|
Neofit Rilski
Neofit Rilski ( bg, –Ě–Ķ–ĺ—Ą–ł—ā –†–ł–Ľ—Ā–ļ–ł) or Neophyte of Rila (Bansko, 1793 ‚Äď January 4, 1881), born Nikola Poppetrov Benin ( bg, –Ě–ł–ļ–ĺ–Ľ–į –ü–ĺ–Ņ–Ņ–Ķ—ā—Ä–ĺ–≤ –Ď–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ) was a 19th-century Bulgarian monk, teacher and artist, and an important figure of the Bulgarian National Revival. He was born in the southwestern town of Bansko (or possibly in the village of Guliyna Banya) of Pirin Macedonia. Benin was educated to become a teacher, initially by his father Petar, and later at the Rila Monastery, where he studied iconography and had access to Greek and Church Slavonic books. He went to Melnik in 1822, where he spent four years as a student of the noted teacher Adam and perfected his Greek and Greek literature knowledge. Initially working as a teacher in the Rila Monastery, he also spent time working in Samokov (1827‚Äď1831), then back in the monastery, then went to Gabrovo and Koprivshtitsa (1835‚Äď1839) and returned to the monastery as a teacher to join the theologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neofit Rilski Grave-rila Monastery
{{dab, geo, given name ...
Neofit (–Ě–Ķ–ĺ—Ą–ł—ā) is the Slavic form of the Greek name Neophytos, and may refer to: * Neofit of Bulgaria (born 1945), Bulgarian Orthodox primate * Neofit II (17781850), Romanian priest, head of the provisional government during the Wallachian Revolution of 1848 * Neofit Bozveli (1848), Bulgarian cleric and enlightener * Neofit Rilski or Neophyte of Rila (17931881), Bulgarian monk, teacher and artist * (18221910), Archbishop of Chi»ôinńÉu 189298 Places *Neofit Peak, mountain in Antarctica named after Neofit Rilski See also *South-West University "Neofit Rilski", university in Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria *Neophyte (other) *Neophytus (other) Neophytus or Neophytos ( el, őĚőĶŌĆŌÜŌÖŌĄőŅŌā, "newly-planted, newcomer") may refer to: * Neophytos of Nicaea, a Christian martyr * Neophytus (freedman), an imperial freedman of emperor Nero * Patriarch Neophytus I of Constantinople, Patriarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
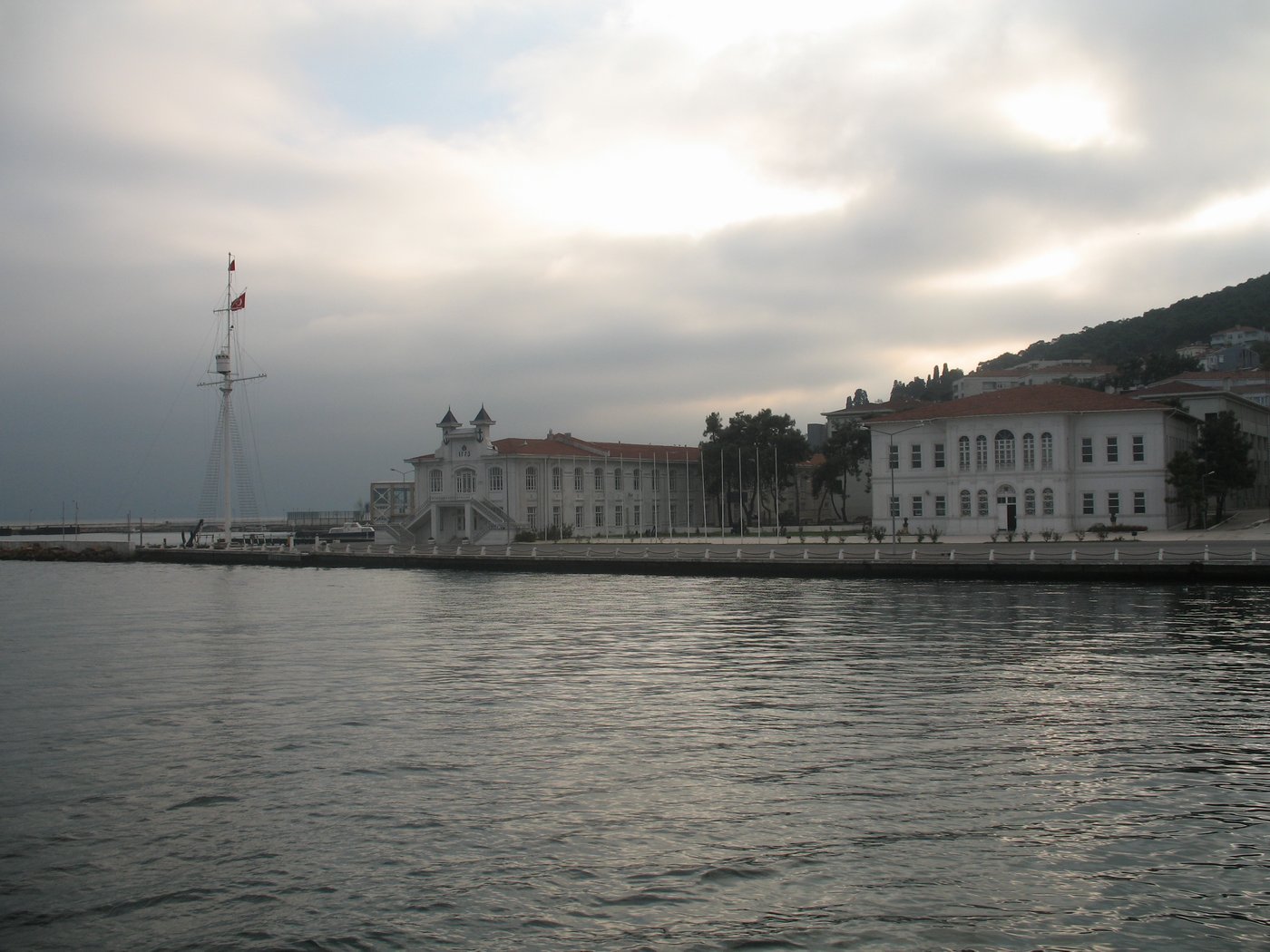
Halki (Turkish Island)
Heybeliada, or Heybeli Ada, is the second largest of the Prince' Islands in the Sea of Marmara, near Istanbull, Turkey. It is officially a neighbourhood of the Adalar district of Istanbul. Its name, meaning 'with a saddlebag' in Turkish, in supposed reference to the valley between two hills. The island was known as ''Halki'', ''Halkitis'' ( el, őßőĪőĽőļőĮŌĄőĻŌā) and ''Demonesos'' ( Greek: őĒő∑őľŌĆőĹő∑ŌÉőŅŌā) in antiquity, the first two toponyms deriving from the Greek word ''halkos'' ( el, ŌáőĪőĽőļŌĆŌā), meaning copper. The island was famous for its copper and copper ores in antiquity. In winter the island's population is only about 5,500, but in summer, the owners of summer houses return and the population swells to approximately 30,000. Launched in 2008, TCG ''Heybeliada'', used by the Turkish Navy is named after the island. Until 2020, the only vehicles permitted on the island were ambulances, fire tenders, police cars etc; the only official form of transport was by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith Island (South Shetland Islands)
