|
Camilla (spacecraft)
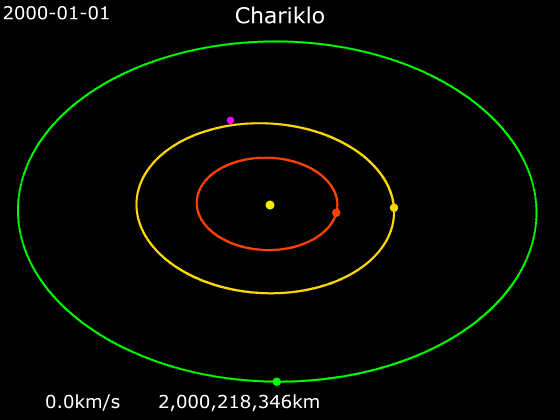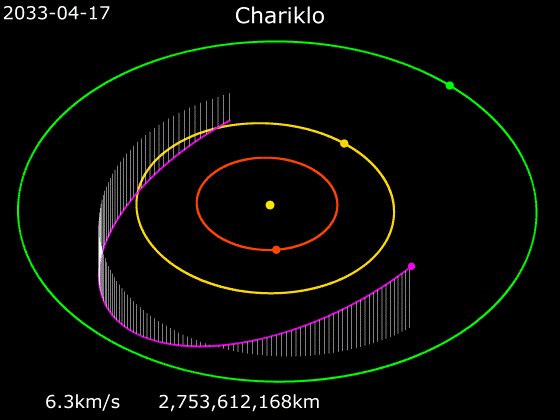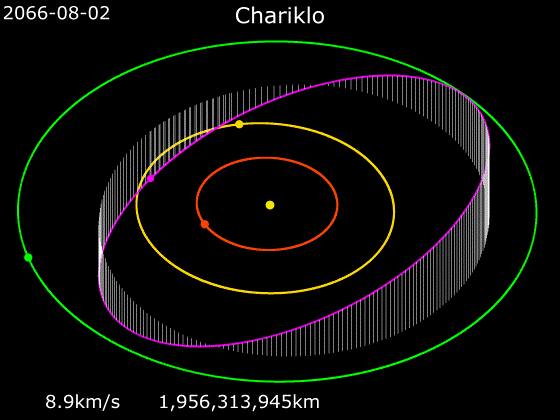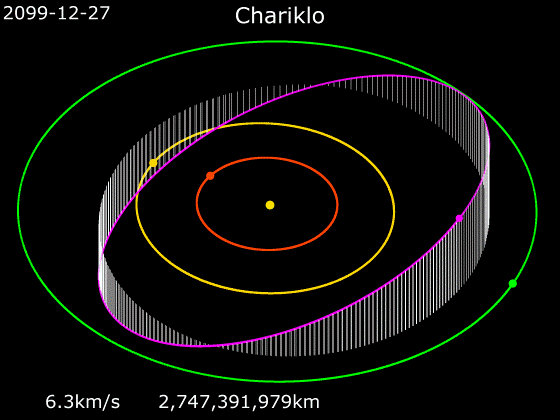
''Camilla'' is a spacecraft and mission concept proposed for NASA’s New Frontiers program. It would be a centaur exploration mission, particularly to minor planet 10199 Chariklo. It consists of a flyby craft (''Camilla''), and tungsten impactor (Halbred). Goals The goals of this mission would be to understand the formation of centaurs, find if shepherd moons exist around Chariklo, and study the nature of the asteroid's rings formation. Mission design The spacecraft would be launched in September 2026, using one gravity assist from Venus in February 2027 and Earth in December 2027 and 2029 to accelerate it out toward Jupiter Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t .... The Jupiter flyby in October 2031 will send it out of the ecliptic toward its Chariklo encounter in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Frontiers Program
The New Frontiers program is a series of space exploration missions being conducted by NASA with the purpose of furthering the understanding of the Solar System. The program selects medium-class missions which can provide high science returns. NASA is encouraging both domestic and international scientists to submit mission proposals for the program. New Frontiers was built on the innovative approach used by the Discovery Program, Discovery and Explorer program, Explorer Programs of principal investigator-led missions. It is designed for medium-class missions that cannot be accomplished within the cost and time constraints of Discovery, but are not as large as Large Strategic Science Missions (Flagship missions). There are currently three New Frontiers missions in progress and one in development. ''New Horizons'', which was launched in 2006 and reached Pluto in 2015, ''Juno (spacecraft), Juno'', which was launched in 2011 and entered Jupiter orbit in 2016, and ''OSIRIS-REx'', la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaur (small Solar System Body)
In planetary astronomy, a centaur is a small Solar System body with either a perihelion or a semi-major axis between those of the outer planets (between Jupiter and Neptune). Centaurs generally have unstable orbits because they cross or have crossed the orbits of one or more of the giant planets; almost all their orbits have dynamic lifetimes of only a few million years, but there is one known centaur, 514107 Kaʻepaokaʻawela, which may be in a stable (though retrograde) orbit. Centaurs typically exhibit the characteristics of both asteroids and comets. They are named after the mythological centaurs that were a mixture of horse and human. Observational bias toward large objects makes determination of the total centaur population difficult. Estimates for the number of centaurs in the Solar System more than 1 km in diameter range from as low as 44,000 to more than 10,000,000. The first centaur to be discovered, under the definition of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
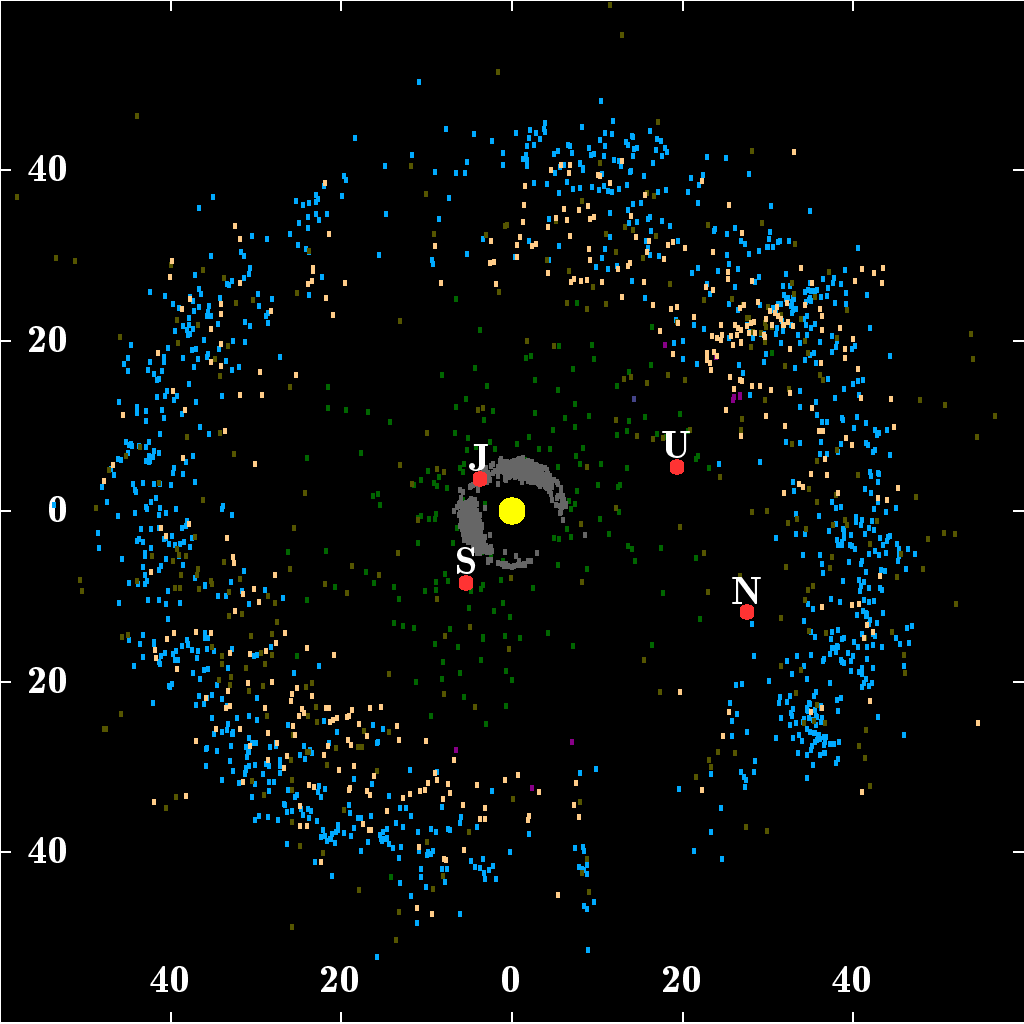
10199 Chariklo
10199 Chariklo is the largest confirmed centaur (small body of the outer Solar System). It orbits the Sun between Saturn and Uranus, grazing the orbit of Uranus. On 26 March 2014, astronomers announced the discovery of two rings (nicknamed as the rivers Oiapoque and Chuí) around Chariklo by observing a stellar occultation, making it the first minor planet known to have rings. A photometric study in 2001 was unable to find a definite period of rotation. Infrared observations of Chariklo indicate the presence of water ice, which may in fact be located in its rings. Michael Brown's website lists it as possibly a dwarf planet with a measured diameter of 232 km. Discovery and naming Chariklo was discovered by James V. Scotti of the Spacewatch program on February 15, 1997. Chariklo is named after the nymph Chariclo ('), the wife of Chiron and the daughter of Apollo. A symbol derived from that for 2060 Chiron, x14px, was devised in the late 1990s by German astrologer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shepherd Moon
A shepherd moon (also herder moon or watcher moon) is a small natural satellite that clears a gap in planetary-ring material or keeps particles within a ring contained. The name is a result of the fact they limit the "herd" of the ring particles as a shepherd. Due to their gravitational effect, they pick up particles and deflect them from their original orbits through orbital resonance. This causes gaps in the ring system, such as the particularly striking Cassini Division, as well as other characteristic bands, or strange "twisted" deformation of rings. Discovery The existence of shepherd moons was theorized in early 1979. Observations of the rings of Uranus show that they are very thin and well defined, with sharp gaps between rings. To explain this, Goldreich and Tremaine suggested that two small satellites that were undetected at the time might be confining each ring. The first images of shepherd satellites were taken later that year by Voyager 1. Examples Jupiter Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rings Of Chariklo
The minor planet and centaur 10199 Chariklo, with a diameter of about , is the smallest celestial object with confirmed rings and the fifth ringed celestial object discovered in the Solar System, after the gas giants and ice giants. Orbiting Chariklo is a bright ring system consisting of two narrow and dense bands, 6–7 km (4 mi) and 2–4 km (2 mi) wide, separated by a gap of . The rings orbit at distances of about from the centre of Chariklo, a thousandth the distance between Earth and the Moon. The discovery was made by a team of astronomers using ten telescopes at various locations in Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Uruguay in South America during observation of a stellar occultation on 3 June 2013, and was announced on 26 March 2014. The existence of a ring system around a minor planet was unexpected because it had been thought that rings could only be stable around much more massive bodies. Ring systems around minor bodies had not previously been discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never far from the Sun, either as morning star or evening star. Aside from the Sun and Moon, Venus is the brightest natural object in Earth's sky, capable of casting visible shadows on Earth at dark conditions and being visible to the naked eye in broad daylight. Venus is the second largest terrestrial object of the Solar System. It has a surface gravity slightly lower than on Earth and has a very weak induced magnetosphere. The atmosphere of Venus, mainly consists of carbon dioxide, and is the densest and hottest of the four terrestrial planets at the surface. With an atmospheric pressure at the planet's surface of about 92 times the sea level pressure of Earth and a mean temperature of , the carbon dioxide gas at Venus's surface is in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since prehistoric times. It was named after the Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet's shape is an oblate spheroid: it has a slight but noticeable bulge around the equator. The outer atmosphere i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
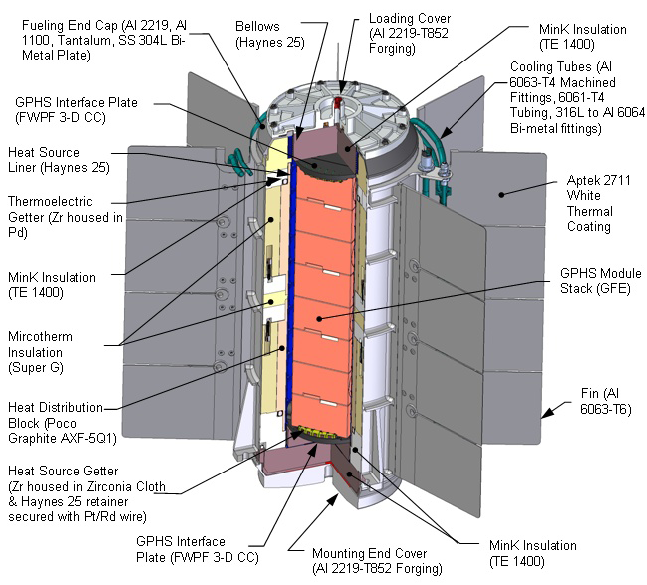
Multi-mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator
The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for NASA space missions such as the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Energy's Office of Space and Defense Power Systems within the Office of Nuclear Energy. The MMRTG was developed by an industry team of Aerojet Rocketdyne and Teledyne Energy Systems. Background Space exploration missions require safe, reliable, long-lived power systems to provide electricity and heat to spacecraft and their science instruments. A uniquely capable source of power is the radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – essentially a nuclear battery that reliably converts heat into electricity. Radioisotope power has been used on eight Earth orbiting missions, eight missions to the outer planets, and the Apollo missions after Apollo 11 to the Moon. The outer Solar System missions are the ''Pioneer 10'' and ''11'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor to polymerization catalysts, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in air bags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. the world hydrazine hydrate market amounted to $350 million. About two million tons of hydrazine hydrate were used in foam blowing agents in 2015. Hydra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missions To Minor Planets
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to: Organised activities Religion *Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity * Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints *The Christian Mission, the former name of the Salvation Army Government and military *Bolivarian missions, a series of social programs created during Hugo Chávez's rule of Venezuela *Diplomatic mission, a diplomatic outpost in a foreign territory *Military operation * Mission statement, a formal, short, written articulation of an organization's purpose * Sortie or combat mission, a deployment or dispatch of a military unit *Space mission, a journey of craft into outer space Geography Australia * Mission River, Queensland, a locality in the Shire of Cook and the Aboriginal Shire of Napranum *Mission River (Queensland), a river in Australia Canada *Mission, British Columbia, a district municipality *Mission, Calgary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |