|
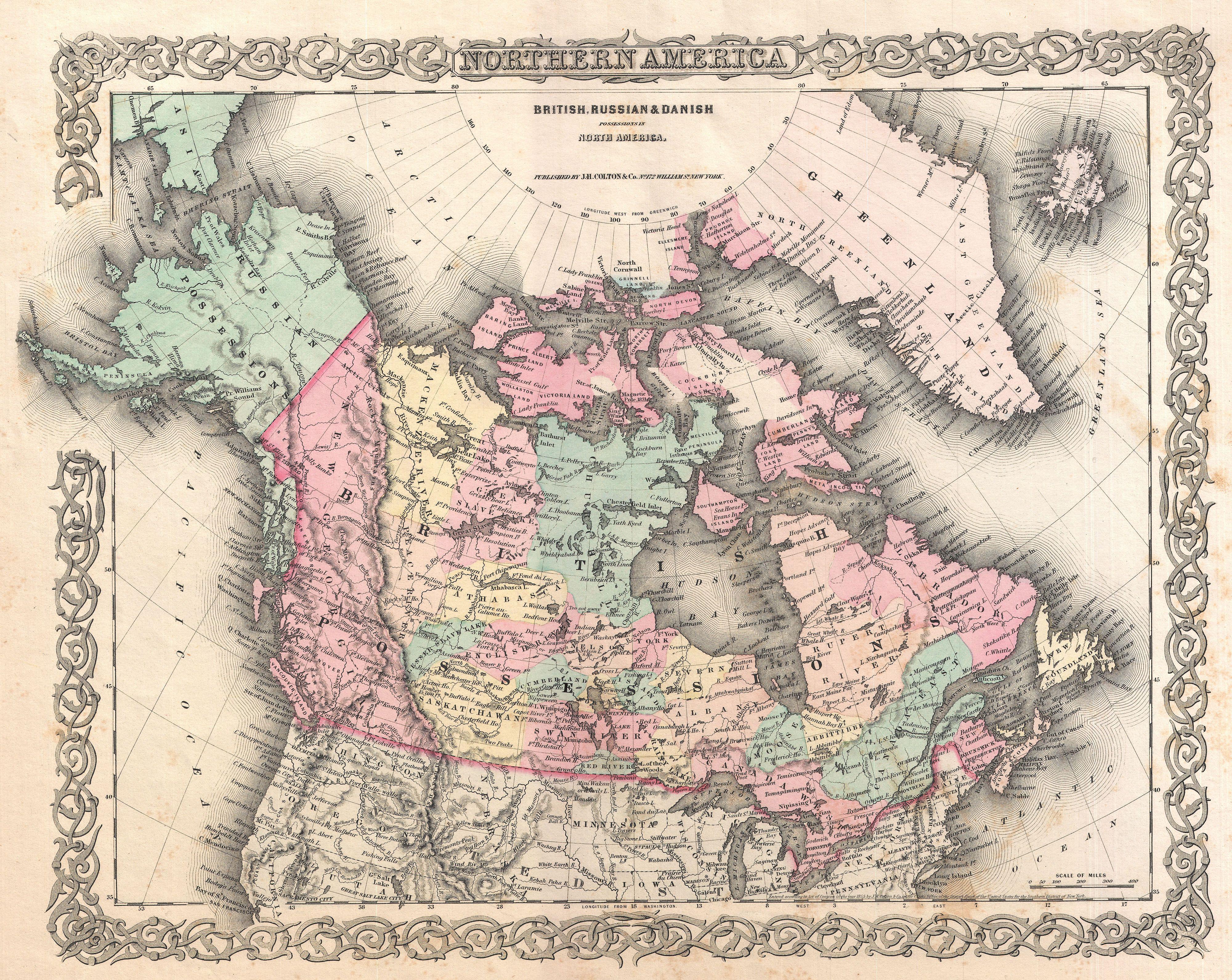
Canada–United Kingdom Relations
Canada–United Kingdom relations () are the bilateral relations between Canada and the United Kingdom. The two countries have had intimate and frequently-co-operative contact since Canada gained independence in 1931, having been self-governing since 1 July 1867, the date that became Canada's independence day. Both are related by mutual migration, through shared military history, a shared system of government, the English language, the Commonwealth of Nations, and their sharing of the same head of state, . Despite the shared legacy, the two nations grew apart economically during the 20th century after the U.K. lost its position as Canada's largest trading partner to the United States during the 19th century. However, that trend has been reversed somewhat in the 21st century as the two countries have been negotiating freer trade. Both share a defence agreement, NATO, and frequently perform military exercises, together with Canada hosting the largest British Military Base outside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Canadian High Commissioners To The United Kingdom
The High Commission of Canada in the United Kingdom (french: Haut-commissariat du Canada au Royaume-Uni) is the diplomatic mission of Canada to the United Kingdom. It is housed at Canada House on Trafalgar Square in central London, with an additional Regional Service Centre at 3 Furzeground Way in Stockley Park, Uxbridge. History The Canadian high commission in London is Canada's oldest diplomatic posting, having been established in 1880. Canada House, in Trafalgar Square, became the site of the mission in 1923. In 1962, Canada also acquired the former American Embassy at 1, Grosvenor Square in London's Mayfair district, and it was renamed Macdonald House. Macdonald House was the official residence of the Canadian High Commissioner until the building was vacated in mid-December 2014, after having been sold for redevelopment. Canada's presence in London goes back to 1869, when Sir John Rose, 1st Baronet was appointed as Canada's informal representative in Britain. This was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implemented the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the perceived threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa. The organization's motto is '' animus in consulendo liber'' (Latin for "a mind unfettered in deliberation"). NATO's main headquarters are located in Brussels, Belgium, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the Seven Years' War. The signing of the treaty formally ended conflict between France and Great Britain over control of North America (the Seven Years' War, known as the French and Indian War in the United States), and marked the beginning of an era of British dominance outside Europe. Great Britain and France each returned much of the territory that they had captured during the war, but Great Britain gained much of France's possessions in North America. Additionally, Great Britain agreed to protect Roman Catholicism in the New World. The treaty did not involve Prussia and Austria as they signed a separate agreement, the Treaty of Hubertusburg, five days later. Exchange of territories During the war, Great Britain had conquered the French co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French And Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the start of the war, the French colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on their native allies. Two years into the French and Indian War, in 1756, Great Britain declared war on France, beginning