|
Capacity Management
Capacity management's goal is to ensure that information technology resources are sufficient to meet upcoming business requirements cost-effectively. One common interpretation of capacity management is described in the ITIL framework. ITIL version 3 views capacity management as comprising three sub-processes: business capacity management, service capacity management, and component capacity management. As the usage of IT services change and functionality evolves, the amount of central processing units (CPUs), memory and storage to a physical or virtual server etc. also changes. If there are spikes in, for example, processing power at a particular time of the day, it proposes analyzing what is happening at that time and making changes to maximize the existing IT infrastructure; for example, tuning the application, or moving a batch cycle to a quieter period. This capacity planning identifies any potential capacity related issues likely to arise, and justifies any necessary inves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITIL
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a set of detailed practices for IT activities such as IT service management (ITSM) and IT asset management (ITAM) that focus on aligning IT services with the needs of business. ITIL describes processes, procedures, tasks, and checklists which are neither organization-specific nor technology-specific, but can be applied by an organization toward strategy, delivering value, and maintaining a minimum level of competency. It allows the organization to establish a baseline from which it can plan, implement, and measure. It is used to demonstrate compliance and to measure improvement. There is no formal independent third party compliance assessment available for ITIL compliance in an organization. Certification in ITIL is only available to individuals. Since 2013, ITIL has been owned by AXELOS, a joint venture between Capita and the UK Cabinet Office. History Responding to growing dependence on IT, the UK Government's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throughput
Network throughput (or just throughput, when in context) refers to the rate of message delivery over a communication channel, such as Ethernet or packet radio, in a communication network. The data that these messages contain may be delivered over physical or logical links, or through network nodes. Throughput is usually measured in bits per second (bit/s or bps), and sometimes in data packets per second (p/s or pps) or data packets per time slot. The system throughput or aggregate throughput is the sum of the data rates that are delivered to all terminals in a network. Throughput is essentially synonymous to digital bandwidth consumption; it can be determined numerically by applying the queueing theory, where the load in packets per time unit is denoted as the arrival rate (), and the drop in packets per unit time is denoted as the departure rate (). The throughput of a communication system may be affected by various factors, including the limitations of the underlying anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OPNET
OPNET Technologies, Inc. was a software business that provided performance management for computer networks and applications. The company was founded in 1986 and went public in 2000. In October 2012, OPNET was acquired by Riverbed Technology, for about $1 billion US dollars. Corporate history "OPNET" was Alain Cohen's (co-founder, CTO & President) graduate project for a networking course while he was at MIT. OPNET stood for Optimized Network Engineering Tools. Alain, along with brother Marc (co-founder, CEO & Chairman) and classmate Steven Baraniuk, decided to commercialize the software. The company's first product was OPNET Modeler, a software tool for computer network modeling and simulation. Since becoming a public company in August 2000, OPNET executed the following acquisitions: *March 2001: NetMaker Division of Make Systems *January 2002: WDM NetDesign B.V.B.A *October 2004: Altaworks Corporation *October 2007: substantially all of the assets of Network Physics, Inc. *A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet Analyzer
A packet analyzer, also known as packet sniffer, protocol analyzer, or network analyzer, is a computer program or computer hardware such as a packet capture appliance, that can intercept and log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the analyzer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications. A packet analyzer used for intercepting traffic on wireless networks is known as a wireless analyzer or WiFi analyzer. While a packet analyzer can also be referred to as a network analyzer or protocol analyzer these terms can also have other meanings. Protocol analyzer can technically be a broader, more general class that includes packet analyzers/sniffers. However, the terms are frequently used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Experience
Quality of experience (QoE) is a measure of the delight or annoyance of a customer's experiences with a service (e.g., web browsing, phone call, TV broadcast).Qualinet White Paper on Definitions of Quality of Experience (2012). European Network on Quality of Experience in Multimedia Systems and Services (COST Action IC 1003), Patrick Le Callet, Sebastian Möller and Andrew Perkis, eds., Lausanne, Switzerland, Version 1.2, March 2013 QoE focuses on the entire service experience; it is a holistic concept, similar to the field of user experience, but with its roots in telecommunication. QoE is an emerging multidisciplinary field based on social psychology, cognitive science, economics, and engineering science, focused on understanding overall human quality requirements. Definition and concepts In 2013, within the context of the COST Action ''QUALINET'', QoE has been defined as:The degree of delight or annoyance of the user of an application or service. It results from the fulfillm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real User Monitoring
Real user monitoring (RUM) is a passive monitoring technology that records all user interaction with a website or client interacting with a server or cloud-based application. Monitoring actual user interaction with a website or an application is important to operators to determine if users are being served quickly and without errors and, if not, which part of a business process is failing. Software as a service (SaaS) and application service providers (ASP) use RUM to monitor and manage service quality delivered to their clients. Real user monitoring data is used to determine the actual service-level quality delivered to end-users and to detect errors or slowdowns on websites. The data may also be used to determine if changes that are propagated to sites have the intended effect or cause errors. Organizations typically use RUM to test changes within the production environment or to anticipate behavioral changes in a website or application by using A/B testing or other techniques. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Monitoring
In software design, web design, and electronic product design, synthetic monitoring (also known as ''active monitoring or proactive monitoring'') is a monitoring technique that is done by using a simulation or scripted recordings of transactions. Behavioral scripts (or paths) are created to simulate an action or path that a customer or end-user would take on a site, application, or other software (or even hardware). Those paths are then continuously monitored at specified intervals for performance, such as functionality, availability, and response time measures. Synthetic monitoring enables a webmaster or an IT/Operations professional to identify problems and determine if a website or application is slow or experiencing downtime before that problem affects actual end-users or customers. This type of monitoring does not require actual traffic, thus the name synthetic, so it enables companies to test applications 24x7, or test new applications prior to a live customer-facing laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Server Log
In computing, logging is the act of keeping a log of events that occur in a computer system, such as problems, errors or just information on current operations. These events may occur in the operating system or in other software. A message or log entry is recorded for each such event. These log messages can then be used to monitor and understand the operation of the system, to debug problems, or during an audit. Logging is particularly important in multi-user software, to have a central overview of the operation of the system. In the simplest case, messages are written to a file, called a log file. Alternatively, the messages may be written to a dedicated logging system or to a log management software, where it is stored in a database or on a different computer system. Specifically, a transaction log is a log of the communications between a system and the users of that system, or a data collection method that automatically captures the type, content, or time of transactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RMON
The Remote Network Monitoring (RMON) MIB was developed by the IETF to support monitoring and protocol analysis of LANs. The original version (sometimes referred to as RMON1) focused on OSI layer 1 and layer 2 information in Ethernet and Token Ring networks. It has been extended by RMON2 which adds support for Network- and Application-layer monitoring and by SMON which adds support for switched networks. It is an industry-standard specification that provides much of the functionality offered by proprietary network analyzers. RMON agents are built into many high-end switches and routers. Overview Remote Monitoring (RMON) is a standard monitoring specification that enables various network monitors and console systems to exchange network-monitoring data. RMON provides network administrators with more freedom in selecting network-monitoring probes and consoles with features that meet their particular networking needs. An RMON implementation typically operates in a client/server mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPFIX
Internet Protocol Flow Information Export (IPFIX) is an IETF protocol, as well as the name of the IETF working group defining the protocol. It was created based on the need for a common, universal standard of export for Internet Protocol flow information from routers, probes and other devices that are used by mediation systems, accounting/billing systems and network management systems to facilitate services such as measurement, accounting and billing. The IPFIX standard defines how IP flow information is to be formatted and transferred from an exporter to a collector. Previously many data network operators were relying on Cisco Systems' proprietary NetFlow technology for traffic flow information export. The IPFIX standards requirements were outlined in the original RFC 3917. Cisco NetFlow Version 9 was the basis for IPFIX. The basic specifications for IPFIX are documented in RFC 7011 through RFC 7015, and RFC 5103. Architecture The following figure shows a typical architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
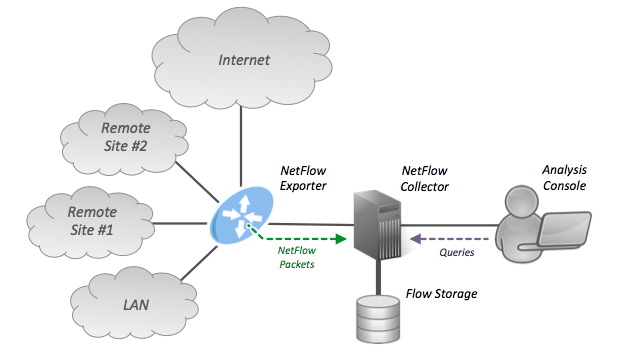
NetFlow
NetFlow is a feature that was introduced on Cisco routers around 1996 that provides the ability to collect IP network traffic as it enters or exits an interface. By analyzing the data provided by NetFlow, a network administrator can determine things such as the source and destination of traffic, class of service, and the causes of congestion. A typical flow monitoring setup (using NetFlow) consists of three main components: * Flow exporter: aggregates packets into flows and exports flow records towards one or more flow collectors. * Flow collector: responsible for reception, storage and pre-processing of flow data received from a flow exporter. * Analysis application: analyzes received flow data in the context of intrusion detection or traffic profiling, for example. Protocol description Routers and switches that support NetFlow can collect IP traffic statistics on all interfaces where NetFlow is enabled, and later export those statistics as NetFlow records toward at least on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FCAPS
FCAPS is the ISO Telecommunications Management Network model and framework for network management. ''FCAPS'' is an acronym for fault, configuration, accounting, performance, security, the management categories into which the ISO model defines network management tasks. In non-billing organizations ''accounting'' is sometimes replaced with ''administration''. Background The ISO, under the direction of the OSI group, has created a network management model as the primary means for understanding the major functions of network management systems. The model in question is interchangeably called either the ''OSI network management model'' or ''ISO network management model'' so the full name could be the ''OSI/ISO network management model''. The comprehensive management of an organization's information technology (IT) infrastructure is a fundamental requirement. Employees and customers rely on IT services where availability and performance are mandated, and problems can be quickly identifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |