|
Trimethyl Phosphite
Trimethyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OCH3)3, often abbreviated P(OMe)3. It is a colorless liquid with a highly pungent odor. It is the simplest phosphite ester and finds used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis. The molecule features a pyramidal phosphorus(III) center bound to three methoxy groups. Synthesis Trimethyl phosphite is in principle obtainable by methanolysis of phosphorus trichloride, say in the presence of a proton accepting base. This method suffers from numerous side reactions however. The use of sodium methoxide is superior: : Reactions Trimethyl phosphite is susceptible to oxidation to trimethyl phosphate: : It reacts with a catalytic amount of methyl iodide in the Arbuzov reaction to give dimethyl methylphosphonate: :P(OCH3)3 → CH3P(O)(OCH3)2 As a ligand, trimethyl phosphite has a smaller cone angle and better acceptor properties relative to trimethylphosphine. A representative d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbuzov Reaction
Arbuzov (masculine, russian: Арбузов) or Arbuzova (feminine, russian: Арбузовa) is a Russian surname, derived from the word арбуз (''arbooz'', meaning "watermelon"). It may refer to: * Aleksandr Arbuzov (1877–1968), Russian and Soviet chemist * Aleksei Arbuzov (1908–1986), Soviet playwright * Boris Arbuzov (1903–1991), Russian and Soviet chemist * Boris Arbuzov (b. 1938), Russian and Soviet physicist * Serhiy Arbuzov Serhiy Hennadiyovych Arbuzov ( uk, Сергій Геннадійович Арбузов, russian: Сергей Геннадьевич Арбузов, translit=Sergey Gennadyevich Arbuzov; born 24 March 1976) is a Ukrainian former banker and polit ... (b. 1976), former bank director and former Vice Prime Minister of Ukraine in 2014 {{surname, Arbuzov Russian-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
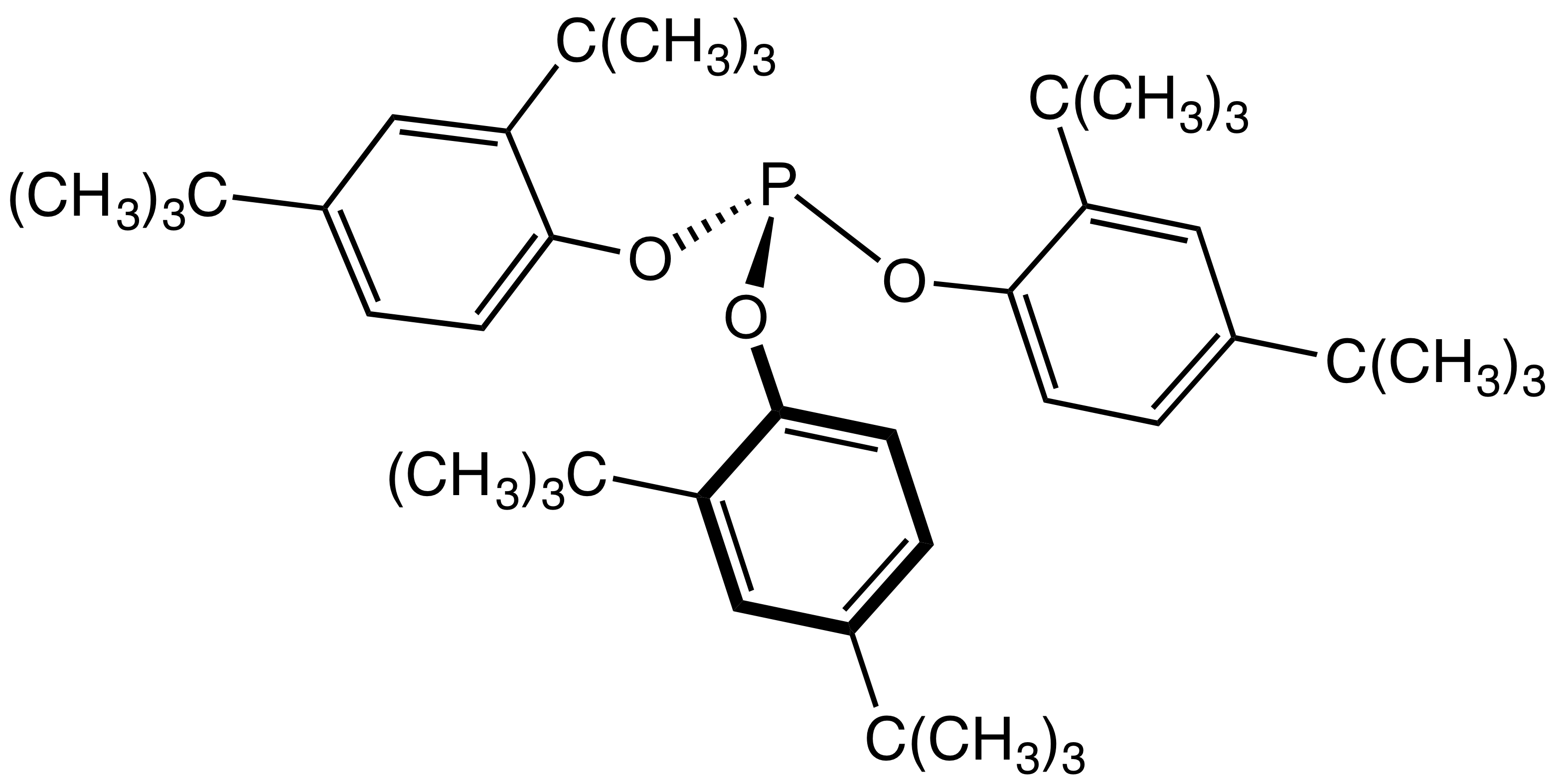
Organophosphites
The general structure of a phosphite ester showing the lone pairs on the P In organic chemistry, a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of an unobserved tautomer phosphorous acid, H3PO3, with the simplest example being trimethylphosphite, P(OCH3)3. Some phosphites can be considered esters of the dominant tautomer of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2). The simplest representative is dimethylphosphite with the formula HP(O)(OCH3)2. Both classes of phosphites are usually colorless liquids. Synthesis ;From PCl3 Phosphite esters are typically prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with an alcohol. Depending on the synthetic details, this alcoholysis can give the diorganophosphites: :PCl3 + 3 C2H5OH → (C2H5O)2P(O)H + 2 HCl + C2H5Cl Alternatively, when the alcoholysis is conducted in the presence of proton acceptors, one obtains the C3-symmetric trialkoxy derivative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LD50
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for "lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a toxic unit that measures the lethal dose of a toxin, radiation, or pathogen. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration. LD50 figures are frequently used as a general indicator of a substance's acute toxicity. A lower LD50 is indicative of increased toxicity. The test was created by J.W. Trevan in 1927. The term semilethal dose is occasionally used in the same sense, in particular with translations of foreign language text, but can also refer to a sublethal dose. LD50 is usually determined by tests on animals such as laboratory mice. In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved alternative methods to LD50 for testing the cosmetic drug Botox without animal tests. Conventions The LD50 is usually expressed as the mass of substance administered per unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrathiafulvalene
Tetrathiafulvalene is an organosulfur compound with the formula (. Studies on this heterocyclic compound contributed to the development of molecular electronics. TTF is related to the hydrocarbon fulvalene, , by replacement of four CH groups with sulfur atoms. Over 10,000 scientific publications discuss TTF and its derivatives. Preparation The high level of interest in TTFs has spawned the development of many syntheses of TTF and its analogues. Most preparations entail the coupling of cyclic building blocks such as 1,3-dithiole-2-thion or the related 1,3-dithiole-2-ones. For TTF itself, the synthesis begins with the trithiocarbonate , which is S-methylated and then reduced to give , which is treated as follows: :H2C2S2CH(SCH3) + HBF4 -> 2C2S2CH+F4- + HSCH3 :2 2C2S2CH+F4- + 2 Et3N -> (H2C2S2C)2 + 2 Et3NHBF4 Redox properties Bulk TTF itself has unremarkable electrical properties. Distinctive properties are, however, associated with salts of its oxidized derivatives, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kläui Ligand
The Kläui ligand is the anion −. The ligand, popularized by Wolfgang Kläui, binds metals and metalloids via a facial O3 donor set. Related tridentate and tripodal anionic ligands include trispyrazolylborates. : 160px, General structure of a metal center coordinated to a κ3-Kläui ligand. The ligand is derived from the cationic complex of trimethylphosphite 2+ via an Arbuzov reaction. Using other phosphites and other cyclopentadienyl ligands, a large variety of derivatives are possible. The parent acid H is highly soluble in water (270 g/100 mL). Its p''K''a is about 2. Many complexes have been described, including bis(chelate Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...) complexes of the type {M 3}2.html" ;"title="CH3O)2PO.html" ;"title="(C5H5)Co[(CH3O)2PO">(C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melting Point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at a standard pressure such as 1 atmosphere or 100 kPa. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from liquid to solid, it is referred to as the freezing point or crystallization point. Because of the ability of substances to supercool, the freezing point can easily appear to be below its actual value. When the "characteristic freezing point" of a substance is determined, in fact, the actual methodology is almost always "the principle of observing the disappearance rather than the formation of ice, that is, the melting point." Examples For most substances, melting and freezing points are approximately equal. For example, the melting point ''and'' freezing point of mercury is . How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylphosphine
Trimethylphosphine is a neutral organophosphorus compound with the formula P(CH3)3, commonly abbreviated as PMe3. This colorless liquid has a strongly unpleasant odor, characteristic of alkylphosphines. The compound is a common ligand in coordination chemistry. Structure and bonding It is a pyramidal molecule with approximate ''C''3''v'' symmetry. The C–P–C bond angles are approximately 98.6°. The C–P–C bond angles are consistent with the notion that phosphorus predominantly uses the 3p orbitals for forming bonds and that there is little sp hybridization of the phosphorus atom. The latter is a common feature of the chemistry of phosphorus. As a result, the lone pair of trimethylphosphine has predominantly s-character as is the case for phosphine, PH3. PMe3 can be prepared by the treatment of triphenyl phosphite with methylmagnesium chloride: : 3 CH3MgCl + P(OC6H5)3 → P(CH3)3 + 3 C6H5OMgCl The synthesis is conducted in dibutyl ether, from which the more volatile PMe3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone Angle
In coordination chemistry, the ligand cone angle (a common example being the Tolman cone angle or ''θ'') is a measure of the steric bulk of a ligand in a transition metal coordination complex. It is defined as the solid angle formed with the metal at the vertex and the outermost edge of the van der Waals spheres of the ligand atoms at the perimeter of the cone (see figure). Tertiary phosphine ligands are commonly classified using this parameter, but the method can be applied to any ligand. The term ''cone angle'' was first introduced by Chadwick A. Tolman, a research chemist at DuPont. Tolman originally developed the method for phosphine ligands in nickel complexes, determining them from measurements of accurate physical models. Asymmetric cases The concept of cone angle is most easily visualized with symmetrical ligands, e.g. PR3. But the approach has been refined to include less symmetrical ligands of the type PRR′R″ as well as diphosphines. In such asymmetric cases, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Methylphosphonate
Ethane ( , ) is an organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural gas and as a petrochemical by-product of petroleum refining. Its chief use is as feedstock for ethylene production. Related compounds may be formed by replacing a hydrogen atom with another functional group; the ethane moiety is called an ethyl group. For example, an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group yields ethanol, the alcohol in beverages. History Ethane was first synthesised in 1834 by Michael Faraday, applying electrolysis of a potassium acetate solution. He mistook the hydrocarbon product of this reaction for methane and did not investigate it further. During the period 1847–1849, in an effort to vindicate the radical theory of organic chemistry, Hermann Kolbe and Edward Frankland produced ethane by the reductions of propionitrile (ethyl cyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethyl Phosphate
Trimethyl phosphate is the trimethyl ester of phosphoric acid. It is a colourless, nonvolatile liquid. It has some specialized uses in the production of other compounds. Production Trimethyl phosphate is prepared by treating phosphorus oxychloride with methanol in the presence of an amine base: :POCl3 + 3 CH3OH + 3 R3N → PO(OCH3)3 + 3 R3NH+Cl− It is a tetrahedral molecule that is a weakly polar solvent. Applications Trimethyl phosphate is a mild methylating agent, useful for dimethylation of anilines and related heterocyclic compounds. The method is complementary to the traditional Eschweiler-Clarke reaction in cases where formaldehyde engages in side reactions. Trimethyl phosphate is used as a solvent for aromatic halogenations and nitrations as required for the preparation of pesticides and pharmaceuticals. Other applications It is used as a color inhibitor for fibers (e.g. polyester) and other polymers. Trimethyl phosphate is used as a simulant for c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Methylphosphonate
Ethane ( , ) is an organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural gas and as a petrochemical by-product of petroleum refining. Its chief use is as feedstock for ethylene production. Related compounds may be formed by replacing a hydrogen atom with another functional group; the ethane moiety is called an ethyl group. For example, an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group yields ethanol, the alcohol in beverages. History Ethane was first synthesised in 1834 by Michael Faraday, applying electrolysis of a potassium acetate solution. He mistook the hydrocarbon product of this reaction for methane and did not investigate it further. During the period 1847–1849, in an effort to vindicate the radical theory of organic chemistry, Hermann Kolbe and Edward Frankland produced ethane by the reductions of propionitrile (ethyl cyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |