|
History Of Zürich
Zurich has been continuously inhabited since Roman times. The vicus of '' Turicum'' was established in AD 90, at the site of an existing Gaulish ( Helvetic) settlement. Gallo-Roman culture appears to have persisted beyond the collapse of the Western empire in the 5th century, and it is not until the Carolingian period. A royal castle was built at the site of the Lindenhof, and monasteries are established at Grossmünster and Fraumünster. Political power lay with these abbeys during medieval times, until the guild revolt in the 14th century which led to the joining of the Swiss Confederacy. Zurich was the focus of the Swiss Reformation led by Huldrych Zwingli, and it came to riches with silk industry in Early Modern times. Early history Numerous lake-side settlements from the Neolithic and Bronze Age have been found, such as those in the Zürich Pressehaus and Zürich Mozartstrasse. The settlements were found in the 1800s, submerged in Lake Zurich. Located on the then swam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tène Culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and the Culture of Golasecca, Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences. La Tène culture's territorial extent corresponded to what is now Prehistory of France#The Iron Age, France, History of Belgium#Celtic and Roman periods, Belgium, Early history of Switzerland#Iron Age, Switzerland, History of Austria#Iron Age, Austria, History of England#Later Prehistory, England, History of Germany#Iron Age, Southern Germany, the History of the Czech lands#Iron Age, Czech Republic, Prehistoric Italy#Iron Age, Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
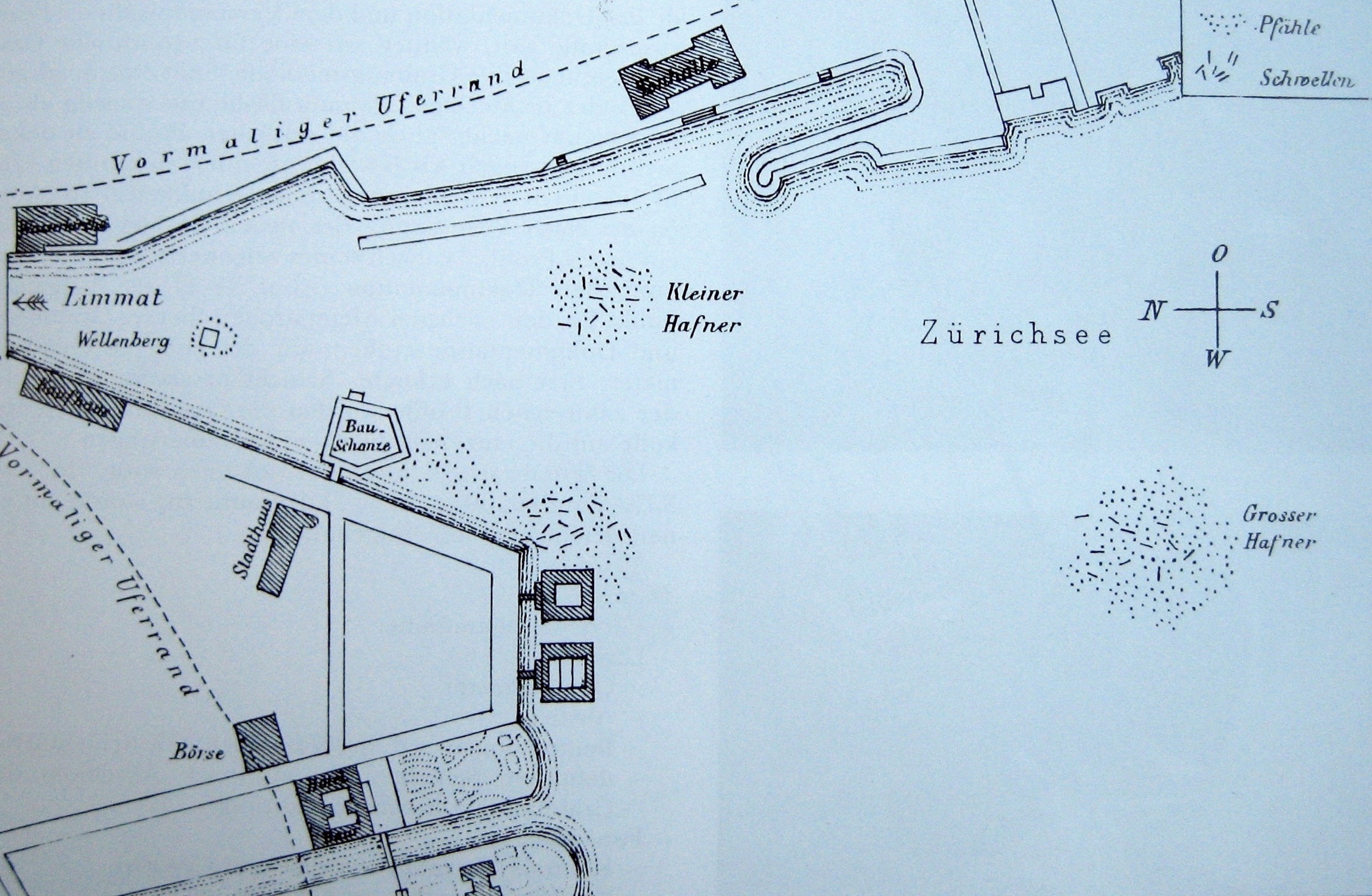
Grosser Hafner
Grossner Hafner is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site '' Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps'', of which are 56 located in Switzerland. Geography Grosser Hafner was located on the then swamp area between the Limmat and Zürichsee around Sechseläutenplatz on a small lake island in Zürich, and as well as the other Prehistoric pile dwellings around Zürichsee set on piles to protect against occasional flooding by the Linth and Jona. The settlement is located on Lake Zurich in Enge, a locality of the municipality of Zürich. It was neighbored by the settlements Zürich–Enge Alpenquai and Kleiner Hafner on a then island in the effluence of the Limmat, within an area of about in the city of Zürich. Grosser and Kleiner Hafner comprise , and the buffer zone including the lake area comprises in all. History Internationally known is the area since 2009, as in the beginning of the construction of the underground parking facility at Sechs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleiner Hafner
Kleiner Hafner is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site '' Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps'', of which are 56 located in Switzerland. Geography Kleiner Hafner was located on the then swamp land between the river Limmat and Zürichsee around Sechseläutzenplatz on a small peninsula in Zürich, and as well as the other Prehistoric pile dwellings around Zürichsee set on piles to protect against occasional flooding by the rivers Linth and Jona. The settlement is located on '' Zürichsee'' lakeshore in Enge, a locality of the municipality of Zürich. It was neighbored by the settlements Zürich–Enge Alpenquai and Grosser Hafner on a then island in the effluence of the Limmat, within an area of about in the city of Zürich. The site Kleiner Hafner comprises , and the buffer zone including the lake area comprises . History The site is internationally known since 2009, when during the beginning of the construction of the underground parki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities In The Canton Of Zurich
There are 160 Municipalities of Switzerland, municipalities in the canton of Zurich in Switzerland. In general, municipalities (German: ''Politische Gemeinden'') in Switzerland are grouped in Canton of Zurich#Political subdivisions, districts (''Bezirke''), their capital municipalities are written in bold letters. Mergers of municipalities There were no changes between 1934 and 2013, but , there occurred in all nine Merger (politics), mergers. * 2014: ''Bertschikon bei Attikon'' and ''Wiesendangen'' → Wiesendangen * 2015: ''Bauma'' and ''Sternenberg ZH, Sternenberg'' → Bauma * 2016: ''Kyburg, Zürich, Kyburg'' and ''Illnau-Effretikon'' → Illnau-Effretikon * 2018: ''Hirzel'' and ''Horgen'' → Horgen * 2018: ''Elgg'' and ''Hofstetten, Switzerland, Hofstetten'' → Elgg * 2019: ''Oberstammheim'', ''Unterstammheim'' and ''Waltalingen'' → Stammheim, Zurich, Stammheim * 2019: ''Hütten ZH, Hütten'', ''Schönenberg ZH, Schönenberg'' and ''Wädenswil'' → Wädenswil * 2023: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enge (Zurich)
Enge is a quarter in district 2 (Zürich), District 2 of Zürich, Switzerland. History Enge was incorporated into Zürich in 1893, along with 11 other formerly independent Municipality, municipalities. In 2011, the population was 8,597. Enge, which is only 2.4 km2, is the smallest neighbourhood in district 2. Transportation Zürich Enge railway station is a stop of Zürich S-Bahn on the lines S2 (ZVV), S2, S8 (ZVV), S8, S21 (ZVV), S21 and S24 (ZVV), S24. Cultural heritage Enge is located in prehistoric swampland on small islands around Sechseläutenplatz, Zürich, Sechseläutenplatz and peninsulas in Zürich. It is situated between the Limmat and Lake Zurich. Prehistoric pile dwellings around Lake Zurich were set on piles in order to protect against the occasional flooding of the rivers Linth and Jona (river), Jona. Zürich–Enge Alpenquai, a locality of the Municipalities in the canton of Zürich, municipality of Zürich, is located on the shore of Lake Zurich in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jona (river)
The Jona is a river in the Swiss cantons of Zürich and St. Gallen, forming partly their mutual border, and one of the main tributaries of '' Obersee'', Lake Zurich. Geography The Jona rises on the eastern slope of Bachtel mountain near Gibswil in the canton of Zurich. Gibswil marks the drainage divide between the rivers Jona and Töss. Flowing eastward through a small valley and passing an impressive waterfall, the river changes its direction towards south by a ravine, which is crossed by a viaduct of the '' Tösstalbahn'' (operated by the S26 service of Zürich S-Bahn). From there, it continues southward until Wald, where the Jona turns to the west, dividing the municipalities of Dürnten and Rüti, then passing the village of Tann and Rüti in the so-called ''Tannertobel'' (). Once again, it changes its direction, flowing now southward again, slightly meandering through Rüti and the so-called ''Joner Wald'' (), where it is followed (and eventually crossed) by the Wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linth
The Linth (pronounced "lint") is a Switzerland, Swiss river that rises near the Linthal, Glarus, village of Linthal in the mountains of the cantons of Switzerland, canton of canton of Glarus, Glarus, and eventually flows into the Obersee (Zürichsee), Obersee section of Lake Zurich. It is about in length. The water power of the Linth was a main factor in the creation of the textile industry of the canton Glarus, and is today used to drive the Linth–Limmern Power Stations, Linth–Limmern power stations in its upper reaches. The river and its upper valley forms the boundary between the mountain ranges of the Glarus Alps, to its east and south, and the Schwyzer Alps, to its west. In its lower part, in the Linth plain (), the Linth Canal forms the boundary between the cantons of Glarus and canton of St. Gallen, St. Gallen and part of the boundary between the cantons of St. Gallen and canton of Schwyz, Schwyz. The river lends its name to the former canton of Linth (1798–1803) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Pile Dwellings Around Lake Zurich
Prehistoric pile dwellings around Lake Zurich are Stilt house, pile dwelling sites located around Lake Zurich in the Cantons of Switzerland, cantons of Canton of Schwyz, Schwyz, Canton of St. Gallen, St. Gallen and Canton of Zurich, Zurich. The article focuses on the 9 Lake Zurich sites that are among the 111 sites included in the UNESCO World Heritage Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps established in 2011. 56 of the 111 UNESCO World Heritage pile dwelling sites are located in Switzerland and 9 thereof are located on the Lake Zurich seashore. The article also includes one UNESCO World Heritage site at the nearby Greifensee (lake), Greifensee and one UNESCO World Heritage site at the Pfäffikersee. The 11 sites described here are only a selection, just like the 111 UNESCO World Heritage sites are only a selection of more than 900 known sites of prehistoric pile dwellings in the Alpine region. Geography The 11 prehistoric pile-dwelling (or stilt house) sites are concentr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |