|
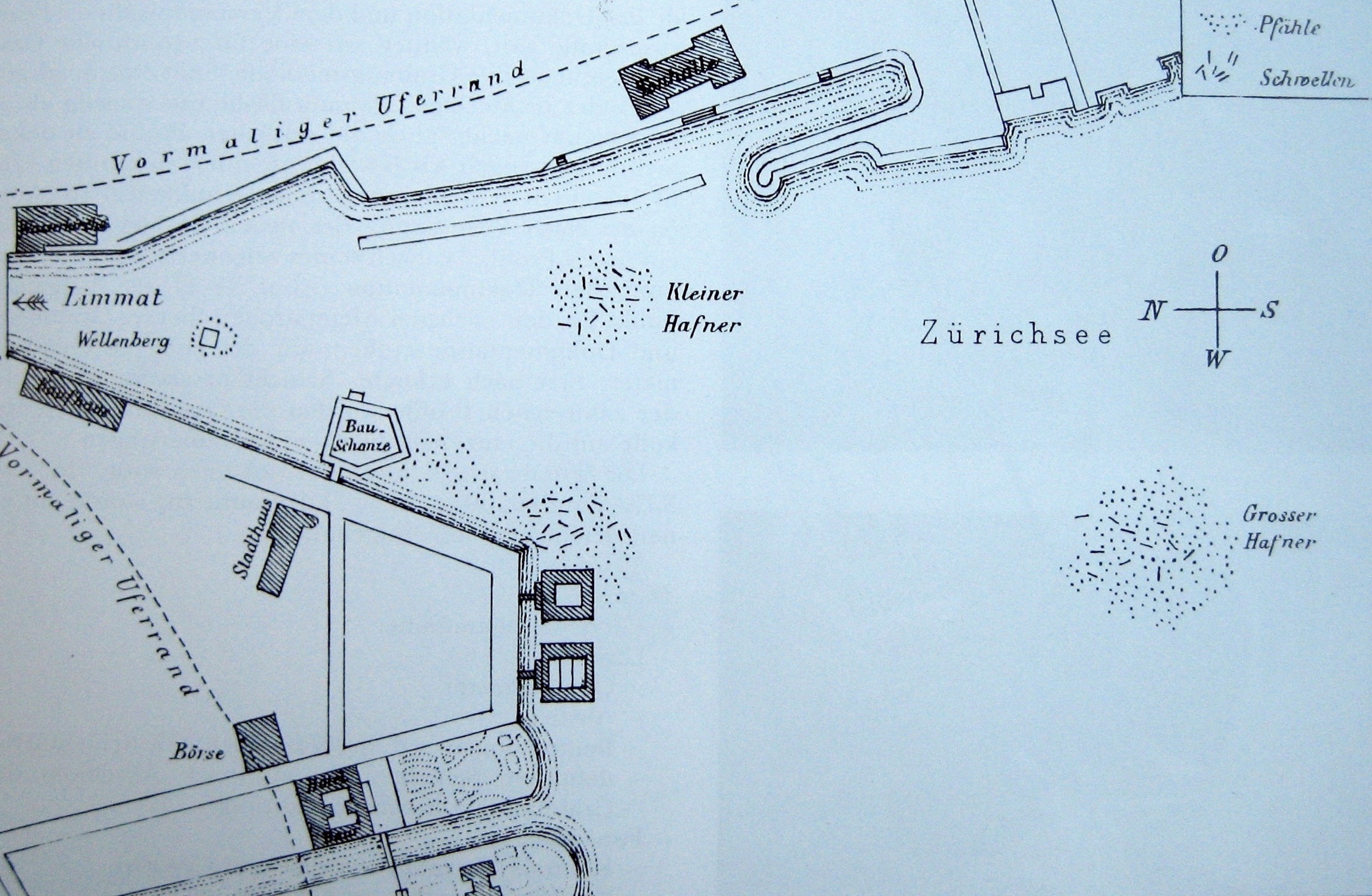
Grosser Hafner
Grossner Hafner is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site ''Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps'', of which are 56 located in Switzerland. Geography Grosser Hafner was located on the then swamp area between the Limmat and Zürichsee around Sechseläutenplatz on a small lake island in Zürich, and as well as the other Prehistoric pile dwellings around Zürichsee set on piles to protect against occasional flooding by the Linth and Jona. The settlement is located on Lake Zurich in Enge, a locality of the municipality of Zürich. It was neighbored by the settlements Zürich–Enge Alpenquai and Kleiner Hafner on a then island in the effluence of the Limmat, within an area of about in the city of Zürich. Grosser and Kleiner Hafner comprise , and the buffer zone including the lake area comprises in all. History Internationally known is the area since 2009, as in the beginning of the construction of the underground parking facility at Sechseläut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zürich–Enge Alpenquai
Zürich–Enge Alpenquai is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site ''Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps'', of which 56 are located in Switzerland. Geography Located on the then-swampland between Limmat and Lake Zurich around Sechseläutzenplatz on small islands and peninsulas in Zürich, the settlements were set on piles to protect against occasional flooding by the Linth and Jona Rivers. Because the lake has grown in size over time, most of the original piles are now around to under the water level of , giving modern observers the false impression that they always had been underwater. Zürich–Enge Alpenquai is located on ''Lake Zurich'' lakeshore in Enge, a locality of the municipality of Zürich in the Canton of Zürich in Switzerland. The settlement comprises , and the buffer zone, including the lake area, comprises in all. It was neighbored by the settlements at Kleiner Hafner and Grosser Hafner on a then peninsula respectively islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Switzerland
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Property Of National Significance In The Canton Of Zürich
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change. Thus in military culture, valor is counted a typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Pile Dwellings In Switzerland
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egolzwil Culture
Wauwilermoos or Egolzwil 3 is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site ''Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps'', of which are 56 located in Switzerland. Geography The site is located on the former Wauwilersee lakeshore in the municipalities of Egolzwil, Wauwil and Schötz in the Canton of Luzern in Switzerland. The settlement comprises , and the buffer zone including the lake area comprises in all. Around 20000 BC a branch of the Reuss glacier formed a valley whose deepest point was approximately below the present surface. At Schötz the glacier stopped, as shown by the impressive moraines. During the retreat of the glacier, meltwater jammed between the moraines. Thus in the Wauwilermoos plain three lakes were formed: ''Wauwilersee'', ''Hagimoos'' and ''Mauensee''; latter still exists. The meltwater outsourced enormous amounts of sand, so that the lakes never were particularly deep. The depth of Wauwilersee amounted only to about . To 17000 BC the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tène Culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscans, and the Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences. La Tène culture's territorial extent corresponded to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Austria, England, Southern Germany, the Czech Republic, parts of Northern Italy and Central Italy, Slovenia and Hungary, as well as adjacent parts of the Netherlands, Slovakia, Serbia, Croatia, Transylvania (western Romania), and Transcarpathia (western Ukraine). The Celtiberians of western Iberia shared many aspects of the culture, though not generally the artistic style. To the north extended the contemporary Pre-Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindenhof Hill
The Lindenhof (lit.: ''courtyard of the lime'') is a moraine hill and a public square in the historic center of Zürich, Switzerland. It is the site of the Roman and Carolingian era Kaiserpfalz around which the city has historically grown. The hilltop area—including its prehistoric, Roman, and medieval remains—is listed as a Swiss heritage site of national significance. Topography Lindenhof (its northern part is called ''Sihlbühl'') dominates the Lindenhof quarter in district 1 (Altstadt), the historical center of Zürich's Altstadt. To the North, it ends at ''Uraniastrasse'' (City police station) and to the South, it ends near St. Peter church. In the West, the hill is limited by the Bahnhofstrasse, and in the east, it ends at the Limmat and the Schipfe quarter. Lindenhof sits atop the remains of a glacier. The hill and its public square are part of the Linth Glacier's moraines in the area of Zürich. The now largely flattened Lindenhof (428 m ü. M) rises about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turicum (Zürich)
Turicum was a Gallo-Roman settlement at the lower end of Lake Zurich, and precursor of the city of Zürich. It was situated within the Roman province of Gallia Belgica (from AD 90 Germania Superior) and near the border to the province of Raetia; there was a tax-collecting point for goods traffic on the waterway Walensee– Obersee-Zürichsee–Limmat–Aare–Rhine. Name The ancient name ''Turicum'', along with the indication of a Roman customhouse, is first attested in the epitaph for Lucius Aelius Urbicus, an infant son of the , ‘head of the toll-station at Zurich’, that was found on Lindenhof hill in 1747 and dates from 185/200 AD. Regula Frei-Stolba/Reinhold Kaiser & al., ''Die Römische Zeit'', in: ''Geschichte des Kantons Zürich'', vol. 1: ''Frühzeit bis Spätmittelalter'', Zürich 1995, . The place name reappears in the Early Middle Ages as ''Turicum'', ''Turico'', ''Doricum'', ''Torico'', ''Turigo'', ''Turegum'', and in its Old High German forms ''Ziurichi'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland In The Roman Era
The territory of modern Switzerland was a part of the Roman Republic and Empire for a period of about six centuries, beginning with the step-by-step conquest of the area by Roman armies from the 2nd century BC and ending with the Fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. The mostly Celtic tribes of the area were subjugated by successive Roman campaigns aimed at control of the strategic routes from Italy across the Alps to the Rhine and into Gaul, most importantly by Julius Caesar's defeat of the largest tribal group, the Helvetii, in the Gallic Wars in 58 BC. Under the ''Pax Romana'', the area was smoothly integrated into the prospering Empire, and its population assimilated into the wider Gallo-Roman culture by the 2nd century AD, as the Romans enlisted the native aristocracy to engage in local government, built a network of roads connecting their newly established colonial cities and divided up the area among the Roman provinces. Roman civilization began to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horgen Culture
The Horgen culture is one of several archaeological cultures belonging to the Neolithic period of Switzerland. The Horgen culture may derive from the Pfyn culture and early Horgen pottery is similar to the earlier Cortaillod culture pottery of Twann, Switzerland.Comparative Archeology Web accessed 28 June 2010 It is named for one of the principal sites, in , Switzerland. Dates  The Horgen culture started around 3500/3400
The Horgen culture started around 3500/3400 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)





