|
Capacitive Dropper
A capacitive power supply, also called a capacitive dropper, is a type of power supply that uses the capacitive reactance of a capacitor to reduce higher AC mains voltage to a lower DC voltage. It is a relatively inexpensive method compared to typical solutions using a transformer, however, a relatively large mains-voltage capacitor is required and its capacitance must increase with the output current, which leads to a higher-cost and bulky capacitor. The primary downside of this type of power supply is the lack of galvanic isolation between the input and output, which means the output side is a dangerous shock hazard. For safety reasons, this type of power supply and every circuit connected to it must be double insulated in all places where a person could come into electrical contact with it. Capacitive power supplies typically have a low power factor. By the equation of state for capacitance, where I_c = C \frac, the current is limited to: 1 amp, per farad, per volt-rms, per ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitive Power Supply
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
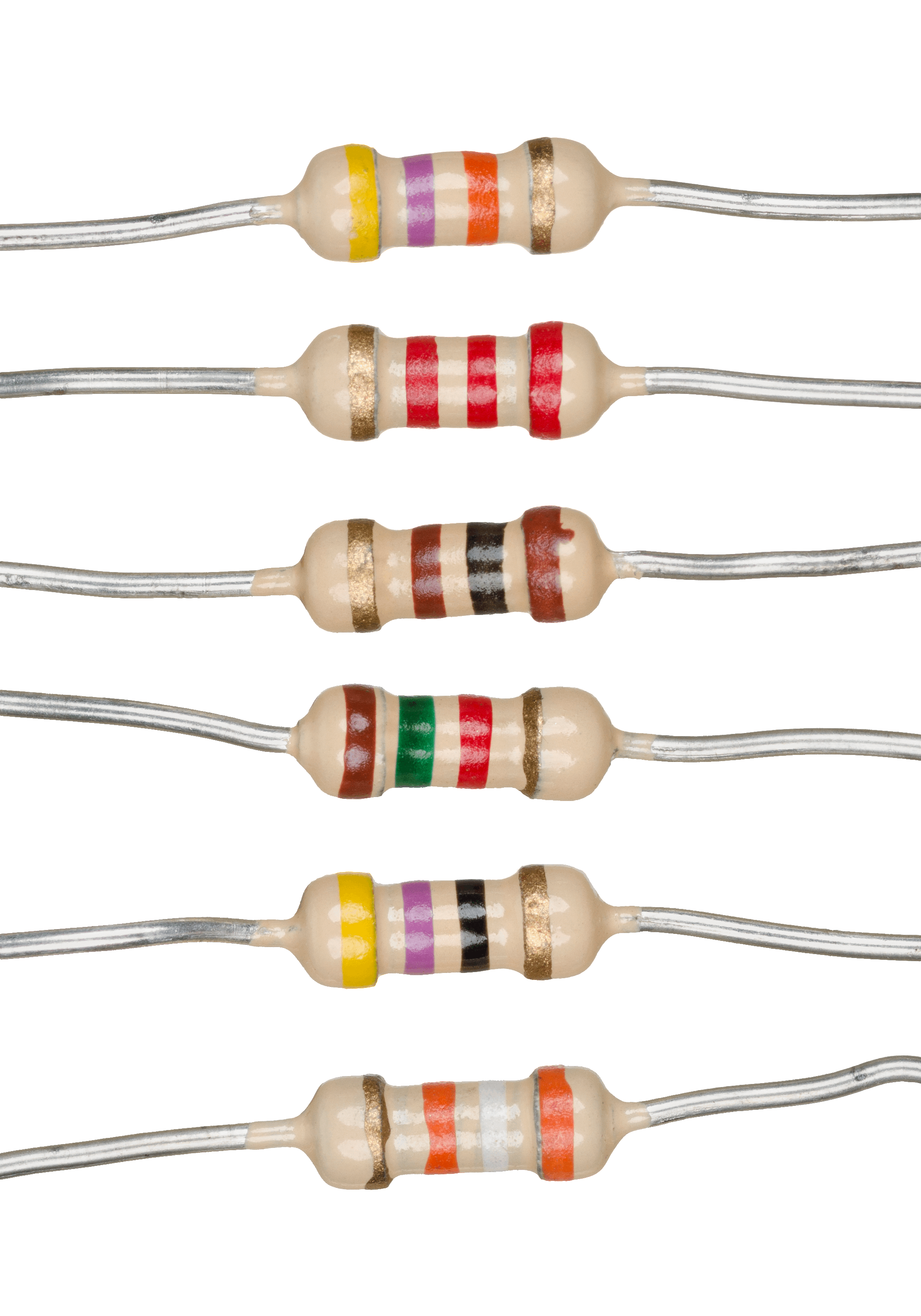
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistive Dropper
Voltage drop is the decrease of electrical potential along the path of a current flowing in an electrical circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are undesirable because some of the energy supplied is dissipated. The voltage drop across the electrical load is proportional to the power available to be converted in that load to some other useful form of energy. For example, an electric space heater may have a resistance of ten ohms, and the wires that supply it may have a resistance of 0.2 ohms, about 2% of the total circuit resistance. This means that approximately 2% of the supplied voltage is lost in the wire itself. An excessive voltage drop may result in the unsatisfactory performance of a space heater and overheating of the wires and connections. National and local electrical codes may set guidelines for the maximum voltage drop allowed in electrical wiring to ensure efficiency of distributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
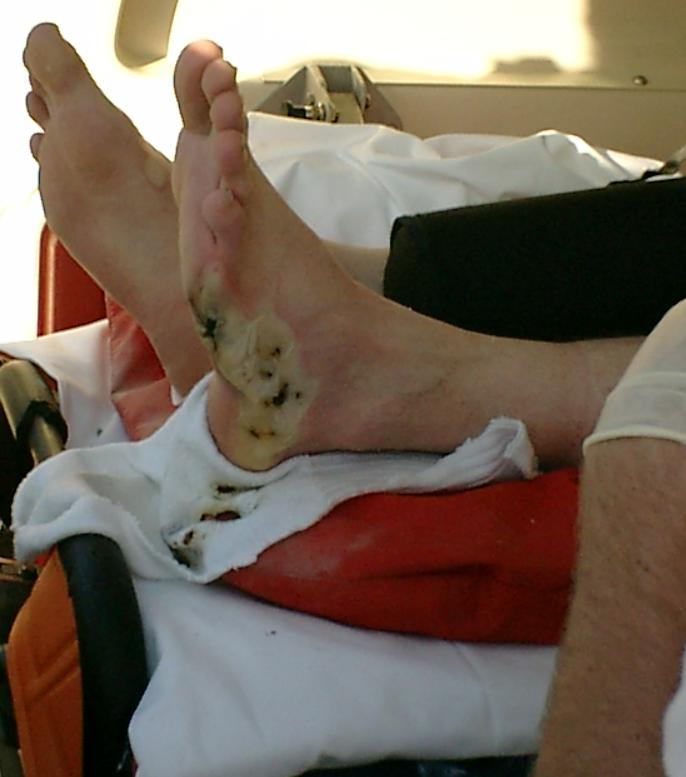
Electrical Injury
Electrical injury is a physiological reaction caused by electric current passing through the body. The injury depends on the density of the current, tissue resistance and duration of contact. Very small currents may be imperceptible or produce a light tingling sensation. A shock caused by low and otherwise harmless current could startle an individual and cause injury due to jerking away or falling. Stronger currents may cause some degree of discomfort or pain, while more intense currents may induce involuntary muscle contractions, preventing the person from breaking free of the source of electricity. Still larger currents result in tissue damage and may trigger ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest. Consequences of injury from electricity may include amputations, bone fractures and orthopedic and musculoskeletal injuries. If death results from an electric shock the cause of death is generally referred to as electrocution. Electric injury occurs upon contact of a body part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Voltage Warning
High may refer to: Science and technology * Height * High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area * High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory * High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift took or takes place * Substance intoxication, also known by the slang description "being high" * Sugar high, a misconception about the supposed psychological effects of sucrose Music Performers * High (musical group), a 1974–1990 Indian rock group * The High, an English rock band formed in 1989 Albums * ''High'' (The Blue Nile album) or the title song, 2004 * ''High'' (Flotsam and Jetsam album), 1997 * ''High'' (New Model Army album) or the title song, 2007 * ''High'' (Royal Headache album) or the title song, 2015 * ''High'' (EP), by Jarryd James, or the title song, 2016 Songs * "High" (Alison Wonderland song), 2018 * "High" (The Chainsmokers song), 2022 * "High" (The Cure song), 1992 * "High" (David Hallyday song), 1988 * "H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LED Light
An LED lamp or LED light bulb is an electric light that produces light using light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED lamps are significantly more energy-efficient than equivalent incandescent lamps and can be significantly more efficient than most fluorescent lamps. The most efficient commercially available LED lamps have efficiencies of 200 lumen per watt (Lm/W). Commercial LED lamps have a lifespan many times longer than incandescent lamps. LED lamps require an electronic LED driver circuit to operate from mains power lines, and losses from this circuit means that the efficiency of the lamp is lower than the efficiency of the LED chips it uses. The driver circuit may require special features to be compatible with lamp dimmers intended for use on incandescent lamps. Generally the current waveform contains some amount of distortion, depending on the luminaires’ technology. The LED lamp market is projected to grow from US$75.8 billion in 2020 and increasing to US$160 billion in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Residual-current Device
A residual-current device (RCD), residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB) or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is an electrical safety device that quickly breaks an electrical circuit with leakage current to ground. It is to protect equipment and to reduce the risk of serious harm from an ongoing electric shock. Injury may still occur in some cases, for example if a human receives a brief shock before the electrical circuit is isolated, falls after receiving a shock, or if the person touches both conductors at the same time. If the RCD device has additional overcurrent protection integrated in the same device, it is referred to as RCBO. An earth leakage circuit breaker may be a RCD, although an older type of voltage-operated earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) also exists. These electrical wiring devices are designed to quickly and automatically isolate a circuit when it detects that the electric current is unbalanced between the supply and return conductors of a ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohm's Law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the usual mathematical equation that describes this relationship: :I = \frac, where is the current through the conductor, ''V'' is the voltage measured ''across'' the conductor and ''R'' is the resistance of the conductor. More specifically, Ohm's law states that the ''R'' in this relation is constant, independent of the current. If the resistance is not constant, the previous equation cannot be called ''Ohm's law'', but it can still be used as a definition of static/DC resistance. Ohm's law is an empirical relation which accurately describes the conductivity of the vast majority of electrically conductive materials over many orders of magnitude of current. However some materials do not obey Ohm's law; these are called non-ohmic. The law was named after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Reactance
In electrical circuits, reactance is the opposition presented to alternating current by inductance or capacitance. Greater reactance gives smaller current for the same applied voltage. Reactance is similar to resistance in this respect, but does not lead to dissipation of electrical energy as heat; instead, energy is momentarily stored in the reactance, and a quarter-cycle later returned to the circuit. Reactance is used to compute amplitude and phase changes of sinusoidal alternating current going through a circuit element. Like resistance, reactance is measured in ohms, with positive values indicating ''inductive'' reactance and negative indicating ''capacitive'' reactance. It is denoted by the symbol X. An ideal resistor has zero reactance, whereas ideal inductors and capacitors have zero resistance. As frequency increases, inductive reactance increases and capacitive reactance decreases. Comparison to resistance Reactance is similar to resistance in that larger react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Divider
In electronics, a voltage divider (also known as a potential divider) is a passive linear circuit that produces an output voltage (''V''out) that is a fraction of its input voltage (''V''in). Voltage division is the result of distributing the input voltage among the components of the divider. A simple example of a voltage divider is two resistors connected in series, with the input voltage applied across the resistor pair and the output voltage emerging from the connection between them. Resistor voltage dividers are commonly used to create reference voltages, or to reduce the magnitude of a voltage so it can be measured, and may also be used as signal attenuators at low frequencies. For direct current and relatively low frequencies, a voltage divider may be sufficiently accurate if made only of resistors; where frequency response over a wide range is required (such as in an oscilloscope probe), a voltage divider may have capacitive elements added to compensate load capacitance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zener Diode
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" (inverted polarity) when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the ''Zener voltage'', is reached. Zener diodes are manufactured with a great variety of Zener voltages and some are even variable. Some Zener diodes have a sharp, highly doped p–n junction with a low Zener voltage, in which case the reverse conduction occurs due to electron quantum tunnelling in the short space between p and n regions − this is known as the Zener effect, after Clarence Zener. Diodes with a higher Zener voltage have a more gradual junction and their mode of operation also involves avalanche breakdown. Both breakdown types are present in Zener diodes with the Zener effect predominating at lower voltages and avalanche breakdown at higher voltages. They are used to generate low-power stabilized supply rails from a higher voltage and to provide reference voltages for circuits, especially stabilized powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)