the worldwide Seven Years' War. Many view the French and Indian War as being merely the American theater of this conflict; however, in the United States the French and Indian War is viewed as a singular conflict which was not associated with any European war. French Canadians call it the ('War of the Conquest').: 1756–1763 The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee tribes, and the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of Spain, and involved much of Europe for over a decade. The main action saw France as the defender of Spain against a multinational coalition. The war was very expensive and bloody and finally stalemated. Essentially, the treaties allowed Philip V (grandson of King Louis XIV of France) to keep the Spanish throne in return for permanently renouncing his claim to the French throne, along with other necessary guarantees that would ensure that France and Spain should not merge, thus preserving the balance of power in Europe. The treaties between several European states, including Spain, Great Britain, France, Portugal, Savoy and the Dutch Republic, helped end the war. The treaties were concluded between the representatives of Louis XIV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humphrey Gilbert
Sir Humphrey Gilbert (c. 1539 – 9 September 1583) was an English adventurer, explorer, member of parliament and soldier who served during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I and was a pioneer of the English colonial empire in North America and the Plantations of Ireland. He was a maternal half-brother of Sir Walter Raleigh and a cousin of Sir Richard Grenville. Biography Early life Gilbert was the fifth son of Otho Gilbert of Compton, Greenway and Galmpton, all in Devon, by his wife Catherine Champernowne. His brothers Sir John Gilbert and Adrian Gilbert, and his half-brothers Carew Raleigh and Sir Walter Raleigh, were also prominent during the reigns of Queen Elizabeth I and King James VI and I. Catherine Champernowne was a niece of Kat Ashley, Elizabeth's governess, who introduced her young kinsmen to the court. Gilbert's uncle, Sir Arthur Champernowne, involved him in the plantation of Ireland between 1566 and 1572. Gilbert's mentor was Sir Henry Sidney. He w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cabot
John Cabot ( it, Giovanni Caboto ; 1450 – 1500) was an Italian navigator and explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England is the earliest-known European exploration of coastal North America since the Norse visits to Vinland in the eleventh century. To mark the celebration of the 500th anniversary of Cabot's expedition, both the Canadian and British governments elected Cape Bonavista, Newfoundland as representing Cabot's first landing site. However, alternative locations have also been proposed. Name and origins Cabot is known today as Giovanni Caboto in Italian, Zuan Caboto in Venetian, Jean Cabot in French, and John Cabot in English. This was the result of a once-ubiquitous European tradition of nativizing names in local documents, something often adhered to by the actual persons themselves. In Venice Cabot signed his name as "Zuan Chabotto", ''Zuan'' being a form of '' John'' typical to Venice. He continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland". Most of the population are native English-speakers, and the province's population is 969,383 according to the 2021 Census. It is the most populous of Canada's Atlantic provinces. It is the country's second-most densely populated province and second-smallest province by area, both after Prince Edward Island. Its area of includes Cape Breton Island and 3,800 other coastal islands. The Nova Scotia peninsula is connected to the rest of North America by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. The province borders the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the south and east, and is separated from Prince Edward Island and the island of Newfoundland by the Northumberland and Cabot straits, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and French as its official languages. New Brunswick is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to the west. New Brunswick is about 83% forested and its northern half is occupied by the Appalachians. The province's climate is continental with snowy winters and temperate summers. New Brunswick has a surface area of and 775,610 inhabitants (2021 census). Atypically for Canada, only about half of the population lives in urban areas. New Brunswick's largest cities are Moncton and Saint John, while its capital is Fredericton. In 1969, New Brunswick passed the Official Languages Act which began recognizing French as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of 1837–1838. The Act of Union 1840, passed on 23 July 1840 by the British Parliament and proclaimed by the Crown on 10 February 1841, merged the Colonies of Upper Canada and Lower Canada by abolishing their separate parliaments and replacing them with a single one with two houses, a Legislative Council as the upper chamber and the Legislative Assembly as the lower chamber. In the aftermath of the Rebellions of 1837–1838, unification of the two Canadas was driven by two factors. Firstly, Upper Canada was near bankruptcy because it lacked stable tax revenues, and needed the resources of the more populous Lower Canada to fund its internal transportation improvements. Secondl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Colonies
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Council. In some cases, this Council was split into two: an Executive Council and a Legislative Council, and was similar to the Privy Council that advises the Monarch. Members of Executive Councils were appointed by the Governors, and British citizens resident in Crown colonies either had no representation in local government, or limited representation. In several Crown colonies, this limited representation grew over time. As the House of Commons of the British Parliament has never included seats for any of the colonies, there was no direct representation in the sovereign government for British subjects or citizens residing in Crown colonies. The administration of Crown colonies changed over time and in the 1800s some became, with a loosening of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Dominions
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire. "Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 Imperial Conference through the Balfour Declaration of 1926, recognising Great Britain and the Dominions as "autonomous within the British Empire, equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs, though united by a common allegiance to the Crown and freely associated as members of the British Commonwealth of Nations". Their full legislative independence was subsequently confirmed in the 1931 Statute of Westminster. Later India, Pakistan, and Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) also became dominions, for short periods of time. With the dissolution of the British Empire after World War II and the formation of the Commonwealth of Nations, it was decided that the term ''Commonwealth country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |