|
Obsolete Taxa
In the history of the Linnaean classification system, many taxa (e.g. species, genera, family (biology), families, and higher taxonomic ranks) have become defunct or obsolete, and are no longer used. Kingdoms Animals Protists References {{DEFAULTSORT:Obsolete taxa Obsolete taxa, Biology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linnaean Classification
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts: # The particular form of Taxonomy (biology), biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus there are three kingdoms, divided into ''classes'', and they, in turn, into lower ranks in a hierarchical order. # A term for rank-based classification of organisms, in general. That is, taxonomy in the traditional sense of the word: rank-based scientific classification. This term is especially used as opposed to cladistics, cladistic systematics, which groups organisms into clades. It is attributed to Linnaeus, although he neither invented the concept of ranked classification (it goes back to Plato and Aristotle) nor gave it its present form. In fact, it does not have an exact present form, as "Linnaean taxonomy" as such does not really exist: it is a collective (abstracting) term for what actually are several separate f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloth
Sloths are a group of Neotropical xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of movement, tree sloths spend most of their lives hanging upside down in the trees of the tropical rainforests of South America and Central America. Sloths are considered to be most closely related to anteaters, together making up the xenarthran order Pilosa. There are six extant sloth species in two genera – '' Bradypus'' (three–toed sloths) and '' Choloepus'' (two–toed sloths). Despite this traditional naming, all sloths have three toes on each rear limb-- although two-toed sloths have only two digits on each forelimb. The two groups of sloths are from different, distantly related families, and are thought to have evolved their morphology via parallel evolution from terrestrial ancestors. Besides the extant species, many species of ground sloths ranging up to the size of ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea. The order was formerly much more diverse during the Pleistocene, but most species became extinct during the Late Pleistocene epoch. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive skin. The trunk is used for breathing, bringing food and water to the mouth, and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears, and convex or level backs. Elephants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North America in the Great American Interchange following the connection of North and South America. The Virginia opossum is the only species found in the United States and Canada. It is often simply referred to as an opossum, and in North America it is commonly referred to as a possum (; sometimes rendered as ''possum'' in written form to indicate the dropped "o"). Possums should not be confused with the Australasian arboreal marsupials of suborder Phalangeriformes that are also called possums because of their resemblance to the Didelphimorphia. The opossum is typically a nonaggressive animal. Etymology The word ''opossum'' is borrowed from the Powhatan language and was first recorded between 1607 and 1611 by John Smith (as ''opassom'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrew
Shrews (family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to different families or orders. Although its external appearance is generally that of a long-nosed mouse, a shrew is not a rodent, as mice are. It is, in fact, a much closer relative of hedgehogs and moles; shrews are related to rodents only in that both belong to the Boreoeutheria magnorder. Shrews have sharp, spike-like teeth, whereas rodents have gnawing front incisor teeth. Shrews are distributed almost worldwide; among the major tropical and temperate land masses, only New Guinea, Australia, and New Zealand have no native shrews; in South America shrews appeared only relatively recently, as a result of the Great American Interchange, and are present only in the northern Andes. The shrew family has 385 known species, making it the fourth-most spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
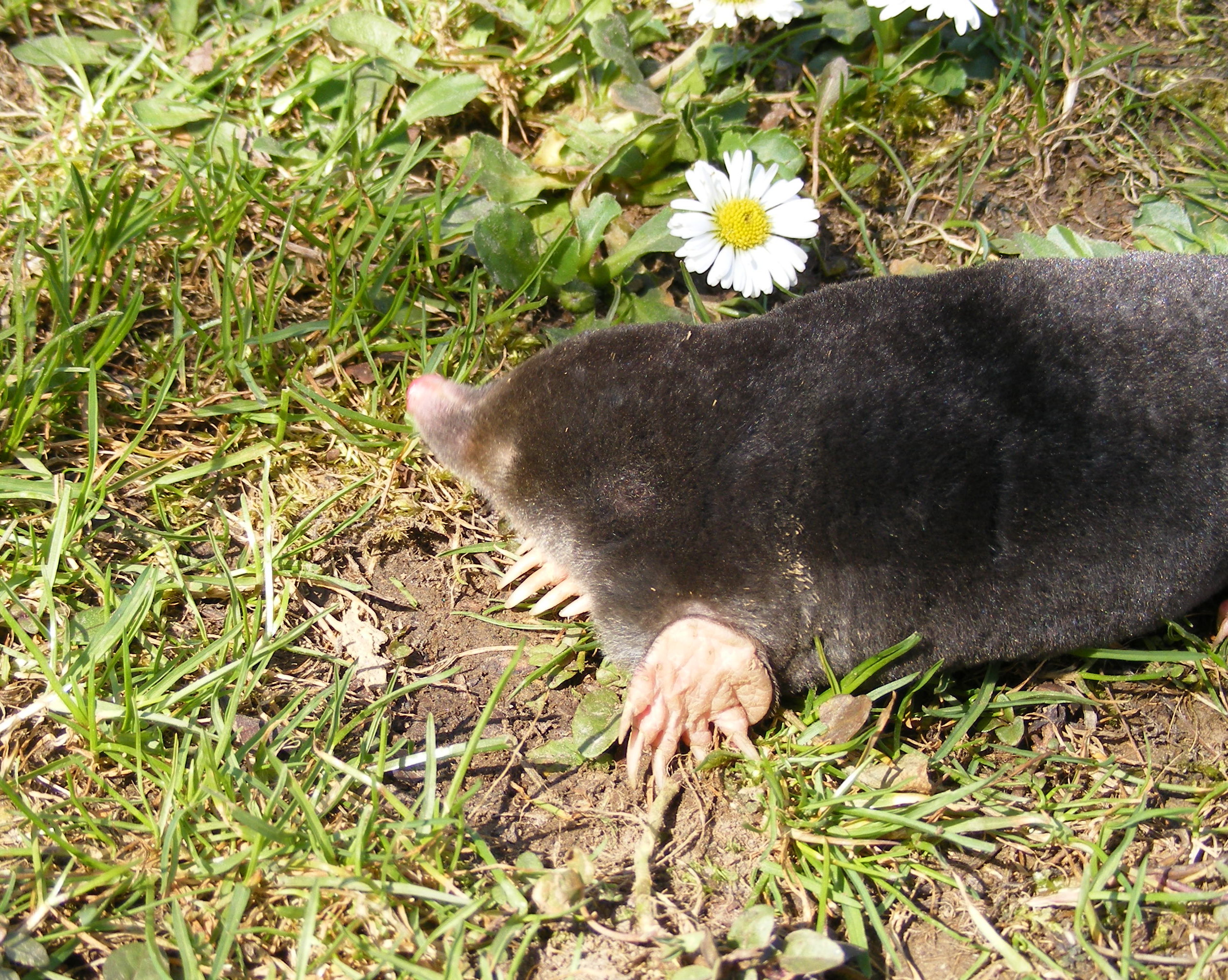
Mole (animal)
Moles are small mammals adapted to a subterranean lifestyle. They have cylindrical bodies, velvety fur, very small, inconspicuous eyes and ears, reduced hindlimbs, and short, powerful forelimbs with large paws adapted for digging. The word “mole” refers to any species in the family Talpidae, which means “mole” in Latin. Moles are found in most parts of North America, Europe and Asia. Moles may be viewed as pests to gardeners, but they provide positive contributions to soil, gardens, and ecosystem, including soil aeration, feeding on slugs and small creatures that eat plant roots, and providing prey for other wildlife. They eat earthworms and other small invertebrates in the soil. Terminology In Middle English, moles were known as ''moldwarp''. The expression "don't make a mountain out of a molehill" (which means "exaggerating problems") was first recorded in Tudor times. By the era of Early Modern English, the mole was also known in English as ''mouldywarp'', a wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introduction. There are no hedgehogs native to Australia and no living species native to the Americas. However, the extinct genus ''Amphechinus'' was once present in North America. Hedgehogs share distant ancestry with shrews (family Soricidae), with gymnures possibly being the intermediate link, and they have changed little over the last fifteen million years. Like many of the first mammals, they have adapted to a nocturnal way of life. Their spiny protection resembles that of porcupines, which are rodents, and echidnas, a type of monotreme. Etymology The name ''hedgehog'' came into use around the year 1450, derived from the Middle English ''heyghoge'', from ''heyg'', ''hegge'' ("hedge"), because it frequents hedgerows, and ''hoge'', ''hogge'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. Nine extinct genera and 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments. Armadillos are characterized by a leathery armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Etymology The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
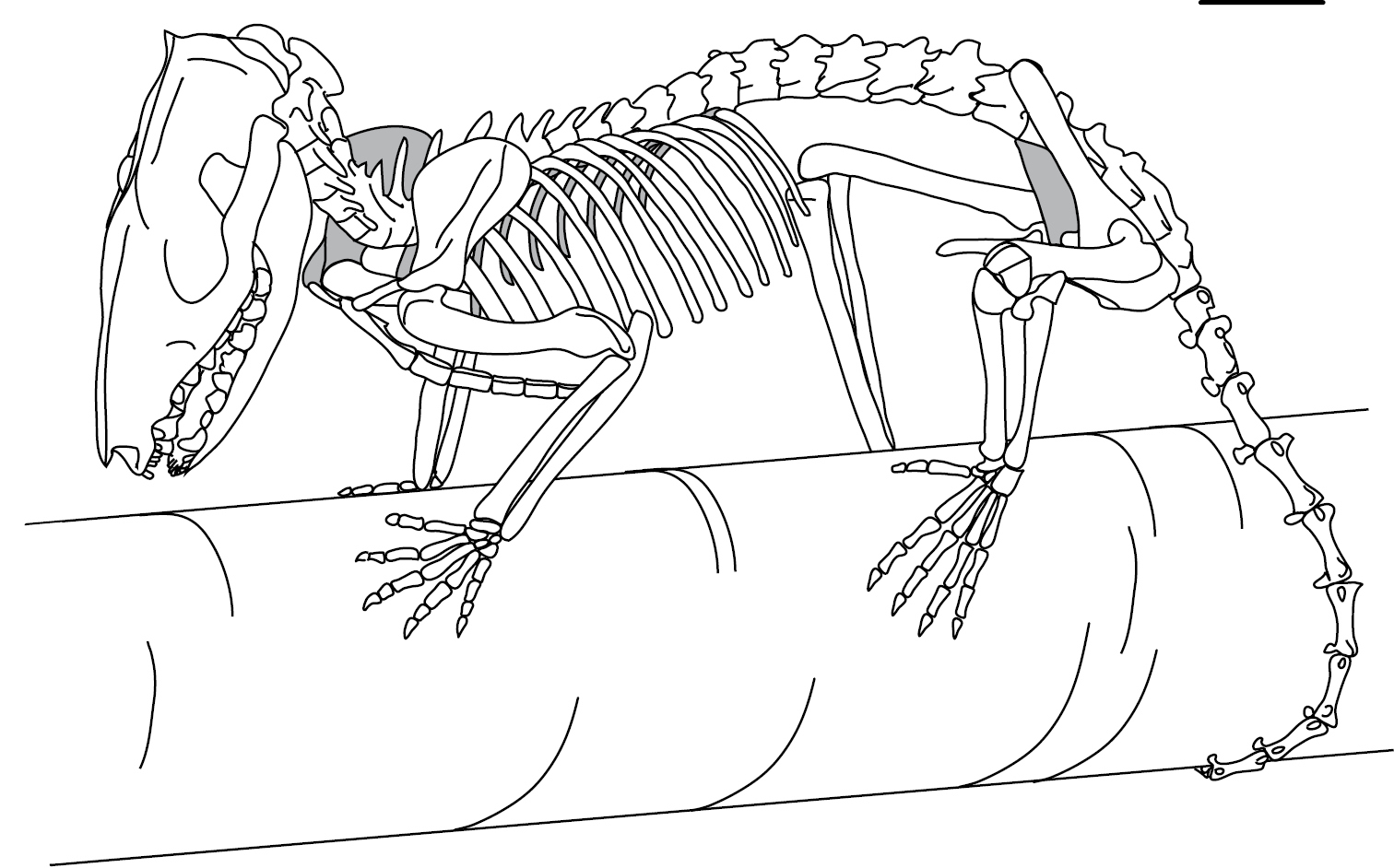
Bestiae
Bestiae is a defunct taxon that contained pigs, armadillos, hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and opossums. It was defined by Linnaeus in its 1758's ''Systema Naturae ' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...'' as "quadrupedal mammals having several front teeth, and more than a pair or laniary (i.e. canine) teeth".Gregory, W. L. (1910). ''The Orders of Mammals''. References Obsolete mammal taxa {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species of the superfamily Rhinocerotoidea.) Two of the extant species are native to Africa, and three to South and Southeast Asia. Rhinoceroses are some of the largest remaining megafauna: all weigh at least one tonne in adulthood. They have a herbivorous diet, small brains (400–600 g) for mammals of their size, one or two horns, and a thick (1.5–5 cm), protective skin formed from layers of collagen positioned in a lattice structure. They generally eat leafy material, although their ability to ferment food in their hindgut allows them to subsist on more fibrous plant matter when necessary. Unlike other perissodactyls, the two African species of rhinoceros lack teeth at the front of their mouths; they rely instead on their lips to pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae, the other being the pygmy hippopotamus (''Choeropsis liberiensis'' or ''Hexaprotodon liberiensis''). Its name comes from the ancient Greek for "river horse" (). Aside from elephants and rhinos, the hippopotamus is the largest land mammal. It is also the largest extant land artiodactyl. Despite their physical resemblance to pigs and other terrestrial even-toed ungulates, the closest living relatives of the hippopotamids are cetaceans (whales, dolphins, porpoises, etc.), from which they diverged about 55 million years ago. Hippos are recognisable for their barrel-shaped torsos, wide-opening mouths with large canine tusks, nearly hairless bodies, pillar-like legs, and large size: adults average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_colourised.png)