|
Organophosphites
The general structure of a phosphite ester showing the lone pairs on the P In organic chemistry, a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of an unobserved tautomer phosphorous acid, H3PO3, with the simplest example being trimethylphosphite, P(OCH3)3. Some phosphites can be considered esters of the dominant tautomer of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2). The simplest representative is dimethylphosphite with the formula HP(O)(OCH3)2. Both classes of phosphites are usually colorless liquids. Synthesis ;From PCl3 Phosphite esters are typically prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with an alcohol. Depending on the synthetic details, this alcoholysis can give the diorganophosphites: :PCl3 + 3 C2H5OH → (C2H5O)2P(O)H + 2 HCl + C2H5Cl Alternatively, when the alcoholysis is conducted in the presence of proton acceptors, one obtains the C3-symmetric trialkoxy derivative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphite
The general structure of a phosphite ester showing the lone pairs on the P In organic chemistry, a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of an unobserved tautomer phosphorous acid, H3PO3, with the simplest example being trimethylphosphite, P(OCH3)3. Some phosphites can be considered esters of the dominant tautomer of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2). The simplest representative is dimethylphosphite with the formula HP(O)(OCH3)2. Both classes of phosphites are usually colorless liquids. Synthesis ;From PCl3 Phosphite esters are typically prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with an alcohol. Depending on the synthetic details, this alcoholysis can give the diorganophosphites: :PCl3 + 3 C2H5OH → (C2H5O)2P(O)H + 2 HCl + C2H5Cl Alternatively, when the alcoholysis is conducted in the presence of proton acceptors, one obtains the C3-symmetric trialkoxy derivatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethylphosphite
Triethyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OCH2CH3)3, often abbreviated P(OEt)3. It is a colorless, malodorous liquid. It is used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis The molecule features a pyramidal phosphorus(III) center bound to three ethoxide groups. Its 31P NMR spectrum features a signal at around +139 ppm vs phosphoric acid standard. Triethylphosphite is prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with ethanol in the presence of a base, typically a tertiary amine: :PCl3 + 3 EtOH + 3 R3N → P(OEt)3 + 3 R3NH + Cl− In the absence of the base, the reaction affords diethylphosphite ((EtO)2P(O)H). Of the many related compounds can be prepared similarly, triisopropyl phosphite is an example (b.p. 43.5 °C/1.0 mm; CAS# 116-17-6). As a ligand In coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis, triethylphosphite finds use as a soft ligand. Its complexes are generally lipophilic and feature met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Ester
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or Aryl, aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Like most functional groups, organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and adenosine triphosphate, ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The popularity of OPEs as flame retardants came as a substitution for the highly regulated brominated flame retardants. The low cost of production and compatibility to diverse polymers made OPEs to be widely used in industry including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethyl Phosphite
Trimethyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OCH3)3, often abbreviated P(OMe)3. It is a colorless liquid with a highly pungent odor. It is the simplest phosphite ester and finds used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis. The molecule features a pyramidal phosphorus(III) center bound to three methoxy groups. Synthesis Trimethyl phosphite is in principle obtainable by methanolysis of phosphorus trichloride, say in the presence of a proton accepting base. This method suffers from numerous side reactions however. The use of sodium methoxide is superior: : Reactions Trimethyl phosphite is susceptible to oxidation to trimethyl phosphate: : It reacts with a catalytic amount of methyl iodide in the Arbuzov reaction to give dimethyl methylphosphonate: :P(OCH3)3 → CH3P(O)(OCH3)2 As a ligand, trimethyl phosphite has a smaller cone angle and better acceptor properties relative to trimethylphosphine. A representative d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylolpropane Phosphite
Trimethylolpropane phosphite, C2H5C(CH2O)3P, is a phosphite ester used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. Trimethylolpropane phosphite is sometimes abbreviated to EtCage. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is also highly toxic. Preparation and reactions It is prepared by reaction of trimethylolpropane with phosphorus trichloride or by transesterification with trimethylphosphite: :P(OMe)3 + EtC(CH2OH)3 → 3 MeOH + EtC(CH2O)3P The first member of this series was derived from trimethylolethane, but these derivatives are often poorly soluble. For this reason, the ethyl derivative has received more attention. Reactions The compound forms an isolable ozonide, which degrades above 0 °C to release singlet O2. Coordination chemistry Several EtCage complexes are known, since the ligand is highly basic (for a phosphite) and has a small ligand cone angle (101°). Illustrative complexes include EtCage)2Mo(CO)4 r4(CO)11(EtCage)and (CpMe5)RuCl(EtCage)2, show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
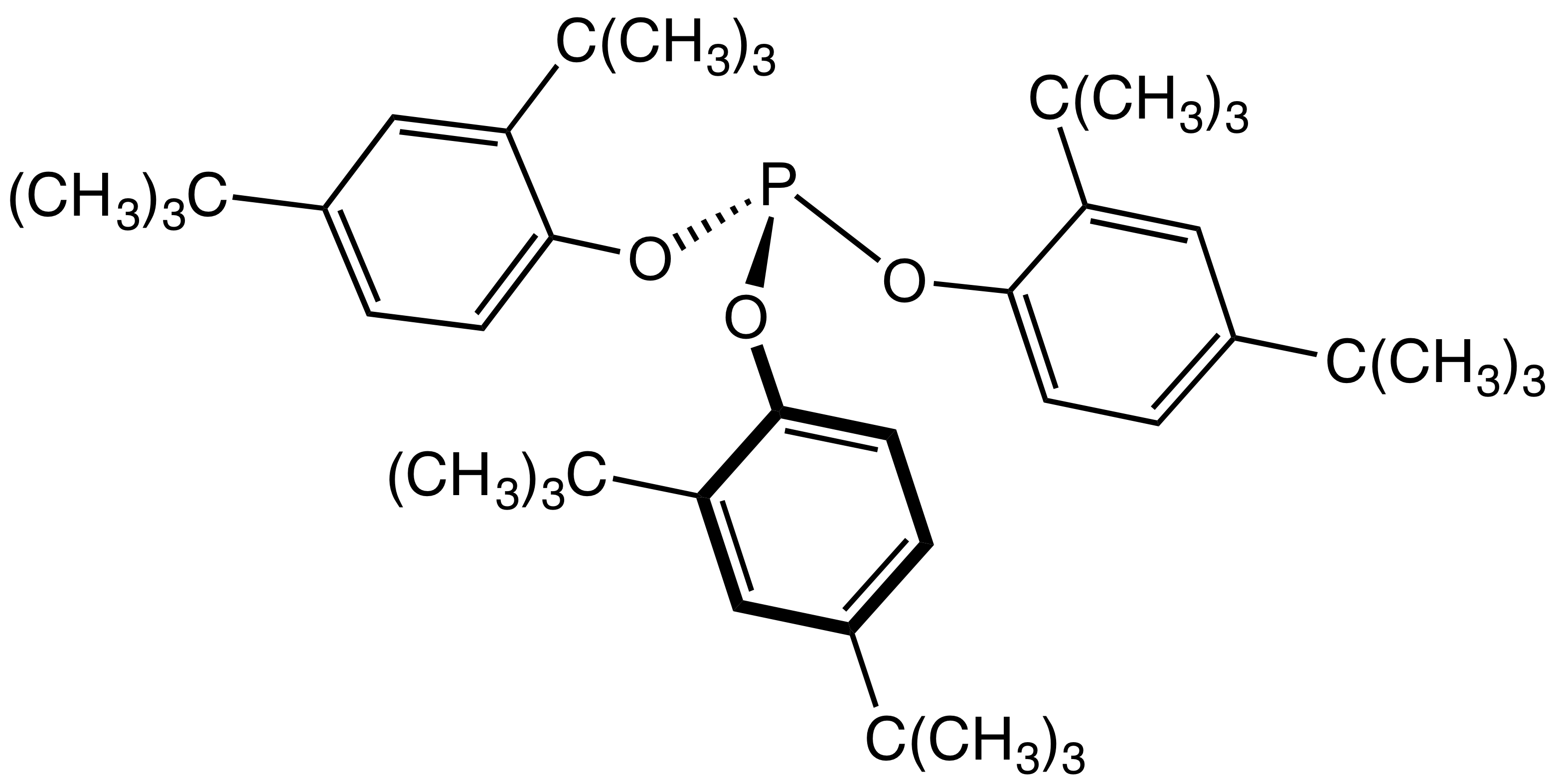
Triphenylphosphite
Triphenyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OC6H5)3. It is a colourless viscous liquid. Preparation Triphenylphosphite is prepared from phosphorus trichloride and phenol in the presence of a catalytic amount of base: :PCl3 + 3 HOC6H5 → P(OC6H5)3 + 3 HCl Reactions Triphenylphosphite is a precursor to trimethylphosphine, it serves as a source of P3+ that is less electrophilic than phosphorus trichloride: : (C6H5O)3P + 3CH3MgBr → P(CH3)3 + 3"MgBrOC6H5" Triphenylphosphite is quaternized by methyl iodide: : (C6H5O)3P + CH3I → H3(C6H5O)3Psup>+I− Coordination complexes Triphenylphosphite is a common ligand in coordination chemistry. It forms zero-valent complexes of the type M (OC6H5)3sub>4 (M = Ni, Pd, Pt). The nickel complex can be prepared by displacement of the diene from bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel: : Ni(COD)2 + 4 P(OC6H5)3 → Ni (OC6H5)3sub>4 + 2 COD Related complexes are homogeneous catalysts for the hydrocyanation of alkenes. It also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylphosphite
Dimethyl hydrogen phosphite (DMHP), also known as Dimethylphosphite, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (CH3O)2P(O)H. It is a reagent for generating other organophosphorus compounds, exploiting the high reactivity of the P-H bond. The molecule is tetrahedral. It is a colorless liquid. The compounds can be prepared by methanolysis of phosphorus trichloride or by heating diethylphosphite in methanol. Due to the presence of hydrogen, a "soft" ligand, the compound resonates. DMHP exists in chemical equilibrium, in two structures. One of the structures has a lone electron cloud, which is nucleophilically attacking the remaining tetrahedral structure. Due to the structural equilibrium tending towards the phosphonate, this reaction is slow, needing a chemical or electromagnetic catalyst (heat). This tautomeric nature of DMHP made it desirable as a precursor to the G-series compounds, and it was the most successful among all other phosphonate precursors. The now obsolete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylphosphite
Trimethyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OCH3)3, often abbreviated P(OMe)3. It is a colorless liquid with a highly pungent odor. It is the simplest phosphite ester and finds used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis. The molecule features a pyramidal phosphorus(III) center bound to three methoxy groups. Synthesis Trimethyl phosphite is in principle obtainable by methanolysis of phosphorus trichloride, say in the presence of a proton accepting base. This method suffers from numerous side reactions however. The use of sodium methoxide is superior: : Reactions Trimethyl phosphite is susceptible to oxidation to trimethyl phosphate: : It reacts with a catalytic amount of methyl iodide in the Arbuzov reaction to give dimethyl methylphosphonate: :P(OCH3)3 → CH3P(O)(OCH3)2 As a ligand, trimethyl phosphite has a smaller cone angle and better acceptor properties relative to trimethylphosphine. A representati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorous
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Like most functional groups, organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The popularity of OPEs as flame retardants came as a substitution for the highly regulated brominated flame retardants. The low cost of production and compatibility to diverse polymers made OPEs to be widely used in industry including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added to the final product phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand Cone Angle
In coordination chemistry, the ligand cone angle (a common example being the Tolman cone angle or ''θ'') is a measure of the steric bulk of a ligand in a transition metal coordination complex. It is defined as the solid angle formed with the metal at the vertex and the outermost edge of the van der Waals spheres of the ligand atoms at the perimeter of the cone (see figure). Tertiary phosphine ligands are commonly classified using this parameter, but the method can be applied to any ligand. The term ''cone angle'' was first introduced by Chadwick A. Tolman, a research chemist at DuPont. Tolman originally developed the method for phosphine ligands in nickel complexes, determining them from measurements of accurate physical models. Asymmetric cases The concept of cone angle is most easily visualized with symmetrical ligands, e.g. PR3. But the approach has been refined to include less symmetrical ligands of the type PRR′R″ as well as diphosphines. In such asymmetric cases, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine Ligand
A metal-phosphine complex is a In coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0). Preparation Many metal phosphine complexes are prepared by reactions of metal halides with preformed phosphines. For example, treatment of a suspension of palladium chloride in ethanol with triphenylphosphine yields monomeric bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) chloride units. : dCl2sub>n + 2PPh3 → PdCl2(PPh3)2 The first reported phosphine complexes were ''cis''- and ''trans''-PtCl2(PEt3)2 reported by Cahours and Gal in 1870. Often the phosphine serves both as a ligand and as a reductant. This property is illustrated by the synthesis of many platinum-metal complexes of triphenylph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroformylation
Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in speciality chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and drugs. The development of hydroformylation is one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry. The process entails treatment of an alkene typically with high pressures (between 10 and 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. In one variation, formaldehyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

2Mo(CO)4-from-xtal-2007-3D-balls.png)


