|
Mare Tyrrhenum Quadrangle
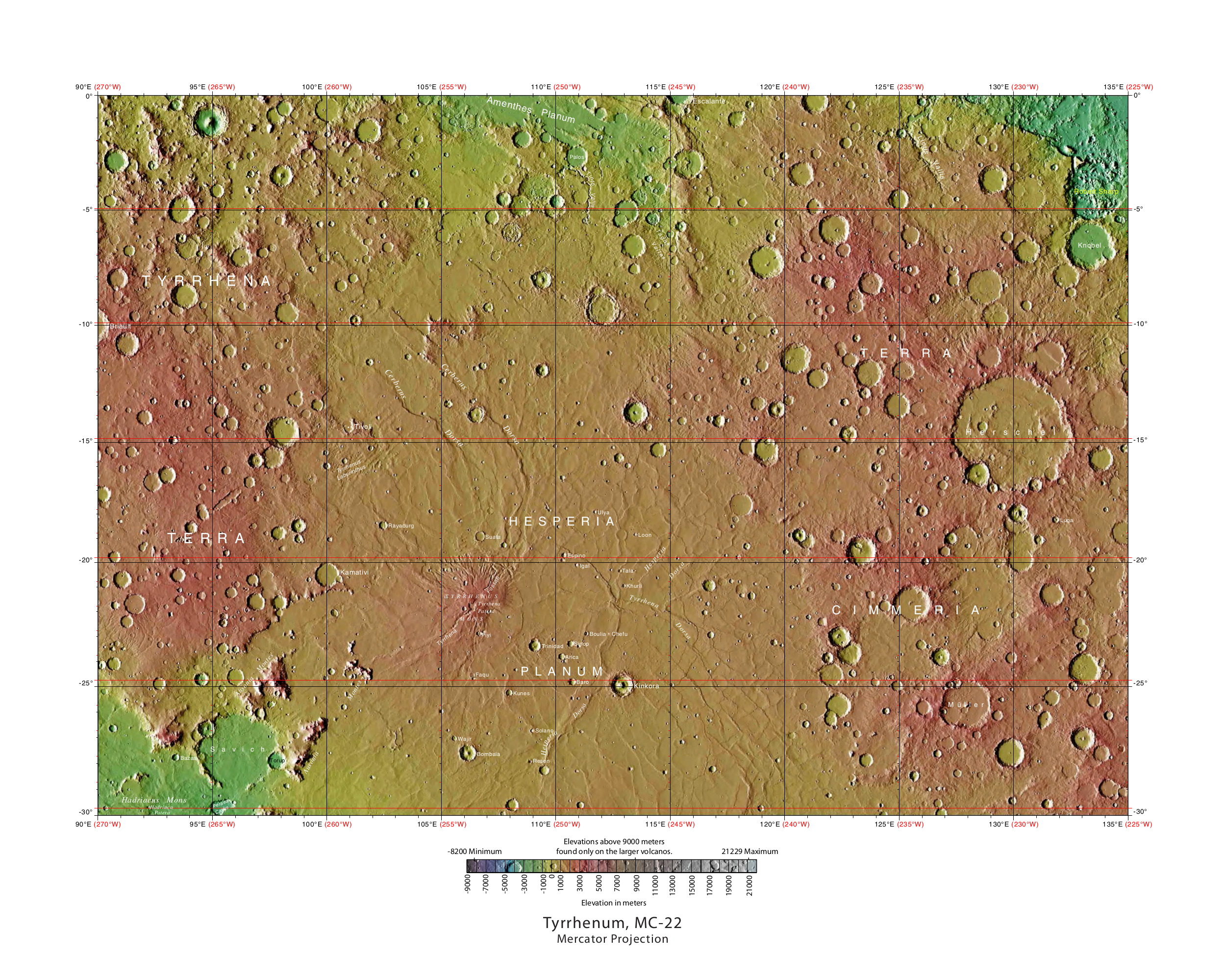
The Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. This quadrangle is also referred to as MC-22 (Mars Chart-22). It contains parts of the regions Tyrrhena Terra, Hesperia Planum, and Terra Cimmeria. The Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle covers the area from 225° to 270° west longitude and 0° to 30° south latitude on Mars. Schiaparelli named the area after Earth's Tyrrhenian Sea, which lies between Italy and Sicily. The region was subsequently renamed to Mare Tyrrhena after spacecraft photos revealed that it is an old, cratered plain rather than a sea. It contains the large volcano Tyrrhenus Mons, one of the oldest, and perhaps the most complex volcanoes on Mars. Mare Tyrrhenum's largest crater is Herschel. Licus Vallis and the Ausonia Montes are other major features in the region. Fossa on Mars Large troughs (long narrow depressions) are called fossae in the geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Half-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiWish Program
HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRISE. The first images were released in April 2010. Over 12,000 suggestions were made by the public; suggestions were made for targets in each of the 30 quadrangles of Mars. Selected images released were used for three talks at the 16th Annual International Mars Society Convention. Below are some of the over 4,224 images that have been released from the HiWish program as of March 2016. Glacial features Some landscapes look just like glaciers moving out of mountain valleys on Earth. Some have a hollowed-out appearance, looking like a glacier after almost all the ice has disappeared. What is left are the moraines—the dirt and debris carried by the glacier. The center is hollowed out because the ice is mostly gone. These supposed alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resen (Martian Crater)
Resen is a crater in the Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle on Mars, located at 28.22° South and 251.13° West. It is measures 7.4 kilometers in diameter and was named after the town of Resen in North Macedonia. The naming was approved by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature on 19 January 2011. Some parts of the crater display a high concentration of closely spaced pits. Pits show little or no evidence of rims or ejecta. The pits are so close to each other that adjacent pits often share the same wall. It is believed that the pits form from steam produced when the heat from the impact process interacts with ice in the ground. The presence of these pits is evidence that the region has ground ice. On Mars, heat from the impact melts ice in the ground. Water from the melting ice dissolves minerals, and then deposits them in cracks or faults that were produced with the impact. This process, called hydrothermal alteration, is a major way in which ore deposits are pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Sharp (crater)
Robert Sharp may refer to: * Robert P. Sharp (1911–2004), expert on the geological surfaces of the Earth and the planet Mars * Robert Sharp (crater), a crater on the planet Mars * Robert Sharp (cricketer) (1893–1961), English cricketer * Robert Cameron Sharp (born 1958), Scottish sprinter * Robert "Bob" D. Sharp, 7th Director of the National Geospatial Intelligence Agency * Robert Sharp (born 1988), pro wrestler better known as Bobby Sharp See also *Robert Sharpe Robert James Sharpe, OC, FRSC (born December 4, 1945) is a Canadian lawyer, author, academic, and judge. He was dean of the University of Toronto Faculty of Law from 1990 to 1995 and a judge of the Court of Appeal for Ontario from 1999 to 202 ... (born 1945), Canadian lawyer, author, academic, and judge * Bob Sharpe (1925–2014), Scottish footballer * Bob Sharpe (basketball) (born 1951), Canadian basketball player * Pepper Sharpe (Robert Ernest Sharpe, 1918–1997), American baseball player {{hndis, Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Müller (Martian Crater)
