Greater Dunfermline area has a population of 76,210. The earliest known settlements in the area around Dunfermline probably date as far back as the Neolithic period. The area was not regionally significant until at least the Bronze Age. The town was first recorded in the 11th century, with the marriage of Malcolm III of Scotland, Malcolm III, King of Scots, and Saint Margaret of Scotland, Saint Margaret at the church in Dunfermline. As his List of Scottish consorts, Queen consort, Margaret established a new church dedicated to the Trinity, Holy Trinity, which evolved into an Dunfermline Abbey, Abbey under their son, David I of Scotland, David I in 1128. During the reign of Alexander I of Scotlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Council For Ethics In International Affairs
The Carnegie Council for Ethics in International Affairs is a New York City-based 501(c)3 public charity serving international affairs professionals, teachers and students, and the attentive public. Founded in 1914, and originally named ''Church Peace Union'', Carnegie Council is an independent and nonpartisan institution, aiming to be the foremost voice of ethics in international affairs. The Council focuses on, ''Ethics, War and Peace'', ''Global Social Justice'', and ''Religion in Politics'' as its three main themes. It is separate and independent from all other Carnegie philanthropies. Carnegie Council publishes ''Ethics & International Affairs'', a quarterly academic journal that examines the intersection of moral issues and the international sphere. Among Carnegie Council's programs is Global Policy Innovations, which publishes '' Policy Innovations,'' an online magazine. Mission The Council convenes agenda-setting forums and creates educational opportunities and inform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Richest Americans In History
Most sources agree that John D. Rockefeller was the richest American in history having amassed a wealth of more than $445 billion in 2022 dollars. There are various methods of comparing individuals' wealth across time, including using simple inflation-adjusted totals or calculating an individual's wealth as a share of contemporary gross domestic product (GDP). For example, economic blogger Scott Sumner noted in 2018 that Rockefeller was worth $1.4 billion when he died in 1937, which was about $24 billion in dollars adjusted to 2018. Meanwhile, Bill Gates in 1999 was worth nearly $150 billion in dollars adjusted to 2018. The second-richest person in terms of wealth vs. contemporary GDP is disputed. Most sources list Andrew Carnegie, but others say Gates, Cornelius Vanderbilt I, John Jacob Astor IV, or Henry Ford. Lower ranks are a matter of even bigger debate. Vanderbilt left a fortune worth $100 million upon his death in 1870 ($ today). As the United States became the foremos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
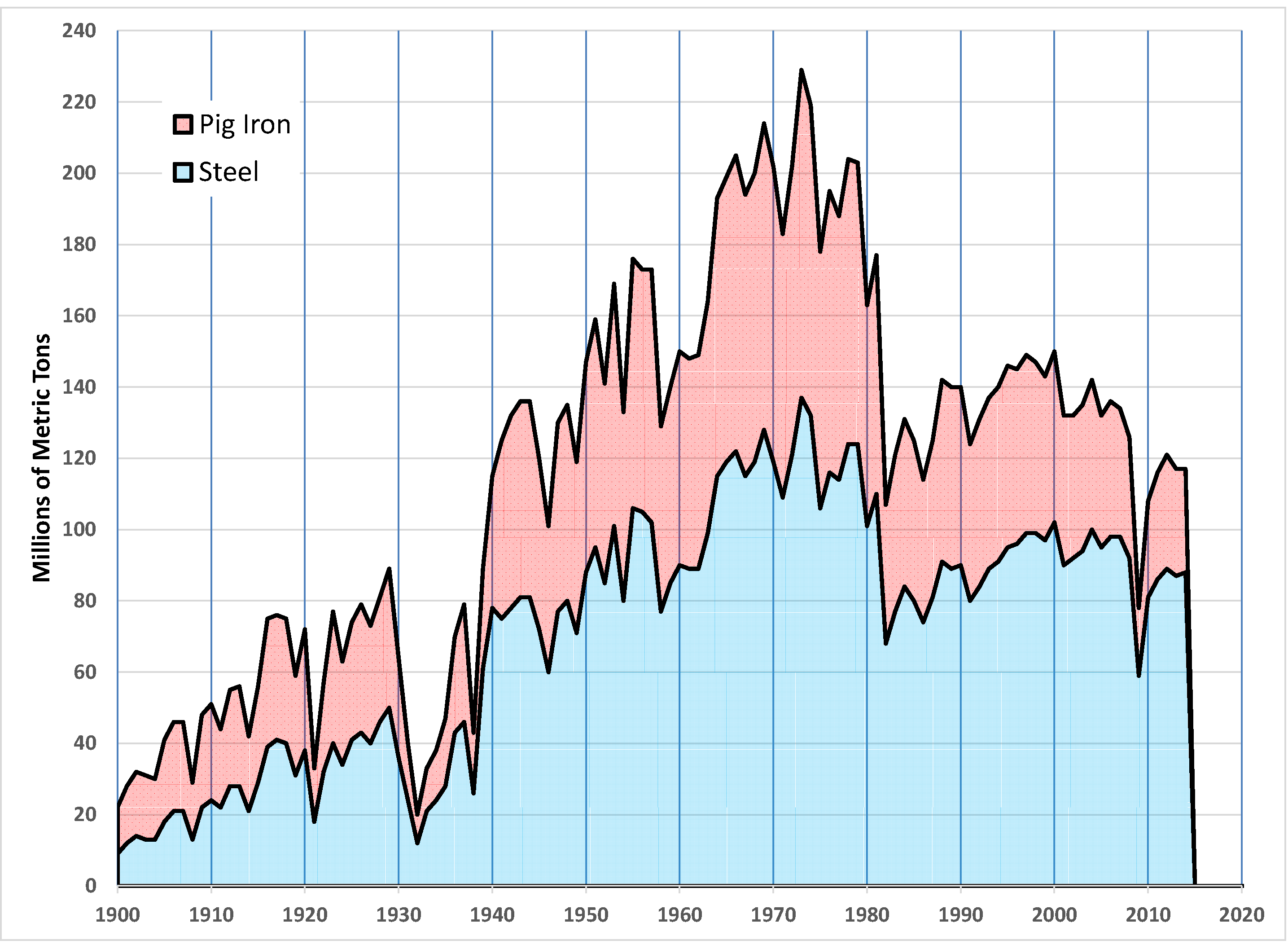
History Of The Iron And Steel Industry In The United States
The US iron and steel industry has paralleled the industry in other countries in technological developments. In the 1800s, the US switched from charcoal to coal in ore smelting, adopted the Bessemer process, and saw the rise of very large integrated steel mills. In the 20th century, the US industry successively adopted the open hearth furnace, then the basic oxygen steelmaking process. Since the American industry peaked in the 1940s and 1950s, the US industry has shifted to small mini-mills and specialty mills, using iron and steel scrap as feedstock, rather than iron ore. Colonial Iron manufacture before the 19th century required charcoal, and Britain's once-vast forests could no longer supply enough charcoal for the nation's increasing need for iron. By 1700, Britain was becoming increasingly dependent on iron imported from its sometimes-adversary Sweden. Britain looked to the seemingly limitless forests of its American colonies to supply Britain with iron. British investors sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philanthropy
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the Public good (economics), public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private good, focusing on material gain; and with government endeavors, which are public initiatives for public good, notably focusing on provision of public services. A person who practices philanthropy is a List of philanthropists, philanthropist. Etymology The word ''philanthropy'' comes , from ''phil''- "love, fond of" and ''anthrōpos'' "humankind, mankind". In the second century AD, Plutarch used the Greek concept of ''philanthrôpía'' to describe superior human beings. During the Middle Ages, ''philanthrôpía'' was superseded in Europe by the Christian theology, Christian cardinal virtue, virtue of ''charity'' (Latin: ''caritas''); selfless love, valued for salvation and escape from purgatory. Thomas Aquinas held that "the habit of charity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Magnate
A business magnate, also known as a tycoon, is a person who has achieved immense wealth through the ownership of multiple lines of enterprise. The term characteristically refers to a powerful entrepreneur or investor who controls, through personal enterprise ownership or a dominant shareholding position, a firm or industry whose goods or services are widely consumed. Such individuals have been known by different terms throughout history, such as industrialists, robber barons, captains of industry, czars, moguls, oligarchs, plutocrats, or taipans. Etymology The term '' magnate'' derives from the Latin word ''magnates'' (plural of ''magnas''), meaning "great man" or "great nobleman". The term ''mogul'' is an English corruption of ''mughal'', Persian or Arabic for "Mongol". It alludes to emperors of the Mughal Empire in Medieval India, who possessed great power and storied riches capable of producing wonders of opulence such as the Taj Mahal. The term ''tycoon'' derives from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Carnegie In National Portrait Gallery IMG 4441
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is frequently shortened to "Andy" or "Drew". The word is derived from the el, Ἀνδρέας, ''Andreas'', itself related to grc, ἀνήρ/ἀνδρός ''aner/andros'', "man" (as opposed to "woman"), thus meaning "manly" and, as consequence, "brave", "strong", "courageous", and "warrior". In the King James Bible, the Greek "Ἀνδρέας" is translated as Andrew. Popularity Australia In 2000, the name Andrew was the second most popular name in Australia. In 1999, it was the 19th most common name, while in 1940, it was the 31st most common name. Andrew was the first most popular name given to boys in the Northern Territory in 2003 to 2015 and continuing. In Victoria, Andrew was the first most popular name for a boy in the 1970s. Canada Andrew was the 20th most popular name chosen for mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Lauder Sr
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-year-old pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Lauder (Scottish Industrialist)
George Lauder Jr. (November 11, 1837 – August 24, 1924) was a Scottish industrialist. A trained mechanical engineer, Lauder was responsible for many of the technical advancements made in the steel industry during the Industrial Revolution including updates to both the Bessemer Process and coal washing machinery while also leading the use of steel in arms and defense. Lauder was the "cousin-brother", and business partner of, steel magnate Andrew Carnegie in the Carnegie Steel Company. The two were among the richest people in the world during their lifetimes with Lauders fortune valued at roughly $19 billion (in 2018 dollars). The sale of Carnegie Steel to J.P. Morgan in 1901 created U.S. Steel where Lauder sat on the board of directors. This became the first corporation in the world with a market capitalization exceeding $1 billion ($ billion today). Early years George Lauder was the son of George Lauder, Sr. and Seaton Morrison. His father owned the general store on the local h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas M
Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the Apostle * Thomas (bishop of the East Angles) (fl. 640s–650s), medieval Bishop of the East Angles * Thomas (Archdeacon of Barnstaple) (fl. 1203), Archdeacon of Barnstaple * Thomas, Count of Perche (1195–1217), Count of Perche * Thomas (bishop of Finland) (1248), first known Bishop of Finland * Thomas, Earl of Mar (1330–1377), 14th-century Earl, Aberdeen, Scotland Geography Places in the United States * Thomas, Illinois * Thomas, Indiana * Thomas, Oklahoma * Thomas, Oregon * Thomas, South Dakota * Thomas, Virginia * Thomas, Washington * Thomas, West Virginia * Thomas County (other) * Thomas Township (other) Elsewhere * Thomas Glacier (Greenland) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Thomas'' (Burton novel) 1969 novel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Carnegie Miller
Margaret Carnegie Miller (March 30, 1897 – April 11, 1990) was the only child of industrialist and philanthropist Andrew Carnegie and Louise Whitfield, and heiress to the Carnegie fortune. A native of Manhattan, New York City, from 1934 to 1973, Miller was a trustee of the Carnegie Corporation of New York, a grant-making foundation. The foundation was established by her father in 1911. From 1973 until her death in 1990, she was an honorary lifetime trustee. Personal life On April 22, 1919, four months before her father's death, Margaret married Roswell Miller Jr. (1894-1983) at the Carnegie family home at 2 East 91st Street on Upper East Side. Officiating at the wedding were Rev. William Pierson Merril, pastor of the Brick Presbyterian Church, where Margaret and Mrs. Carnegie were members, and Rev. Henry Sloane Coffin, pastor of the Madison Avenue Presbyterian Church where Mr. Carnegie was a member. Margaret Carnegie's marriage to Roswell Miller ended in divorce in 1953. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louise Whitfield Carnegie
Louise Whitfield Carnegie (March 7, 1857 – June 24, 1946) was the wife of philanthropist Andrew Carnegie. Biography Early life Louise Whitfield was born on March 7, 1857 in the Chelsea neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. Her parents—John D. Whitfield (died 1878), a prosperous New York City textile merchant, and Fannie Davis—descended from families who emigrated from England in the 1600s. Reaching relative success, John moved the family from Chelsea to Gramercy Park and finally to a brownstone on West 48th Street and Fifth Avenue. Adult life At the age of 23, Whitfield met Andrew Carnegie, himself aged 45, through her father. On April 22, 1887, Whitfield (now 30) married Carnegie (51) at her family's home in New York City in a private ceremony officiated by a pastor from the Church of the Divine Paternity, a Universalist church to which the Whitfields belonged. As wedding gifts from her husband, Louise received a home (formerly owned by Collis Potter Huntington) at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

