Capacitive Dropper on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A capacitive power supply, also called a capacitive dropper, is a type of
A capacitive power supply, also called a capacitive dropper, is a type of
/ref>
/ref> The primary downside of this type of power supply is the lack of
 By changing the value of the example in the diagram by a capacitor with a value of 330 nF, a current of approximately 20 mA can be provided, as the reactance of the 330 nF capacitor at 50 Hz calculates to and applying
By changing the value of the example in the diagram by a capacitor with a value of 330 nF, a current of approximately 20 mA can be provided, as the reactance of the 330 nF capacitor at 50 Hz calculates to and applying
 *
*
Transformerless Power Supplies: Resistive and Capacitive
- Microchip
Transformerless Power Supply Design
- Designer Circuits
- WIMA Power supplies
 A capacitive power supply, also called a capacitive dropper, is a type of
A capacitive power supply, also called a capacitive dropper, is a type of power supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a ...
that uses the capacitive reactance
In electrical circuits, reactance is the opposition presented to alternating current by inductance or capacitance. Greater reactance gives smaller current for the same applied voltage. Reactance is similar to resistance in this respect, but does ...
of a capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of a ...
to reduce higher AC mains
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which ...
voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge t ...
to a lower DC voltage.
It is a relatively inexpensive method compared to typical solutions using a transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
, however, a relatively large mains-voltage capacitor is required and its capacitance must increase with the output current, which leads to a higher-cost and bulky capacitor.Low cost PSU using a capacitor instead of a transformer (English Translation)/ref>
/ref> The primary downside of this type of power supply is the lack of
galvanic isolation
Galvanic isolation is a principle of isolating functional sections of electrical systems to prevent current flow; no direct conduction path is permitted.John Huntington ''Show Networks and Control Systems: Formerly Control Systems for Live ...
between the input and output, which means the output side is a dangerous shock hazard. For safety reasons, this type of power supply and every circuit connected to it must be double insulated in all places where a person could come into electrical contact with it.
Capacitive power supplies typically have a low power factor
In electrical engineering, the power factor of an AC power system is defined as the ratio of the '' real power'' absorbed by the load to the '' apparent power'' flowing in the circuit. Real power is the average of the instantaneous product of ...
.
By the equation of state for capacitance
Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized a ...
, where , the current is limited to: 1 amp, per farad, per volt-rms, per radian (of phase). Or amps, per farad, per volt-rms, per hertz.
Structure
A capacitive power supply usually has a rectifier and filter to generate a direct current from the reduced alternating voltage. Such a supply comprises acapacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of a ...
, C1 whose reactance limits the current flowing through the rectifier bridge
A diode bridge is a bridge rectifier circuit of four diodes that is used in the process of converting alternating current (AC) from the input terminals to direct current (DC, i.e. fixed polarity) on the output terminals. Its function is to co ...
D1. A resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias activ ...
, R1, connected in series with it protects against voltage spikes during switching operations. An electrolytic capacitor, C2, is used to smooth the DC ''voltage'' and the peak current (in the range of amps) in switching operations. Above right a voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. A voltage regulator may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components ...
can be seen, formed by the current limiting resistor, R3, and the zener shunt regulator
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. A voltage regulator may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components ...
, IC1. If the voltage stability is not too important a Zener diode
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" (inverted polarity) when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the ''Zener voltage'', is reached.
Zener diodes are manufactured with a great var ...
can be used as a regulator; the two-terminal device would eliminate R4 and R5 used as a resistive voltage divider
In electronics, a voltage divider (also known as a potential divider) is a passive linear circuit that produces an output voltage (''V''out) that is a fraction of its input voltage (''V''in). Voltage division is the result of distributing the i ...
in the schematic above.
Example
 By changing the value of the example in the diagram by a capacitor with a value of 330 nF, a current of approximately 20 mA can be provided, as the reactance of the 330 nF capacitor at 50 Hz calculates to and applying
By changing the value of the example in the diagram by a capacitor with a value of 330 nF, a current of approximately 20 mA can be provided, as the reactance of the 330 nF capacitor at 50 Hz calculates to and applying Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the usual mathematical equatio ...
, that limits the current to . This way up to 48 white LEDs in series can be powered (for example, 3.1 V/20 mA/20000 mcd).
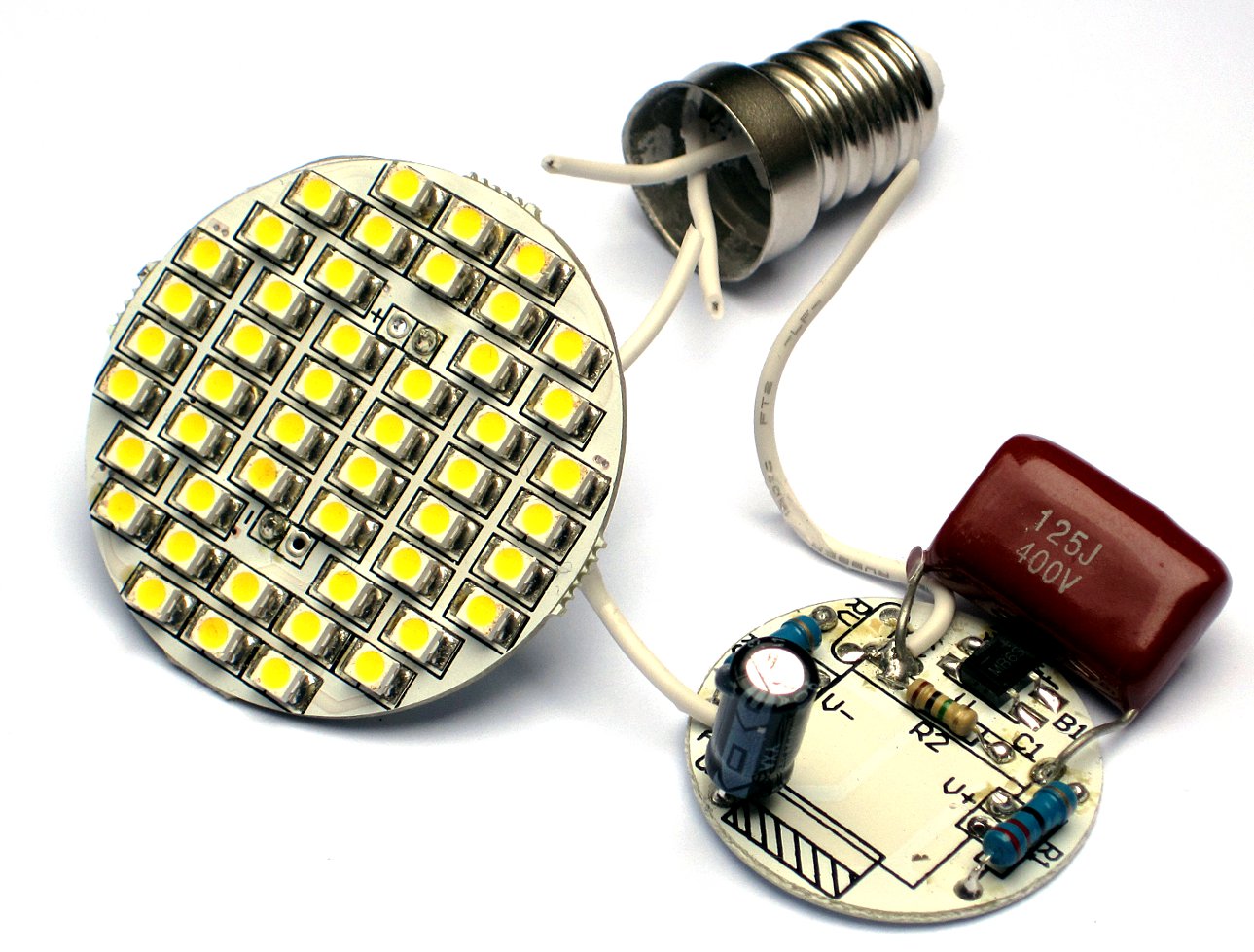
Analyzing the circuit of the lamp shown in the image on the right, at 50 Hz, the 1.2 μF capacitor has a reactance of 2.653 kΩ. By Ohm's law, the current is limited to , assuming that voltage and frequency remain constant. The LEDs are connected in parallel with the 10 μF electrolytic filter capacitor. There are four parallel branches, each having 12 LEDs in series; these branches consume about 20 mA each, or 4 x 20 = 80 mA total. The diodes limit the voltage to about 40 V per branch. Since normally the circuit is connected directly to the mains network without galvanic isolation, a residual-current circuit breaker
A residual-current device (RCD), residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB) or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is an electrical safety device that quickly breaks an Electrical Circuit, electrical circuit with Leakage (electronics), leakage ...
is needed in any type of protection circuit used for this kind of LED light
An LED lamp or LED light bulb is an electric light that produces light using light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED lamps are significantly more energy-efficient than equivalent Incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamps
and can be significantly ...
.
See also
Electrical injury
Electrical injury is a physiological reaction caused by electric current passing through the body. The injury depends on the density of the current, tissue resistance and duration of contact. Very small currents may be imperceptible or produce a ...
* Resistive dropper
* UL (safety organization)
The UL enterprise is a global safety science company headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, composed of three organizations, UL Research Institutes, UL Standards & Engagement and UL Solutions.
Established in 1894, the UL enterprise was founded as ...
References
External links
{{Commons category, Capacitive power supplyTransformerless Power Supplies: Resistive and Capacitive
- Microchip
Transformerless Power Supply Design
- Designer Circuits
- WIMA Power supplies