Müller may refer to: * ''Die schöne Müllerin'' (1823) (sometimes referred to as ''Müllerlieder''; ''Müllerin'' is a female miller) is a song cycle with words by Wilhelm Müller and music by Franz Schubert * Doctor Müller, fictional character in ''The Adventures of Tintin'' by Hergé * Geiger–Müller tube, the sensing element of a Geiger counter instrument * GMD Müller, Swiss aerial lift manufacturing company * Müller (company), a German multinational dairy company * Müller (footballer, born 1966), nickname of ''Luís Antônio Corrêa da Costa'', Brazilian footballer * Muller glia, a macroglial cell in the retina * Müller (German trade company), Müller Ltd. & Co. KG, a German pharmacy chain * Müller (lunar crater), impact crater on the lunar surface * Müller (Martian crater), impact crater on the Martian surface * Müller (store), a German retail store chain * Müller (surname), a common German surname * Müller-Thurgau, German wine grape * Müller Brothers, 19th-centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinkora (crater)
{{dab ...
Kinkora may refer to: * Kinkora, Prince Edward Island, Canada **Kinkora Regional High School * Kinkora, New Jersey * Kinkora (crater) * Kinkora-Pemberton rail-trail See also *Borden-Kinkora Borden-Kinkora is a provincial electoral district for the Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island The Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island (french: Assemblée législative de l'Île-du-Prince-Édouard) is the sole chamber of the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Briault (crater)
Briault may refer to: * Jean-Claude Briault (born 1947), New Caledonian politician * P. Briault (died 1922), French astronomer * Briault (crater), an impact crater in the Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle of Mars {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auki (crater)
Auki is an impact crater in the Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle of Mars, at 15.76 °S latitude and 263.13 °W longitude. It is 40.0 km in diameter and was named after Auki, a town in the Solomon Islands, in 2015 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). Auki Crater has a central peak. Impact craters generally have a rim with ejecta around them, in contrast volcanic craters usually do not have a rim or ejecta deposits. As craters get larger (greater than 10 km in diameter) they usually have a central peak. The peak is caused by a rebound of the crater floor following the impact. Strong evidence for hydrothermalism was reported by a team of researchers studying Auki. This crater contains ridges that may have been produced after fractures formed with an impact. Using instruments on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter they found the minerals smectite, silica, zeolite, serpentine, carbonate, and chlorite that are common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinkholes
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openings where surface water enters into underground passages known as ''ponor'', swallow hole or swallet. A ''cenote'' is a type of sinkhole that exposes groundwater underneath. A ''sink'' or ''stream sink'' are more general terms for sites that drain surface water, possibly by infiltration into sediment or crumbled rock. Most sinkholes are caused by karst processes – the chemical dissolution of carbonate rocks, collapse or suffosion processes. Sinkholes are usually circular and vary in size from tens to hundreds of meters both in diameter and depth, and vary in form from soil-lined bowls to bedrock-edged chasms. Sinkholes may form gradually or suddenly, and are found worldwide. Formation Natural processes Sinkholes may capture surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)