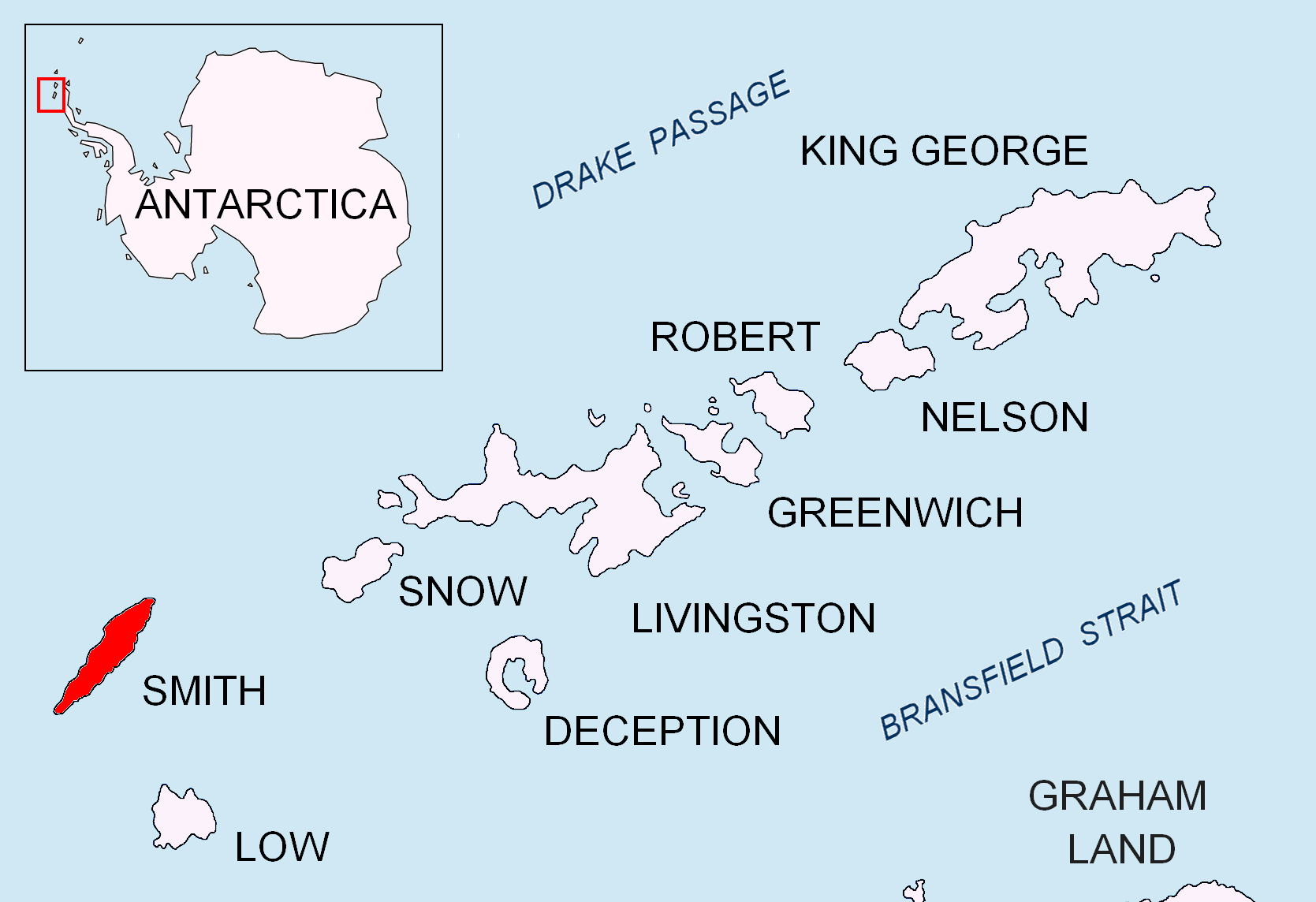
__NOTOC__ Smith Island is long and wide, lying west of Deception Island in the South Shetland Islands of the British Antarctic Territory. Surface area .L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. (First edition 2009. ) The discovery of the South Shetland Islands was first reported in 1819 by Capt. William Smith, for whom the island is named. This island was known to both American and British sealers as early as 1820, and the name Smith has been well established in international usage for over 100 years, although in Russian literature it is often referred to as Borodino Island, sometimes marked as Borodino (Smith) Island. The island hosts no research stations or camps, and is seldom visited by scientists or mountaineers. Its interior is entirely occupied by Imeon Range rising to (Mount Foster).L. Ivanov and N. Ivanova. South Shetlands. In''The World of An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neofit Peak
Neofit Peak ( bg, –≤—Ä—ä—Ö –Ě–Ķ–ĺ—Ą–ł—ā, vrah Neofit, ) is an ice-covered peak rising to 1750 m in Imeon Range on Smith Island (South Shetland Islands), Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Situated 1.12 km south-southwest of Slaveykov Peak, 3.1 km southwest of the summit Mount Foster, 2.38 km northeast of Riggs Peak and 10.98 km northeast of Cape James. Overlooking Gramada Glacier to the south, and Armira Glacier to the east and southeast. Bulgarian early mapping in 2009. Named after the Bulgarian monk, scholar and artist Neofit Rilski (1793‚Äď1881) who translated the Bible into modern Bulgarian language. MapsChart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822. * L.L. Ivanov. :commons:File:Livingston-Island-Map-2010.jpg, Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Dialects
Bulgarian dialects are the regional varieties of the Bulgarian language, a South Slavic language. Bulgarian dialectology dates to the 1830s and the pioneering work of Neofit Rilski, ''Bolgarska gramatika'' (published 1835 in Kragujevac, Serbia, then Ottoman Empire). Other notable researchers in this field include Marin Drinov, Konstantin Josef Jireńćek, Lyubomir Miletich, Aleksandar Teodorov-Balan, Stoyko Stoykov. The dialects of Macedonian are classified as part of Bulgarian in the older literature.Mazon, Andre. ''Contes Slaves de la Mac√©doine Sud-Occidentale: Etude linguistique; textes et traduction''; Notes de Folklore, Paris 1923, p. 4. The Bulgarian linguistics continue to treat it as such in. Since the second half of the 20th century, foreign authors have mostly adopted the convention of treating these in terms of a separate Macedonian language, following the codification of Macedonian as the literary standard language of Yugoslav Macedonia. However, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Bulgarian
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic () was the first Slavic literary language. Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with standardizing the language and using it in translating the Bible and other Ancient Greek ecclesiastical texts as part of the Christianization of the Slavs. It is thought to have been based primarily on the dialect of the 9th-century Byzantine Slavs living in the Province of Thessalonica (in present-day Greece). Old Church Slavonic played an important role in the history of the Slavic languages and served as a basis and model for later Church Slavonic traditions, and some Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic churches use this later Church Slavonic as a liturgical language to this day. As the oldest attested Slavic language, OCS provides important evidence for the features of Proto-Slavic, the reconstructed common ancestor of all Slavic languages. Nomenclature The name of the language in Old Church Slavonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic () was the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language. Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with Standard language, standardizing the language and using it in translating the Bible and other Ancient Greek ecclesiastical texts as part of the Christianization of the Slavs. It is thought to have been based primarily on the dialect of the 9th-century Sclaveni, Byzantine Slavs living in the Thessalonica (theme), Province of Thessalonica (in present-day Greece). Old Church Slavonic played an important role in the history of the Slavic languages and served as a basis and model for later Church Slavonic traditions, and some Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic churches use this later Church Slavonic as a liturgical language to this day. As the oldest attested Slavic language, OCS provides important evidence for the features of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elias Riggs
Elias Riggs (November 19, 1810 ‚Äď January 17, 1901) was an American Presbyterian missionary and linguist. Biography Elias Riggs was born on November 19, 1810 in New Providence, New Jersey. He was the second son of Elias and Margaret (Congar) Hudson Riggs. His father was the pastor of the local Presbyterian church. During his missionary activities in the Ottoman Empire he contributed greatly to the Bulgarian National Revival. He organized with Albert Long the first translation (by Neofit Rilski), and worked on editing, printing and dissemination of a translation of the Bible into modern Bulgarian. In 1844 he published the first Grammar of the modern Bulgarian language. Riggs did research on Chaldee Language, and also guided the translation of the Bible into modern Armenian language.Georgi GenovAmerican Elias Riggs and his contribution to the Bulgarian National Revival. ''Historical Archives''. Sofia, Issue 9-10, November 2000 - May 2001. (in Bulgarian) The government a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible Translations Into Bulgarian
The royal Tetraevangelia of Ivan Alexander is an illuminated manuscript Gospel Book in middle Bulgarian, prepared and illustrated in 1355‚Äď1356 for Tsar Ivan Alexander of the Second Bulgarian Empire. The manuscript is regarded as one of the most important manuscripts of medieval Bulgarian culture. The manuscript, now in the British Library (Add. MS 39627), contains the text of the Four Gospels illustrated with 366 miniatures and consists of 286 parchment folios, 33 by 24.3 cm in size. Bible translations into modern Bulgarian date from the 1820s and were largely organised by Protestant missionaries. The Bulgarian Orthodox Church initially preferring the continued use of Old Church Slavonic. The Archimandrite Theodosius, abbot of the Bistritsa Monastery in Romania, translated the New Testament for the British and Foreign Bible Society, which was printed at St. Petersburg in 1823 . "It was begun by the Archimandrite Theodosius, with the sanction of Gregory, Patriarch of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family. The Slavic languages are conventionally (that is, also on the basis of extralinguistic features) divided into three subgroups: East, South, and West, which together constitute more than 20 languages. Of these, 10 have at least one million speakers and official status as the national languages of the countries in which they are predominantly spoken: Russian, Belarusian and Ukrainian (of the East group), Polish, Czech and Slovak (of the West group) and Bulgarian and Macedonian (eastern dialects of the South group), and Serbo-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Language
Bulgarian (, ; bg, label=none, –Ī—ä–Ľ–≥–į—Ä—Ā–ļ–ł, bńÉlgarski, ) is an Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeastern Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians. Along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the East South Slavic languages), it is a member of the Balkan sprachbund and South Slavic dialect continuum of the Indo-European language family. The two languages have several characteristics that set them apart from all other Slavic languages, including the elimination of case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article, and the lack of a verb infinitive. They retain and have further developed the Proto-Slavic verb system (albeit analytically). One such major development is the innovation of evidential verb forms to encode for the source of information: witnessed, inferred, or reported. It is the official language of Bulgaria, and since 2007 has been among the official languages of the Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |